히스토그램은 Excel(Excel) 의 데이터에서 생성할 수 있는 차트 유형입니다 . 데이터세트에서 특정 값의 빈도를 쉽게 요약할 수 있습니다. Excel 을 사용하면 히스토그램이 실제로 필요한 것이라고 가정하고 히스토그램을 간단하게 만들 수 있습니다!

히스토그램이란 무엇입니까?
히스토그램은 세로 막대를 사용하여 데이터 범위를 요약하는 차트 유형입니다. 막대 차트(bar chart) 처럼 보일 수 있지만 상당한 차이가 있습니다. 막대(Bar) 차트는 변수 간의 차이를 표시하는 반면 히스토그램은 일반적으로 다른 변수의 관점에서 변수 간의 차이를 표시하는 데 사용됩니다.
설명을 위해 히스토그램을 사용하여 IQ 점수의 공통 범위를 보여 줄 수 있습니다. 각 막대는 "빈" 또는 점수 범위를 나타냅니다. 따라서 0-10,11-20 등과 같은 것입니다.

수직 Y축은 해당 변수의 측정값이 각 빈 범위에 속하는지 보여줍니다. 따라서 100명의 사람들이 IQ 테스트를 작성하게 하면 점수가 특정 빈에 속하는 모든 사람이 해당 빈의 빈도 점수에 포함됩니다.
막대 차트를 사용하여 국가 간의 평균 IQ 점수와 같은 것을 비교할 수 있습니다. 이 경우 각 막대는 국가를 나타내고 세로 Y축은(Y-axis) 해당 국가의 평균 IQ를 나타냅니다.
히스토그램은 언제 사용해야 합니까?
히스토그램은 도수 분포를 시각화한 것입니다. 데이터가 어떤 종류의 분포를 가지고 있는지 한 눈에 알 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, "정규 분포"는 독특한 종 곡선 모양을 가지고 있습니다. 바이모달 분포에는 두 개의 범프가 있습니다. 점수 빈도가 어떤 식으로든 치우쳐 있는지 확인할 수도 있습니다.

물론 도수 분포가 정상적인지 여부를 확인하려면 Excel 에서 데이터에 대해 정규성 테스트를 실행해야 합니다. 이러한 테스트는 여전히 히스토그램을 기초로 사용하며 히스토그램을 만들고 관찰하는 것은 처리할 수 있는 분포의 종류를 대략적으로 보여주는 중요한 첫 번째 단계입니다.
히스토그램을 만드는 데 필요한 것
히스토그램을 만들려면 몇 가지가 필요합니다.
- 단일 변수에 대한 측정 집합입니다.
- 값 범위의 정의된 "빈"입니다.
첫 번째 요구 사항은 매우 간단합니다. 예를 들어 사람 그룹의 체중이 있는 경우 데이터 세트에 각각의 측정된 체중이 기록됩니다. 측정하지 않으려는 그룹의 데이터를 하나의 히스토그램으로 혼합하지 않도록 주의하십시오. 예를 들어 특정 연령 그룹이나 성별의 체중 분포만 보려면 해당 그룹에 대한 데이터만 포함해야 합니다.
단일 변수에서 두 그룹 간의 빈도 분포를 비교하려면 여러 히스토그램이 필요합니다. 각 인구 그룹에 대해 하나씩.
쓰레기통에 관한 모든 것(All About Bins)

다음 요구 사항이 가장 까다롭습니다. 빈도 카운트가 정렬될 "빈"을 결정해야 합니다. 문제는 이것이 임의적일 수 있다는 것입니다. 0에서 100 사이의 점수 빈도를 보려면 가능한 각 점수에 대해 하나씩 100개의 빈을 가질 수 있습니다. 그러나 이는 히스토그램에서 100개의 막대를 의미합니다.
이는 세분화된 분포이지만 그다지 유용하지는 않을 것입니다. 시험 점수의 경우 이미 등급 기호 형태의 "빈"이 있으므로 운이 좋은 것입니다. 그래서 당신은 그것들과 일치하도록 당신의 쓰레기통을 배열할 수 있습니다. 그러나 다른 유형의 데이터에 대해서는 빈 범위를 발명해야 합니다.
점수를 빈으로 나누는 방법과 특정 "빈 너비"를 결정한 경우 히스토그램이 원하는 그림을 그릴지 여부를 고려하는 데 시간을 할애하십시오.
데이터에 가장 적합한 빈 너비를 결정하려고 시도하는 Excel 의 자동 기능에 그대로 두도록 선택할 수도 있습니다 . Excel 에서는 선택적 소위 오버플로 및 언더플로 빈을 포함하는 빈 수를 지정할 수도 있습니다. 이들은 지정된 값 이상 및 이하의 모든 점수를 캡처합니다.
Excel 에서 히스토그램(Histogram) 만들기 : 단계별
몇 번의 클릭만으로 히스토그램을 생성할 수 있습니다. 여기 에서는 최신 버전의 Microsoft 365 를 사용하고 있지만 2016부터 시작하는 모든 Office 버전은 동일한 방식으로 작동합니다.(Office)
히스토그램 생성(Create the Histogram)
- 데이터세트에 대한 모든 값을 입력했다고 가정 하고 히스토그램에 포함되어야 하는 모든 값을 선택합니다(select all the values that should be included in the histogram) .

- 그런 다음 삽입 탭(Insert tab) 으로 전환합니다 .
- 이제 차트 섹션(chart section) 에서 히스토그램/막대 차트처럼 보이는 그림을 선택합니다.
- 팝업 메뉴에서 히스토그램(histogram) 을 선택 합니다.

가로 축 사용자 지정(Customize the Horizontal Axis)
이제 히스토그램이 시트에 있지만 원하는 대로 표시되지 않을 수 있습니다. 다음으로 가로 축을 사용자 지정합니다.
- 수평 축(horizontal axis) 을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭합니다 .
- 축 형식(Format axis) 을 선택합니다 .
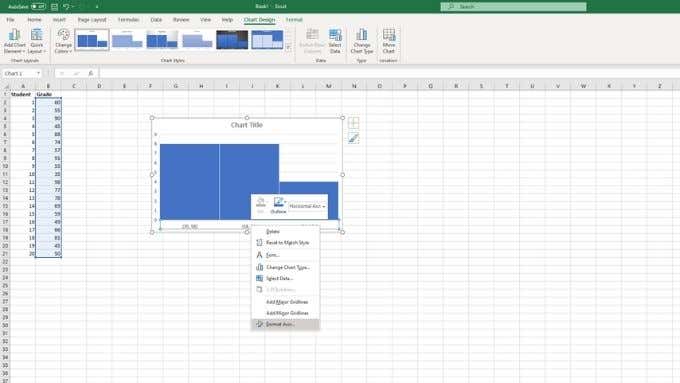
이제 형식 축 창이 열립니다. 여기에는 히스토그램을 조정하는 데 사용할 수 있는 여러 가지 중요한 옵션이 있습니다.
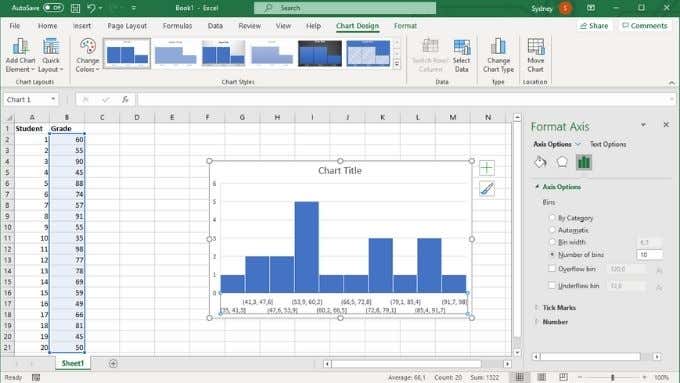
축 옵션(Axis Options) 아래에서 앞에서 설명한 저장소를 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다. 여기서 가장 중요한 두 가지 설정은 bin 너비(bin width) 와 bin 수입니다(number of bins) . 이러한 옵션은 상호 배타적입니다. 빈 너비를 숫자로 지정하면 빈 수가 자동으로 변경되고 그 반대의 경우도 마찬가지입니다. 여기에서 오버플로 및 언더플로 빈을 활성화하도록 선택할 수도 있습니다.
히스테리아그램에서 히스토그램으로
이제 히스토그램을 쉽게 만들 수 있기를 바랍니다. 하지만 기본 Excel 개념 을 검토해야 하는 경우 Microsoft Excel 기본 자습서 - Excel 사용 방법 학습을 읽어보세요.(Microsoft Excel Basics Tutorial – Learning How to Use Excel)
How to Make a Histogram in Excel
Α histogram іs a type of chart you can generate from data in Excel. It makes іt easy to summarize the frequency of particular values in your dataset. Excel makes it simple to create a histogram, assuming that a histogram is actually what you need!

What Is a Histogram?
A histogram is a type of chart that uses vertical bars to summarize ranges of data. While it may look like a bar chart, there are significant differences. Bar charts show the differences among variables, whereas histograms are generally used to show the differences among variables in terms of another variable.
To illustrate, a histogram may be used to show us how common ranges of IQ scores are. Each bar represents a “bin” or range of scores. So something like 0-10,11-20, etc.

The vertical Y-axis shows us how many measurements of that variable fall within each bin range. So if you have 100 people write an IQ test, every person whose score falls within a particular bin is counted towards the frequency score of that bin.
With a bar chart, you might want to compare something like average IQ scores between countries. In this case, each bar might represent a country and the vertical Y-axis would represent the average IQ of that country.
When Should You Use a Histogram?
HIstograms are a visualization of frequency distribution. It can help you see, at a glance, what sort of distribution your data has. For example, the “Normal Distribution” has the distinctive bell-curve look. A bimodal distribution will have two bumps. You can also see if score frequencies are skewed one way or another.

Of course, if you really want to determine whether your frequency distribution is normal or not, you’d run a normality test in Excel on your data. Those tests still use histograms as a basis though and creating and observing a histogram is a crucial first step in showing you roughly what sort of distribution you may be dealing with.
What You Need To Make a Histogram
In order to make a histogram, you need a few things:
- A set of measurements for a single variable.
- Defined “bins” of value ranges.
The first requirement is fairly straightforward. For example, if you have the weights of a group of people, you’d have each measured weight recorded in your dataset. Be careful not to mix the data from groups you don’t want to measure together into one histogram. For example, if you only wanted to look at the weight distribution of a certain age group or gender, you should only include data for that group.
If you wanted to compare the frequency distributions between two groups on a single variable, you’d need multiple histograms. One for each population group.
All About Bins

The next requirement is the trickiest. You need to decide on the “bins” that your frequency counts will be sorted into. The problem is that these may be arbitrary. If you’re going to look at the frequency of scores between 0 and 100, you could have 100 bins, one for each possible score. However, that means 100 bars in your histogram.
That’s a finely-grained distribution, but it’s probably not all that useful. In the case of test scores, you’re in luck since there are already “bins” in the form of grade symbols. So you could arrange your bins to coincide with those. However, for other types of data you have to invent the bin ranges.
Spend some time considering how you’d like to divide scores into bins and whether the histogram will paint the picture you’re looking for if you decide on a particular “bin width”.
You can also choose to leave it to an automatic function in Excel, where it will try to decide on a bin width that’s best suited to your data. In Excel, you can also specify the number of bins, which includes optional so-called overflow- and underflow- bins. These capture all scores over and under a specified value.
Creating a Histogram in Excel: Step-by-Step
Creating a histogram takes just a few clicks. We’re using the latest version of Microsoft 365 here, but any version of Office starting with 2016 will work the same way.
Create the Histogram
- Assuming you’ve entered all the values for your dataset, select all the values that should be included in the histogram.

- Next, switch to the Insert tab.
- Now, under the chart section, select on the picture that looks like a histogram/bar chart.
- From the popup menu, select histogram.

Customize the Horizontal Axis
Now your histogram is in the sheet, but it probably doesn’t look the way you want it to. So next, we’re going to customize the horizontal axis:
- Right-click the horizontal axis.
- Choose Format axis.

The format axis pane will now be open. There are a number of important options here that you can use to tune your histogram so that it looks exactly like you need it to.

Under Axis Options, you can customize the bins we discussed earlier. The two most important settings here are bin width and the number of bins. These options are mutually exclusive. If you specify a bin width in numbers, the number of bins will change automatically and vice versa. You can choose to activate overflow and underflow bins here as well.
From Hysteriagram to Histogram
Hopefully you can now make a histogram easily, but if you need to review basic Excel concepts, try reading Microsoft Excel Basics Tutorial – Learning How to Use Excel








