Windows 명령 프롬프트 는 오랫동안 Windows 운영 체제 의 핵심 부분이었던 기능입니다 . 일반 사용자도 Windows(Windows) 명령 프롬프트를 운영 체제의 핵심 부분으로
볼 정도로 유용하고 사용하기 쉬운
일부 CMD 명령이 있습니다.(CMD)
어느 시점에서 단계적으로 중단된다는 소문이 항상 있지만 곧 일어날 것 같지 않습니다.

The following are 21 of the best CMD commands you should know if you want to have more control over your Windows PC.
Also, be sure to check out our YouTube video where we go over the commands listed in this article:
1. ASSOC: Fix File Associations
One of the most powerful tools in the CMD command library is
the ASSOC command.
Your computer associates certain file extensions with
certain programs. This is how your computer knows to open Adobe when you double
click a PDF file, or Microsoft Word when you double click a DOC file.

명령 창에 ASSOC 를 입력하여 컴퓨터가 알고 있는 모든 파일 연결을 볼 수 있습니다 . 파일 확장자와 관련 프로그램이 표시됩니다.
assoc .doc=Word.Document.8 과 같이 입력하여 연결을 설정할 수 있습니다 .
2. FC: 파일 비교

시간이 지남에 따라 파일이 변경되면 버전 간의 차이점이 무엇인지 기억하기 어려울 때가 있습니다. CMD 명령이 파일을 비교하고 모든 차이점을 확인하는 기능을 제공 한다는 사실을 모를 수도
있지만 사실입니다.
FC 명령 은 ASCII 또는 이진 파일 비교를 수행하고 찾은 모든 차이점을 나열합니다.
Fc /a File1.txt
File2.txt 는 두 개의 ASCII 파일을 비교합니다.
Fc /b Picture1.jpg
Picture2.jpg 는 두 이미지에 대해 이진 비교를 수행합니다.
3. IPCONFIG: IP 구성

네트워크(Network) 문제 해결은 결코 간단하지 않지만 훨씬 쉽게 만드는 명령 중 하나는 IPCONFIG 입니다.
CMD 명령 프롬프트 에서 이 명령을 사용하면 다음 을 포함한 현재 네트워크 어댑터 연결에 대한 자세한 정보가 반환됩니다.
- 현재 IP 주소
- 서브넷 마스크
- 기본 게이트웨이 IP
- 현재 도메인
이 정보는 네트워크 어댑터에 발생할 수 있는 라우터 문제 및 기타 연결 문제를 해결하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
4. NETSTAT: 네트워크 통계

자신도 모르는 사이에 인터넷 위치에 연결하는 컴퓨터에서 맬웨어가 실행될 수 있다는 사실이 걱정되십니까?
명령 프롬프트에서 NETSTAT(NETSTAT)
명령 을 실행하면 컴퓨터에서 모든 활성 TCP 연결 목록을 가져올 수 있습니다.
5. PING: 테스트 패킷 보내기

IT 분석가의 가장 친한 친구는 PING 명령입니다. 이 명령을 실행하면 네트워크를 통해 대상 시스템으로 테스트 패킷이 전송됩니다.
PING 명령을 사용하여 컴퓨터가 다른 컴퓨터, 서버 또는 웹 사이트에 액세스할 수 있는지 여부를 테스트할 수 있습니다. 네트워크 연결 끊김을 표시하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 또한 패킷에 대한 전송 시간을 밀리초 단위로 제공하므로 잘못된 네트워크 연결도 드러납니다.
6. TRACERT: 경로 추적

TRACERT 는 사용하기에 매력적인 Windows 명령(Windows Command) 입니다. 인터넷 트래픽이 브라우저에서 Google
서버 와 같은 원격 시스템으로 이동하는 경로가 궁금하다면 TRACERT 를 사용하여 확인할 수 있습니다.
이 명령은 패킷을 원격 대상(서버 또는 웹사이트)으로 보내는 "경로 추적"의 약자이며 다음 정보를 모두 제공합니다.
- (Number)목적지에 도달하기 전의 홉 수 (중간 서버)
- 각 홉에 도달하는 데 걸리는 시간
- IP 및 때때로 각 홉의 이름
TRACERT는 웹에 액세스하는 위치에 따라 인터넷 요청 경로가 어떻게 변경되는지 표시할 수 있습니다. 또한 라우터 문제를 해결하거나 문제가 될 수 있는 로컬 네트워크를 켜는 데 도움이 됩니다.
7. POWERCFG: 전원 구성

노트북의 전원이 얼마나 빨리 소모되는 것 같아 답답 합니까(Are) ? 전원 설정이 가능한 한 효율적으로 구성되어 있을 수 있습니다. 도움이 될 수 있는 POWERCFG(POWERCFG) (전원 구성) 라는 Windows CMD 명령 이 있습니다. 명령 프롬프트를 관리자로 실행하고 powercfg – 에너지(powercfg – energy) 를 입력하여 전체 전력 효율성 보고서를 가져옵니다.
이 프로세스는 최대 1분 정도 걸릴 수 있지만 완료되면 시스템의 전력 효율성을 개선하는 데 도움이 될 수 있는 경고나 오류가 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다.

해당 오류 및 경고에 대한 세부 정보를 보려면 energy-report.html 파일을 보십시오.
8. 종료: 컴퓨터 끄기

SHUTDOWN 명령 은
컴퓨터를 종료할 수 있지만 해당 종료 동작을 제어할 수 있는 매우 다양한 명령입니다. 패치가 컴퓨터 시스템에 적용된 후 예약된 작업 또는 IT 배치 작업의 일부로 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
shutdown /i 를 입력
하면 종료가 시작되지만 GUI 에서 사용자에게 다시 시작할지 또는 완전히 종료할지에 대한 옵션을 제공합니다. GUI 팝업을 원하지 않으면 shutdown /s 명령을 실행하면 됩니다.
로그오프, 최대 절전 모드, 다시 시작 등을 수행하는 데 사용할 수 있는 기타 매개변수의 긴 목록이 있습니다. 인수(Just) 없이 종료(shutdown) 를 입력 하면 모두 볼 수 있습니다.
9. SYSTEMINFO: 시스템 정보

가지고 있는 네트워크 카드 브랜드, 프로세서 세부 정보 또는 Windows OS 의 정확한 버전을 알아야 하는 경우 SYSTEMINFO 명령이 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
이 명령은 시스템을 폴링하고 시스템에 대한 가장 중요한 정보를 가져옵니다. 읽기 쉬운 깨끗한 형식으로 정보를 나열합니다.
10. SFC: 시스템 파일 검사기

바이러스나 다른 소프트웨어가 핵심 시스템 파일을 손상시킬 수 있다는 우려가 있는 경우 해당 파일을 검사하고 무결성을 확인할 수 있는 Windows 명령이 있습니다.(Windows)
CMD 를 관리자 로 시작해야 합니다 (오른쪽 클릭하고 관리자 권한 으로 실행(Run as Administrator) 선택 ). SFC /SCANNOW 를 입력
하면 보호된 모든 시스템 파일의 무결성을 검사합니다. 문제가 발견되면 백업된 시스템 파일로 파일을 복구합니다.
SFC 명령을 사용하여 다음을 수행할 수도 있습니다.
- /VERIFYONLY : 무결성을 확인하지만 파일을 복구하지 않습니다.
- /SCANFILE : 특정 파일의 무결성을 검사하고 손상된 경우 수정합니다.
- /VERIFYFILE : 특정 파일의 무결성을 확인하지만 복구하지는 않습니다.
- /OFFBOOTDIR : 오프라인 부트 디렉터리에서 복구를 수행하는 데 사용합니다.
- /OFFWINDIR : 오프라인 Windows 디렉터리에서 복구를 수행하는 데 사용합니다.
- /OFFLOGFILE : 검사 결과와 함께 로그 파일을 저장할 경로를 지정합니다.
스캔하는 데 최대 10분 또는 15분이 소요될 수 있으므로 시간을 내십시오.
11. NET USE: 드라이브 매핑
새 드라이브를 매핑하려면 항상 파일 탐색기를 열고 이 PC를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭한 다음 네트워크 드라이브 매핑(Map Network Drive) 마법사로 이동할 수 있습니다. 그러나 NET USE 명령을 사용하면 하나의 명령 문자열로 동일한 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
\\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE\ 라는 공유 폴더가 있는 경우 다음 명령을 입력하여 이를 고유한 Z: 드라이브로 매핑할 수 있습니다.
Net use Z: “\\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE”
/persistent:yes
영구(persistent) 스위치 는
컴퓨터에 다시 로그인할 때마다 이 드라이브를 다시 매핑하도록 지시합니다.
12. CHKDSK: 디스크 확인
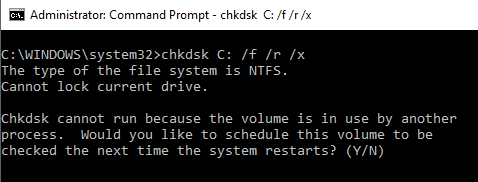
SFC 명령은 핵심 시스템 파일의 무결성만 검사 하지만 CHKDSK
명령을 사용하여 전체 드라이브를 검사할 수 있습니다.
C: 드라이브를 확인하고 문제를 복구하는 명령은 관리자로 명령 창을 실행하고 CHKDSK /f C: 를 입력 합니다.
이 명령은 다음과 같은 사항을 확인합니다.
이 명령은 모든 디스크 오류를 수정할 수 있습니다(가능한 경우). 명령이 완료되면 스캔 상태와 수행된 작업이 표시됩니다.
13. SCHTASKS: 작업 예약
Windows에는 예약된 작업을 생성하기 위한 마법사가 함께 제공됩니다. 예를 들어, 매일 정오에 실행하려는 BAT 파일이 C: emp에 저장되어 있을 수 있습니다.(BAT)
이것을 구성하려면 예약된 작업(Scheduled Task) 마법사를 클릭해야 합니다. 또는 단일 SCHTASKS
명령을 입력하여 설정할 수 있습니다.
SCHTASKS /Create /SC
HOURLY /MO 12 /TR Example /TN c:\temp\File1.bat
예약된 전환은 분, 시간별, 매일 및 매월과 같은 인수를 허용합니다. 그런 다음 /MO 명령으로 주파수를 지정합니다.
명령을 올바르게 입력했다면
SUCCESS: 예약된 작업 "예제"가 성공적으로 생성되었습니다(SUCCESS: The scheduled task “Example”
has successfully been created) .
14. ATTRIB: 파일 속성 변경
In Windows, you can change file attributes by right clicking
on a file and finding the right property to change. However, instead of hunting
around for the file attribute, you can use the ATTRIB command to set the file attributes.
For example, if you type: ATTRIB +R +H C:\temp\File1.bat, it’ll set File1.bat as a hidden,
read-only file.
There is no response when it’s successful, so unless you see
an error message, the command worked.
Other Windows CMD Commands
As you can see, there are some powerful and useful things
you can do with the Windows command prompt, if you know the right commands.
믿거 나 말거나 간단한 명령을 입력하는 것만으로는 결코 깨닫지 못했던 일을 수행할 수 있는 기능을 제공하는 훨씬 더 많은 명령이 있습니다.
- BITSADMIN : 네트워크 또는 인터넷을 통해 업로드 또는 다운로드 작업을 시작하고 해당 파일 전송의 현재 상태를 모니터링합니다.
- COLOR : 명령 프롬프트 창의 배경색을 변경합니다.
- COMP : 두 파일의 내용을 비교하여 차이점을 확인합니다.
- FIND/FINDSTRASCII 파일 내부의 문자열을 검색 합니다.
- PROMPT : 명령 프롬프트를 C:>에서 다른 것으로 변경합니다.
- TITLE : 명령 프롬프트 창의 제목을 변경합니다.
- REGEDIT : Windows 레지스트리 에서 키를 편집합니다 (주의해서 사용).
- ROBOCOPY : Windows 에 내장된 강력한 파일 복사 유틸리티 입니다.
더 자세히 알아보고 싶다면 Microsoft 에서 최신 버전의 Windows OS 에 포함된 모든 (Windows OS)Windows CMD 명령(Windows CMD commands) 의 전체 목록을 제공합니다 .
21 CMD Commands All Windows Users Should Know
The Windows command prompt is a feature that’s been а сore
part of the Windows operatіng sуstem for а long time. There are some CMD
commandѕ that are so useful and еasy to use that even regular users ѕee the
Windows command prompt as a key part of the operating system.
There are always rumors that it will be phased out at some
point, but that’s unlikely to happen any time soon.

The following are 21 of the best CMD commands you should know if you want to have more control over your Windows PC.
Also, be sure to check out our YouTube video where we go over the commands listed in this article:
1. ASSOC: Fix File Associations
One of the most powerful tools in the CMD command library is
the ASSOC command.
Your computer associates certain file extensions with
certain programs. This is how your computer knows to open Adobe when you double
click a PDF file, or Microsoft Word when you double click a DOC file.

You can view all the file associations your computer knows
about by typing ASSOC in the command
window. You’ll see the file extension and the program it’s associated with.
You can set the association by typing something like assoc .doc=Word.Document.8.
2. FC: File Compare

Sometimes when files are changed over time, it’s hard to
remember what the differences were between versions. You may not know that a
CMD command offers the ability to compare files and see all differences, but
it’s true.
The FC command
performs either an ascii or a binary file comparison and will list all of the
differences that it finds.
Fc /a File1.txt
File2.txt will compare two ascii files.
Fc /b Picture1.jpg
Picture2.jpg will do a binary compare on two images.
3. IPCONFIG: IP Configuration

Network troubleshooting is never simple, but one command
that makes it much easier is IPCONFIG.
Using this command in the CMD command prompt returns detailed
information about your current network adapter connection including:
- Current IP Address
- Subnet Mask
- Default Gateway IP
- Current domain
This information can help you troubleshoot router issues and
other connection issues you could be having with your network adapter.
4. NETSTAT: Network Statistics

Concerned that you could have malware running on your
computer that’s connecting to internet locations without you knowing about it?
If you run a NETSTAT
command in the command prompt, you can get a list of all active TCP connections
from your computer.
5. PING: Send Test Packets

An IT Analyst’s best friend is the PING command. Running this
command sends test packets over the network to the target system.
You can use the PING command to test whether your computer
can access another computer, a server, or even a website. It can help with
revealing network disconnections. It also provides transit time for the packets
in milliseconds, so it also reveals a bad network connection as well.
6. TRACERT: Trace Route

TRACERT is a
fascinating Windows Command to use. If you’re ever curious to see the path your
internet traffic takes to get from your browser to a remote system like Google
servers, you can use TRACERT to see it.
The command stands for “Trace Route”, which sends packets
out to a remote destination (server or website), and provides you with all of
the following information:
- Number of hops (intermediate servers) before
getting to the destination
- Time it takes to get to each hop
- The IP and sometimes the name of each hop
TRACERT can reveal how the routes of your internet requests
change depending where you’re accessing the web. It also helps with
troubleshooting a router or switch on a local network that may be problematic.
7. POWERCFG: Power Configuration

Are you frustrated with how quickly your laptop seems to run
out of power? It could be that your power settings are configured as
efficiently as possible. There’s a windows CMD command called POWERCFG (power configuration) that can
help. Run the command prompt as an administrator and type powercfg – energy to get a full power efficiency report.
The process can take up to about a minute, but when it’s done,
you’ll see whether there are any warnings or errors that might help you improve
the power efficiency of your system.

View the energy-report.html file to see the details of those
errors and warnings.
8. SHUTDOWN: Turn Off Computer

The SHUTDOWN
command is a pretty versatile command that lets you shutdown the computer but
control the behavior of that shutdown. It’s commonly used as a scheduled task
or part of an IT batch job after patches have been applied to a computer
system.
Typing shutdown /i
from the command prompt will initiate a shutdown, but it’ll upon a GUI to give
the user an option on whether to restart or do a full shutdown. If you don’t
want to have any GUI pop up, you can just issue a shutdown /s command.
There is a long list of other parameters you can use to do a
log off, hibernate, restart, and more. Just type shutdown without any arguments to see them all.
9. SYSTEMINFO: System Information

If you need to know what brand of network card you have,
processor details, or the exact version of your Windows OS, the SYSTEMINFO command can help.
This command polls your system and pulls the most important
information about your system. It lists the information in a clean format
that’s easy to read.
10. SFC: System File Checker

If you’re ever concerned that a virus or some other software
might have corrupted your core system files, there’s a Windows command that can
scan those files and ensure their integrity.
You need to launch CMD as administrator (right click and
choose Run as Administrator). Typing
SFC /SCANNOW will check the integrity of all protected system files. If a
problem is found, the files will be repaired with backed-up system files.
The SFC command also lets you:
- /VERIFYONLY:
Check the integrity but don’t repair the files.
- /SCANFILE:
Scan the integrity of specific files and fix if corrupted.
- /VERIFYFILE:
Verify the integrity of specific files but don’t repair them.
- /OFFBOOTDIR:
Use this to do repairs on an offline boot directory.
- /OFFWINDIR:
Use this to do repairs on an offline Windows directory.
- /OFFLOGFILE:
Specify a path to save a log file with scan results.
The scan can take up to 10 or 15 minutes, so give it time.
11. NET USE: Map drives
If you want to map a new drive, you could always open File
Explorer, right click on This PC, and go through the Map Network Drive wizard.
However, using the NET USE command,
you can do the same thing with one command string.
For example, if you have a share folder on a computer on
your network called \\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE\, you can
map this as your own Z: drive by typing the command:
Net use Z: “\\OTHER-COMPUTER\SHARE”
/persistent:yes
The persistent
switch tells your computer that you want this drive remapped every time you log
back into your computer.
12. CHKDSK: Check Disk

While the SFC command only checks the integrity of core
system files, you can use the CHKDSK
command to scan an entire drive.
The command to check the C: drive and repair any problems,
launch the command window as an administrator and type CHKDSK /f C:.
This command checks for things like:
- File fragmentation
- Disk errors
- Bad sectors
The command can fix any disk errors (if possible). When the
command is finished, you’ll see a status of the scan and what actions were
taken.
13. SCHTASKS: Schedule Tasks
Windows comes with a wizard for creating scheduled tasks.
For example, maybe you have a BAT file stored on C:\temp that you want to run
every day at noon.
You’d have to click through the Scheduled Task wizard to
configure this. Or you can type a single SCHTASKS
command to set it up.
SCHTASKS /Create /SC
HOURLY /MO 12 /TR Example /TN c:\temp\File1.bat
The scheduled switch accepts arguments like minute, hourly,
daily, and monthly. Then you specify the frequency with the /MO command.
If you typed the command correctly, you’ll see the response,
SUCCESS: The scheduled task “Example”
has successfully been created.
14. ATTRIB: Change File Attributes
In Windows, you can change file attributes by right clicking
on a file and finding the right property to change. However, instead of hunting
around for the file attribute, you can use the ATTRIB command to set the file attributes.
For example, if you type: ATTRIB +R +H C:\temp\File1.bat, it’ll set File1.bat as a hidden,
read-only file.
There is no response when it’s successful, so unless you see
an error message, the command worked.
Other Windows CMD Commands
As you can see, there are some powerful and useful things
you can do with the Windows command prompt, if you know the right commands.
Believe it or not, there are even more commands that will
give you the ability to do some things you probably never realized just by
typing a simple command.
- BITSADMIN:
Initiate upload or download jobs over the network or internet and monitor the
current state of those file transfers.
- COLOR:
Change the background color of the command prompt window.
- COMP:
Compare the contents of any two files to see the differences.
- FIND/FINDSTR:
Search for strings inside of any ASCII files.
- PROMPT:
Change the command prompt from C:\> to something else.
- TITLE:
Change the title of the command prompt window.
- REGEDIT:
Edit keys in the Windows registry (use with caution).
- ROBOCOPY:
A powerful file copy utility built right into Windows.
If you’re interested in learning more, Microsoft offers a full list of all of the Windows CMD commands included in the latest version of the Windows OS.













