Windows 에는 일반적으로 (Windows)제어판(Control Panel) 과 같은 영역에서 볼 수 없는 시스템 설정을 구성 및 수정할 수 있는 모든 종류의 작은 유틸리티가 숨겨져 있습니다 . Windows 98 이후로 내가 가장 좋아하는 도구 중 하나 는 MSCONFIG 입니다. 기본적으로 Microsoft 시스템 구성(Microsoft System Configuration) 의 약자이며 다양한 설정을 구성하는 데 분명히 사용됩니다. 이 기사에서는 MSCONFIG 에 액세스 하는 방법과 사용 방법을 보여줍니다.
Windows 7 에서 (Windows 7)MSCONFIG 를 열어 시작하겠습니다 . 이 도구는 Windows Vista(Windows Vista) 이상과 거의 동일하며 Windows 8 에서는 약간만 변경되었으며 나중에 설명하겠습니다. 계속해서 시작 버튼을(Start button and type) 클릭 하고 msconfig 를 입력 하십시오.

여러 탭 이 있는 시스템 구성 대화 상자 가 나타납니다. (system configuration dialog)탭 수는 실행 중인 Windows(Windows) 버전에 따라 다를 수 있습니다 . Windows 7 및 8 에는 일반(General) , 부팅(Boot) , 서비스(Services) , 시작 및 도구(Startup and Tools) 의 5가지 탭이 있습니다 .
MSCONFIG 일반 탭
기본적으로 선택되는 첫 번째 탭은 일반적으로 항상 일반(General ) 탭입니다.
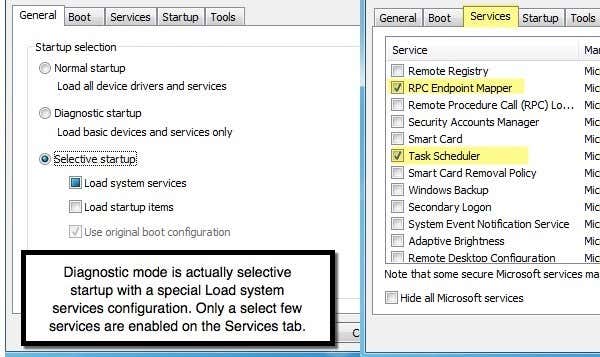
여기에서 시작 선택(Startup Selection) 제목 아래에 선택 가능한 세 개의 라디오 버튼이 표시됩니다. 변경하지 않는 한 기본적으로 정상 시작 이 선택됩니다. (Normal Startup)진단 시작(Diagnostic Startup) 은 안전 모드(Mode) 와 유사하지만 동일하지는 않은 "제거된 " 기능 모드에서 (” functionality)Windows 를 시작 합니다. 이 옵션을 선택한 경우 문제 해결을 완료한 후 다시 변경하지 않으면 Windows 가 이 방식으로 계속 시작됩니다.

또한 진단 시작을 선택하고 적용 을 클릭 하면 (startup and click Apply)시스템 서비스 로드(Load system services) 상자 만 채워진 상태로 선택적 시작이 자동으로 선택되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 진단 모드에서는 안전 모드(Mode) 보다 기본적으로 더 많은 드라이버와 서비스가 시작됩니다 . 아래에 설명합니다. 제어판 항목 이나 단순히 안전 (Control Panel item)모드(Mode) 에서 실행되지 않는 프로그램 을 사용해야 하는 경우 정상 시작보다 로드가 적지만 안전 모드(Mode) 보다 많은 진단 모드를 시도할 수 있습니다 .
진단 시작(Diagnostic startup) 을 클릭 하고 적용(Apply) 을 클릭하면 시스템 서비스 로드(Load system services) 상자가 선택되지 않고(not checked) 완전히 채워져 있음을 알 수 있습니다. 서비스 (Services) 탭을 클릭하고 스크롤(tab and scroll) 하면 소수의 서비스만 선택되어 있음을 볼 수 있기 때문에 이는 중요합니다 . 이제 일반(General) 탭 으로 돌아가서 선택적 시작(Selective startup) 을 다시 클릭 하고 실제 확인 표시가 있는 시스템 서비스 로드 상자를 선택하면 일부 (Load system services)서비스(Services) 탭뿐만 아니라 모든(ALL) 서비스가 서비스 탭 아래에 선택되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
시작 항목 로드(Load startup items) 상자를 사용 하면 시작(Startup) 탭 의 모든 시작 항목을 활성화하거나 모든 항목을 비활성화하는 확인 표시로만 확인할 수 있습니다. 시스템(Load system) 서비스 로드와 시작(Load startup) 항목 로드 모두에서 확인 표시가 있는 선택적 시작을 선택한 경우 모든 것이 활성화되어 있기 때문에 일반 시작을 수행하는 것과 거의 동일합니다.
선택적 시작을 수행하고 하나 또는 두 항목을 모두 확인하는 유일한 이유는 특정 서비스 또는 시작 항목이 문제를 일으키는지 파악하기 위한 것입니다. 그렇게 하는 방법은 일반(General) 탭 에서 해당 확인란을 선택한 다음 서비스(Services) 또는 시작 으로 이동하여 (Startup)모두 비활성화(Disable all) 를 클릭 한 다음 한 항목만 선택하는 것입니다. 컴퓨터를 다시 시작하고 해당 서비스 또는 시작 항목이 시스템 문제를 일으키는지 확인합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 서비스(Services) 또는 시작(Startup) 탭으로 다시 이동하여 다른 항목을 확인합니다. 문제가 있는 서비스(problem service) 또는 시작 항목 을 찾을 때까지 이 프로세스를 계속하십시오 .
MSCONFIG 부팅 탭
이제 일반 탭 과 이 탭이 (General tab)서비스(Services) 및 시작(Startup) 탭 모두에 연결되는 방식을 명확하게 이해 했으므로 두 번째 탭인 부팅에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다. 이것은 Windows 시작 방법에 대한 많은 옵션이 있기 때문에 중요한 탭입니다.
이 탭의 요점인 부팅 (Boot) 옵션(options) 부터 시작하겠습니다 . 고급 옵션(Advanced options) 버튼 은 일반적으로 실제 하드웨어용 장치 드라이버를 작성하는 프로그래머만 사용합니다.
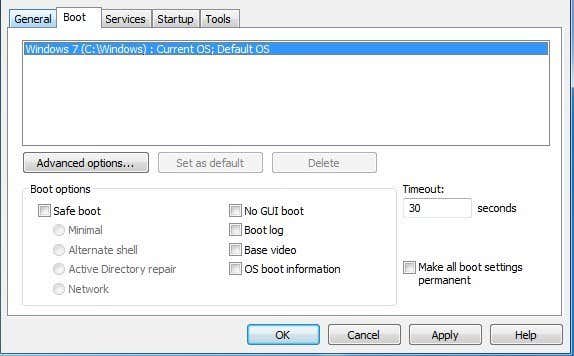
안전 부팅 을 선택하면 (Boot)최소(Minimal) , 대체 셸(Alternate shell) , Active Directory 복구 및 네트워크(Active Directory repair and Network) 의 네 가지 옵션 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다 . 각 옵션을 살펴보겠습니다.
– 최소(Minimal) – 가장 기본적인 드라이버와 서비스만 활성화된 상태에서 GUI 를 로드하는 표준 안전 모드입니다 . 이 모드에서는 네트워킹(Networking) 이 비활성화됩니다. 거의 익스플로러를(explorer and browse) 열고 주변을 탐색할 수 있습니다.
– 대체 셸 – (Alternate shell)명령 프롬프트(command prompt) 만으로 안전 모드를 로드 합니다 . GUI와 네트워킹(GUI and networking) 이 모두 비활성화됩니다. DOS 명령 을 실행하려는 경우에만 이 모드를 사용하십시오 .
– Active Directory 복구(Active Directory repair) – 이는 기업 환경에만 유용하며 네트워크 관리자(network administrator) 가 사용할 수 있습니다.
– 네트워크(Network) – 네트워킹이 활성화되어 있다는 점을 제외하면 Minimal 과 비슷 합니다. 파일 다운로드 를 위해 네트워크 리소스 또는 웹사이트(network resource or website) 에 연결해야 하는 경우에 유용 합니다.
오른쪽에 4개의 확인란이 표시되어 필요한 경우 최대 4개의 확인란을 모두 선택할 수 있습니다. 다음 옵션을 살펴보겠습니다.
– GUI 부팅 없음(No GUI boot) – 부팅할 때 Windows 시작 화면을 표시 하지(Will) 않습니다 .
– 부팅 로그(Boot log) – %SystemRoot% Ntbtlog.txt(Will) 에 있는 전체 부팅 프로세스(boot process) 의 로그 파일 을 (log file)만듭니다(Ntbtlog.txt) .
– 기본 비디오(Base video) – 시스템에 설치된 비디오 카드(video card) 에 특정한 드라이버 대신 표준 VGA 드라이버를 사용하는 최소 VGA (Will)모드 에서 (VGA mode)Windows 를 로드 합니다.
– OS 부팅 정보(OS boot information) – 부팅 과정에서 드라이버가 로드되므로 드라이버 이름이 출력에 표시됩니다.
시간 초과는 기본 옵션(default option) 을 선택하기 전에 부팅 메뉴(boot menu) 가 표시 되는 시간 입니다. 모든 부팅 설정을 영구적으로 만들기(Make all boot settings permanent) 확인란 을 선택한 경우 일반 탭 에서 (General tab)정상 시작(Normal startup) 을 클릭 해도 원래 설정으로 되돌아가지 않습니다. 부팅 설정을 수동으로 변경해야 합니다.
다시 말하지만, 시스템 구성 유틸리티(system configuration utility) 로 돌아가 선택을 취소하거나 정상 시작을 선택할 때까지 Windows 는 (Windows)안전 모드(Safe Mode) 에서 계속 로드됩니다 .
MSCONFIG 서비스 탭
다음 은 꽤 자명 한 서비스 탭입니다. (Services)여기서 중요한 것은 Microsoft 시스템(Microsoft system) 서비스 를 비활성화하고 싶지 않다는 것 입니다. 비활성화해야 하는 쓸모없는 Windows(Windows) 서비스 에 대한 많은 기사를 온라인에서 읽을 수 있지만 실제로는 좋은 생각이 아닙니다.

계속해서 모든 Microsoft 서비스 숨기기(Hide all Microsoft services) 확인란 을 선택하면 타사 서비스만 남게 됩니다. 타사 서비스를 비활성화하는 것이 유용할 수 있지만 특정 상황에서만 가능합니다. 대부분 이 탭은 Windows(Windows) 정지, 블루 스크린 또는(screen or something) 기타 좋지 않은 문제 를 일으키는 서비스를 비활성화하는 데 사용됩니다 .
MSCONFIG 시작 탭
시작 탭(startup tab) 은 단연코 가장 좋아하는 탭이며 실제로 내가 MSCONFIG 유틸리티(MSCONFIG utility) 를 처음 사용하는 유일한 이유입니다. 많은 수의 시작 프로그램으로 인해 일부 클라이언트 컴퓨터가 얼마나 느린지 놀랍습니다. 내가 많이 가지고 있어도 일반적으로 필요하지 않기 때문에 80 %를 비활성화합니다.
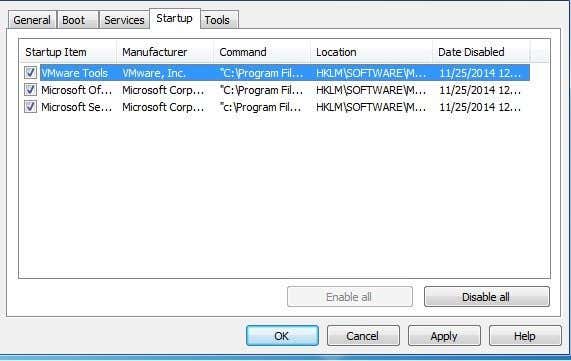
물론 일부 시작 항목은 무선 네트워크 카드(wireless network card) 나 터치패드를 제어하고 선택을 취소하면 둘 다 작동을 중지하기 때문에 특히 랩톱에서는 주의해야 합니다. Command 에서 볼 수 있는 시작 항목 이름 또는 EXE 파일로 간단한 (startup item name or EXE)Google 검색(Google search) 을 수행하는 것이 가장 좋습니다 .
또한 Windows(Windows) 에서 시작 프로그램을 비활성화하는 방법에 대한 심층 기사를 이미 작성했으며 비활성화 할 항목과 비활성화하지 않을 항목에 대한 추가 정보와 포인터를 제공합니다.
MSCONFIG 도구 탭
마지막으로 기본적으로 Windows 의 다른 유용한 유틸리티 전체에 연결되는 도구(Tools) 라는 유용한 탭이 있습니다.
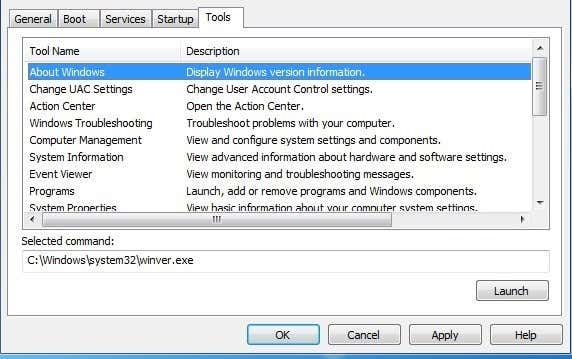
여기에는 Windows , UAC 설정, 관리 센터(action center) , 문제 해결사, 컴퓨터 관리(computer management) , 이벤트 뷰어(event viewer) , 프로그램, 시스템 속성, 인터넷(Internet) 옵션, 명령 프롬프트(command prompt) , 레지스트리 편집기(registry editor) , 작업 관리자(task manager) , 시스템 복원(system restore) 등에 대한 모든 정보가 포함됩니다. 기억이 나지 않는 경우 도구 또는 설정(tool or setting) 을 찾을 수 있는 곳 , 아마도 여기에 나열되어 있을 것입니다.
전반적으로 시스템 구성 유틸리티 는 (system configuration utility)Windows PC(Windows PCs) 를 관리하는 데 매우 편리한 도구 이며 고급 사용자(power user) 가 되려면 반드시 배워야 하는 것 입니다. 질문이 있으면 의견을 게시하십시오. 즐기다!
How to Use MSCONFIG in Windows
Windows has all ѕorts оf hidden little utilitіeѕ that let you configure аnd modify system settingѕ not normally visible in areas like the Control Panel. One of my favorite tools that has been around sincе Windows 98 is MSCONFIG. It basicаlly stands for Microsoft System Cоnfiguration and is obviously used to configure various settingѕ. In this artiсle, I’ll show you how to access MSCONFIG and how to use it.
Let’s start off by opening MSCONFIG on Windows 7. The tool is pretty much the same from Windows Vista and higher, with only a minor change in Windows 8 that I will talk about later. Go ahead and click on the Start button and type in msconfig.

The system configuration dialog will pop up with several tabs. The number of tabs may vary depending on which version of Windows you are running. In Windows 7 and 8, there are 5 tabs: General, Boot, Services, Startup and Tools.
MSCONFIG General Tab
The first tab, which is selected by default, will normally always be the General tab.
Here you will see three selectable radio buttons under the Startup Selection heading. Normal Startup will be selected by default unless changed. Diagnostic Startup will start Windows up in a “stripped down” functionality mode, similar to, but not the same as Safe Mode. If you choose this option, remember to change it back when you are done troubleshooting, or Windows will keep starting up in this manner.

Also, when you select Diagnostic startup and click Apply, you will see that it automatically selects Selective startup with only the Load system services box filled in. In diagnostic mode, you get more drivers and services started by default than with Safe Mode, which I explain below. If you find you need to use a Control Panel item or a program that simply won’t run on Safe Mode, then you can try diagnostic mode, which loads less than a normal startup, but more than Safe Mode.
You’ll notice that when you click Diagnostic startup and click Apply, the Load system services box is not checked, but is filled in entirely. That is significant because if you click on the Services tab and scroll through, you’ll see that only a handful of services are checked. Now if you go back to the General tab, click on Selective startup again and check the Load system services box with an actual checkmark, you’ll see that ALL services are checked under the Services tab not just a select few.

With the Load startup items box, you can only check it with a checkmark, which either enables all the startup items on the Startup tab or disables all of them. It should be noted that if you chose selective startup with a checkmark in both Load system services and Load startup items, then that’s pretty much the same thing as doing a normal startup because everything is enabled.
The only reason to do selective startup and check one or both items is to figure out if a particular service or startup item is causing problems. The way to do that is to check the appropriate box on the General tab and then go to Services or Startup, click Disable all, and then check off only one item. You restart the computer and see if that service or startup item is causing the issue with your system. If not, you go to the Services or Startup tab again and check another item. Continue this process until you find your problem service or startup item.
MSCONFIG Boot Tab
Now that we have a clear understanding of the General tab and how it’s connected to both the Services and Startup tabs, let’s talk about the second tab: Boot. This is an important tab because it has a lot of options for how Windows starts up.

Let’s start with Boot options as that’s the main point of this tab. The Advanced options button will normally only be used by programmers writing device drivers for actual hardware.
If you check Safe Boot, you can then pick from four options: Minimal, Alternate shell, Active Directory repair and Network. Let’s go through each option:
– Minimal – This is the standard safe mode that will load the GUI with only the most basic drivers and services enabled. Networking will be disabled in this mode. You can pretty much only open explorer and browse around.
– Alternate shell – This will load safe mode with just the command prompt. The GUI and networking will both be disabled. Only use this mode if you want to run DOS commands.
– Active Directory repair – This is only useful for corporate environments and will probably something your network administrator would use.
– Network – This is like Minimal, except networking is enabled. Useful if you need to connect to a network resource or website for downloading files.
On the right, you’ll see four checkboxes, which means you can check up to all four, if needed. Let’s go through these options:
– No GUI boot – Will simply not show the Windows welcome screen when booting.
– Boot log – Will make a log file of the entire boot process located at %SystemRoot%Ntbtlog.txt.
– Base video – Will load Windows in minimal VGA mode, which uses standard VGA drivers instead of the drivers that are specific to the video card installed on the machine.
– OS boot information – As drivers are being loaded during the boot up process, the names of the drivers will be shown in the output.
Timeout is the amount of time the boot menu is shown before it selects the default option. If you check the Make all boot settings permanent box, then clicking Normal startup on the General tab will not revert you back to your original settings. You’ll have to manually change any boot settings.
Again, Windows will continue to load in Safe Mode until you go back to the system configuration utility and uncheck it or choose normal startup.
MSCONFIG Services Tab
Next up is the Services tab, which is pretty self-explanatory. The main thing here is that you really don’t want to disable any Microsoft system services. You’ll read lots of articles online about useless Windows services that you should disable, but it’s really not a good idea.

Go ahead and check the Hide all Microsoft services box and you’ll only be left with third-party services. Disabling third-party services can be useful, but only in certain circumstances. Mostly this tab is used to disable a service that is causing Windows to freeze, blue screen or something else that is not good.
MSCONFIG Startup Tab
The startup tab is by far by favorite tab and really the only reason I actually use the MSCONFIG utility in the first place. It amazes me how slow some client computers are because of the massive number of startup programs. Even if I have a lot, I normally disable 80 percent of them because they aren’t necessary.

Of course you do have to be careful, especially on laptops, because some startup items control your wireless network card or your touchpad and both will stop working if you uncheck them. It’s best to perform a simple Google search with the startup item name or EXE file that you can see under Command.
I’ve also already written an in-depth article on disabling startup programs in Windows, which gives you more tips and pointers on what to and what not to disable.
MSCONFIG Tools Tab
Lastly, there is a useful tab called Tools that basically links out to a whole bunch of other useful utilities in Windows.

This includes everything from information about Windows, UAC settings, action center, troubleshooters, computer management, event viewer, programs, system properties, Internet options, command prompt, registry editor, task manager, system restore, etc. If you can’t remember where to find a tool or setting, it’s probably listed here.
Overall, the system configuration utility is a very handy tool to manage Windows PCs and definitely something you should learn if you want to become a power user. If you have any questions, post a comment. Enjoy!







