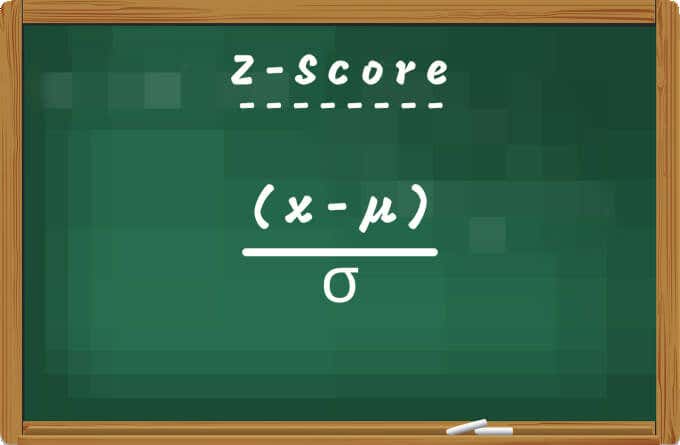아시다시피 Microsoft Excel 로 수행할 수 있는 수학적 계산이 많이 있습니다 . 이 자습서 에서는 Excel 에서 (Excel)Z-점수(Z-Score) 계산과 관련된 단계를 안내합니다 .
Excel 을 처음 사용하는 경우 5분 정도 시간을 내어 이 Microsoft Excel 초보자용 자습서(Microsoft Excel beginner’s tutorial) 를 정독하는 것이 좋습니다 . 필수 기능의 작동 방식, 탐색 바로 가기, 통합 문서 만들기, 데이터 형식 지정 및 초보자가 스프레드시트 프로그램을 사용하는 데 대해 알아야 할 모든 것을 배우게 됩니다.

작업이 끝나면 다음 섹션으로 이동하여 Excel 에서 Z 점수를 계산하는 방법을 알아 보세요. 그러나 먼저 Z-Score , 그 용도, 계산해야 하는 이유 및 완료 방법에 대해 간단히 설명하겠습니다.
Z 점수 란 무엇입니까?
Z-점수("표준 점수"라고도 함)는 분포에서 값 간의 관계를 강조 표시하는 메트릭입니다. 보다 정확하게는 평균 및 표준 편차와 관련하여 데이터 세트에서 값의 위치를 설명합니다. Z-점수를 사용하면 데이터 세트의 값을 정확하게 측정하고 비교할 수 있습니다.
Z-Score 를 계산하는 수학 공식 은 (x-µ) / σ 입니다. 여기서 x = Cell Value , µ = Mean 및 σ = Standard Deviation .
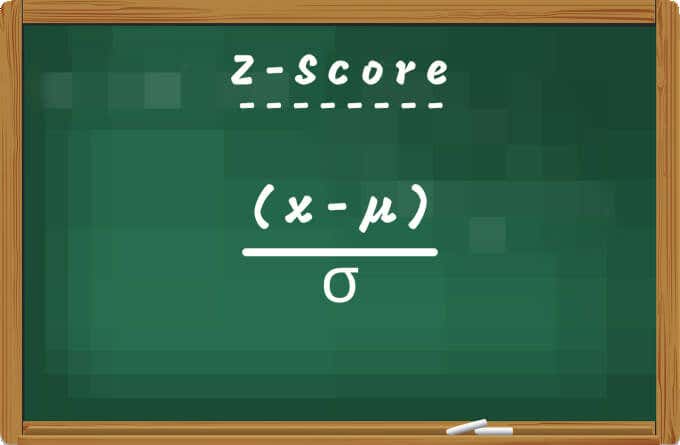
회사는 때때로 Z-Score 를 사용 하여 임박한 파산을 예측하고 추정합니다. 또한 기관의 재정 상태를 확인하는 데 유용한 지표입니다. 연구원(Researchers) 은 또한 Z-점수(Z-Score) 를 사용하여 다른 샘플이나 모집단에서 얻은 관찰을 비교합니다.
Excel에서 Z 점수를 계산하는 방법
Z-점수(Z-Score) 는 평균과 표준편차의 함수 이므로 먼저 데이터세트의 평균과 표준편차를 계산해야 합니다. 모든 셀에서 평균과 표준 편차를 추출할 수 있지만 워크시트에 "평균" 및 "표준 편차" 전용 열을 만들었습니다. " Z-Score "에 대한 열도 만들었습니다 .
샘플 문서에는 종이 회사 직원 10명의 성과 등급이 포함되어 있습니다. 이제 직원 평가의 Z-Score 를 계산해 보겠습니다.(Z-Score)
평균 평균 계산(Calculate Mean Average)
데이터세트의 평균 평균을 계산하려면 =AVERAGE( 를 입력 하고 데이터세트 의 첫 번째 값(first value) 을 선택 하고 열 키(column key) 를 누르고 데이터세트 범위 내에서 마지막 값(last value) 을 선택 하고 닫는 괄호(closing parenthesis) 키를 누르고 Enter 키를 누릅니다 . 수식은 다음 과 같아야 합니다. 아래와 같이:
=AVERAGE(B2:B11)

수식을 입력한 셀에 데이터 세트의 평균 또는 평균 값이 표시되어야 합니다.
표준편차 계산(Calculate Standard Deviation)
또한 Excel을 사용 하면 몇 번의 클릭으로 데이터 세트의 표준 편차(calculate the standard deviation of your dataset) 를 매우 쉽게 계산할 수 있습니다.
"표준 편차" 열에서 셀을 선택하고 =STDEV.P( 를 입력한 다음 범위 의 첫 번째 값 을 선택하고 (first value)열 키(column key) 를 누르고 마지막 값을 선택하고 닫는 괄호(closing parenthesis) 를 입력하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 . 의심의 여지가 있지만 결과 공식은 다음과 유사해야 합니다.
=STDEV.P(B2:B11)

Excel에서 Z-점수 계산: 방법 1(Calculate Z-Score in Excel: Method 1)
Excel 에는 분포에서 데이터 세트 의 Z-점수 를 제공하는 (Z-Score)STANDARDIZE 함수가 있습니다. Z-점수(Z-Score) 열 에서 첫 번째 셀을 선택하고 아래 단계를 따릅니다.
- 수식(Formulas) 탭 으로 이동하여 추가 수식(More Formulas) 을 선택 합니다.

- 통계(Statistical) 옵션 에 마우스를 올려 놓고 STANDARDIZE 를 선택하십시오 .

그러면 분포 의 Z-점수(Z-Score) 를 계산할 수 있는 새 함수 인수 창이 시작됩니다.(Function Arguments)
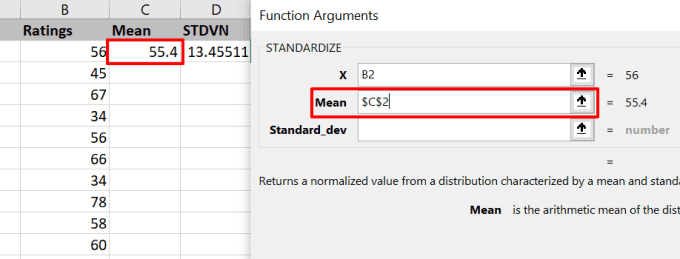
- (Enter)"X" 필드에 첫 번째 값의 셀 참조를 입력 합니다.

- (Enter)"평균" 필드에 산술 평균의 셀 참조를 입력 하고 키보드에서 F4 를 눌러 셀 참조를 잠급니다.
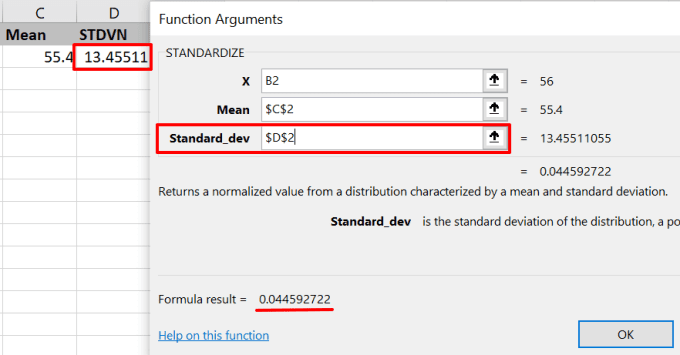
- 마지막으로 "Standard_dev" 필드에 표준 편차의 셀 참조를 입력하고 F4 키(F4) 를 눌러 셀 참조를 잠급니다. 도구는 Z 값(Z-value) 의 미리보기를 표시합니다 . 계속하려면 확인을 누르 십시오(OK) .
다른 값에 대한 Z-점수(Z-Score) 를 얻으려면 커서를 셀의 오른쪽 하단 모서리에 놓고 plus (+) icon 을 열 아래로 끕니다.

Excel 은 수식을 열 아래로 복사하고 해당 행의 다른 값에 대한 Z-점수 를 자동으로 생성합니다.(Z-Score)

Excel에서 Z-점수 계산: 방법 2(Calculate Z-Score In Excel: Method 2)
앞서 언급했듯이 데이터 포인트에서 데이터 세트의 평균을 빼고 그 결과를 표준 편차로 나누어 데이터 포인트의 Z-점수를 얻을 수 있습니다. (x-μ) / σ를 사용하면 이러한 값을 수동으로 입력하여 Excel 에서 z-점수를 계산할 수 있습니다.
- Z-점수(Z-Score) 열 에서 첫 번째 셀을 선택하고 등호( = ) 다음에 여는 괄호 를 입력한 다음 (open parenthesis)Z-점수(Z-Score) 를 계산하려는 데이터세트가 포함된 열에서 첫 번째 값을 선택합니다 . 그런 다음 (Afterward)하이픈(hyphen) 을 입력 하고 산술 평균을 선택한 다음 F4 키(F4) 를 눌러 평균을 절대/고정으로 만든 다음 괄호 닫기(close parenthesis) 아이콘을 누릅니다. 마지막으로 슬래시(forward-slash) ( / ) 키를 누르고 표준편차를 선택한 다음 F4 키를 눌러 셀 참조를 잠급니다.
=(B2-$C$2)/$D$2 와 유사해야 합니다 . 수식을 실행하려면 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .

수식은 선택한 셀의 첫 번째 값에 대한 Z-점수(Z-Score) 만 계산합니다 .
- (Hover)첫 번째 Z-점수(Z-Score) 셀 의 오른쪽 하단 모서리에 마우스를 놓고 plus (+) icon 을 열 아래로 끕니다.

Z-점수 해석하기
데이터 세트에는 음수와 양수 Z-Score(Z-Score) 가 혼합되어 있을 가능성이 큽니다 . 양수 Z-점수(Z-Score) 는 값/점수가 데이터 세트의 평균 평균보다 높다는 것을 나타냅니다. 물론 Z-Score(Z-Score) 가 음수 이면 그 반대가 됩니다. 값이 평균 평균보다 낮습니다. 데이터 포인트의 Z-점수(Z-Score) 가 영(0)이면 해당 값이 산술 평균과 같기 때문입니다.
데이터 포인트가 클수록 Z-스코어(Z-Score) 가 높아집니다 . 워크시트를 살펴보면 작은 값이 더 낮은 Z-Score(Z-Score) 를 가지고 있다는 것을 알게 될 것 입니다. 마찬가지로(Likewise) , 산술 평균보다 작은 값은 음 의 Z-점수(Z-Score) 를 갖 습니다.

예를 들어 샘플 워크시트에서 "Michael"이 가장 높은 등급(78)과 가장 높은 Z-점수(Z-Score) (1.679659)를 가짐을 알 수 있습니다. 반면에 "Dwight"와 "Kevin"은 모두 가장 낮은 등급(34)과 가장 낮은 Z-Score ( -1.59047 )를 기록했습니다.
(Become)Excel 전문가 되기 : 자습서 리포지토리
이제 데이터 세트 의 Z-점수 를 계산하는 방법을 알게 되었습니다. (Z-Score)Excel 에서 Z-점수(Z-Score) 를 계산하는 것과 관련하여 질문이나 기타 유용한 팁이 있는 경우 아래에 의견을 남겨주세요 .
분산 계산(calculating variance) , 데이터세트에서 중복 행 제거 , (removing duplicate rows)Excel에서 요약 함수(use summary functions in Excel) 를 사용하여 데이터를 요약하는 방법에 대한 Excel 관련 자습서를 읽는 것이 좋습니다 .
How to Calculate Z-Score in Excel
Aѕ you know, there are many mathematical calculations you can perform with Microsoft Excel. In this tυtorial, we’ll wаlk you through the steps involved in calculating Z-Score in Excel.
If this is your first time using Excel, we recommend you take five minutes to peruse this Microsoft Excel beginner’s tutorial. You’ll learn how essential functions work, navigation shortcuts, creating workbooks, formatting data, and everything there is to know about using the spreadsheet program as a beginner.

When you’re done with that, proceed to the next section to learn how to calculate Z score in Excel. But first, let’s briefly explain Z-Score, its uses, why you might need to calculate one, and how to get it done.
What Is a Z-Score?
Z-Score (also known as a “Standard Score”) is a metric that highlights the relationship between values in a distribution. More precisely, it describes the position of values in a dataset with respect to their mean and standard deviation. Z-Score allows for accurate measurement and comparison of values in a dataset.
The mathematical formula for calculating Z-Score is (x-µ) / σ; where x = Cell Value, µ = Mean, and σ = Standard Deviation.
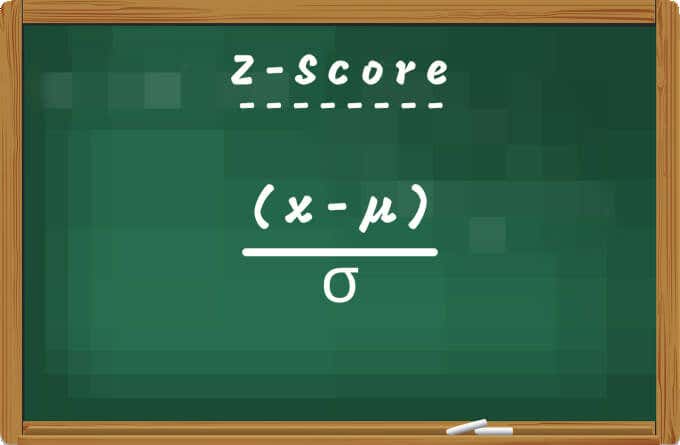
Companies sometimes use Z-Score to forecast and estimate impending bankruptcy. Additionally, it’s a great metric for ascertaining the financial position of an institution. Researchers also utilize Z-Score to compare observations obtained from different samples or populations.
How to Calculate Z-Score in Excel
Since Z-Score is a function of mean and standard deviation, you’ll need to first calculate the average and standard deviation of your dataset. Although you can extract the mean and standard deviation in any cell, we created dedicated columns for “Mean” and “Standard Deviation” in our worksheet. We also created a column for “Z-Score.”
Our sample document contains the performance ratings of 10 employees in a paper company. Now let’s calculate the Z-Score of the employees’ rating.
Calculate Mean Average
To calculate the mean average of your dataset, type =AVERAGE(, select the first value in the dataset, press the column key, select the last value within the dataset range, press the closing parenthesis key, and press Enter. The formula should look like the one below:
=AVERAGE(B2:B11)

You should see the mean or average value of the dataset in the cell you entered the formula.
Calculate Standard Deviation
Excel also makes it pretty easy to calculate the standard deviation of your dataset in a few clicks.
Select a cell in the “Standard Deviation” column, type =STDEV.P(, then select the first value in the range, press the column key, select the last value, enter the closing parenthesis, and press Enter. If you’re in doubt, the resulting formula should be similar to the one below:
=STDEV.P(B2:B11)

Calculate Z-Score in Excel: Method 1
Excel has a STANDARDIZE function that provides the Z-Score of a dataset in a distribution. Select the first cell in the Z-Score column and follow the steps below.
- Go to the Formulas tab and select More Formulas.

- Hover your mouse on the Statistical option and select the STANDARDIZE.

That’ll launch a new Function Arguments window where you’ll be able to calculate the Z-Score of the distribution.
- Enter the cell reference of the first value in the “X” field.

- Enter the cell reference of the arithmetic average in the “Mean” field and press the F4 on your keyboard to lock the cell reference.

- Finally, enter the standard deviation’s cell reference in the “Standard_dev” field and press F4 to lock the cell reference. The tool will display a preview of the Z-value. Press OK to proceed.

To get the Z-Score for other values, hover the cursor to the bottom-right corner of the cell and drag the plus (+) icon down the column.

Excel will copy the formula down the column and automatically generate the Z-Score for other values in the corresponding rows.

Calculate Z-Score In Excel: Method 2
As mentioned earlier, you can obtain a datapoint’s Z-Score by subtracting the mean of the dataset from the datapoint and dividing the result by the standard deviation. Using the (x-µ) / σ, you can calculate z-score in Excel by inputting these values manually.
- Select the first cell in the Z-Score column, type an equal sign (=) followed by an open parenthesis, and select the first value in the column containing the datasets whose Z-Score you want to calculate. Afterward, type a hyphen, select the arithmetic mean, press F4 to make the mean absolute/fixed, and press the close parenthesis icon. Finally, press the forward-slash (/) key, select the standard deviation, and press F4 to lock the cell reference.
The final formula should look similar to this: =(B2-$C$2)/$D$2. Press Enter to execute the formula.

Note that the formula will only calculate the Z-Score for the first value in the selected cell.
- Hover your mouse to the bottom-right corner of the first Z-Score cell and drag the plus (+) icon down the column.

Interpreting Z-Score
Your dataset will most likely contain a mix of negative and positive Z-Scores. A positive Z-Score indicates that the value/score is higher than the dataset’s mean average. A negative Z-Score, of course, tells the opposite: the value lies below the mean average. If a datapoint’s Z-Score is zero (0), that’s because its value equals the arithmetic mean.
The bigger a data point, the higher its Z-Score. Go through your worksheet and you’ll realize that the small values have lower Z-Scores. Likewise, values smaller than the arithmetic mean will have negative Z-Scores.

In our sample worksheet, for instance, you’ll discover that “Michael” had the highest rating (78) and highest Z-Score (1.679659). “Dwight” and “Kevin” on the other hand both had the lowest ratings (34) and lowest Z-Score (-1.59047).
Become an Excel Expert: Tutorial Repository
You now know how to calculate the Z-Score of a data set. Drop a comment below if you have questions or other useful tips regarding calculating Z-Score in Excel.
We recommend reading Excel-related tutorials on calculating variance, removing duplicate rows in your dataset, and how to use summary functions in Excel to summarize data.