그래프와 Excel 차트는(Excel charts) 복잡한 데이터 세트를 시각화하는 좋은 방법이며 종형(Bell) 곡선도 예외는 아닙니다. 정규분포를 쉽게 분석할 수 있으며 Excel 에서 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다 . 방법을 알아봅시다.
종형 곡선의 목적은 단순히 데이터를 아름답게 만드는 것 이상이라는 점을 명심하세요. 이러한 차트에서 수행할 수 있는 다양한 형태의 데이터 분석이 있으며, 이를 통해 데이터 세트의 많은 추세와 특성을 알 수 있습니다. 하지만 이 가이드에서는 분석이 아닌 종형 곡선 생성에만 중점을 둘 것입니다.

정규분포(Normal Distribution) 소개
종형(Bell) 곡선은 정규 분포를 따르는 데이터세트를 시각화하는 데에만 유용합니다. 따라서 종형 곡선에 대해 알아보기 전에 정규 분포가 무엇을 의미하는지 살펴보겠습니다.
기본적으로 값이 평균을 중심으로 크게 밀집되어 있는 모든 데이터 세트를 정규 분포(또는 가우스 분포라고도 함)라고 부를 수 있습니다. 자연적으로 수집되는 대부분의 데이터 세트는 직원 성과 수치부터 주간 매출 수치까지 이와 같은 경향이 있습니다.
종형 곡선(Bell Curve) 이란 무엇 이며 왜 유용한(Useful) 가요 ?
정규 분포의 데이터 포인트는 평균을 중심으로 밀집되어 있으므로 절대값보다는 중앙 평균에서 각 데이터 포인트의 분산을 측정하는 것이 더 유용합니다. 그리고 이러한 분산을 그래프 형태로 표시하면 종형 곡선이(Bell Curve) 생성됩니다 .
이를 통해 이상값을 한 눈에 확인할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 평균과 관련하여 데이터 포인트의 상대적인 성능도 확인할 수 있습니다. 직원 평가, 학생 점수 등의 경우 이를 통해 실적이 저조한 직원을 구분할 수 있습니다.
종형 곡선을 만드는 방법
Excel의(simple charts in Excel) 많은 간단한 차트와 달리 데이터 세트에 대해 마법사를 실행하는 것만으로는 종형 곡선을 만들 수 없습니다. 데이터에는 먼저 약간의 전처리가 필요합니다. 수행해야 할 작업은 다음과 같습니다.
- 데이터를 오름차순으로 정렬하는 것부터 시작합니다. 전체 열을 선택한 다음 Data > Sort Ascending 로 이동하면 쉽게 이 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다 .

- 다음으로 Average 함수를 사용하여 평균값(또는 Mean)을 계산합니다 . (calculate the average value (or Mean))결과가 십진수로 표시되는 경우가 많으므로 Round(Round) 함수와 함께 사용하는 것도 좋습니다 .
샘플 데이터세트의 경우 함수는 다음과 같습니다.
=ROUND(AVERAGE(D2:D11),0)

- 이제 표준 편차를(Standard Deviation) 계산하는 두 가지 함수가 있습니다 . STDEV.S 는 모집단 표본(일반적으로 통계 연구)만 있을 때 사용되는 반면, STDEV.P는(STDEV.P) 전체 데이터세트가 있을 때 사용됩니다.
대부분의 실제 응용 프로그램(직원 평가, 학생 점수 등)에는 STDEV.P가(STDEV.P) 이상적입니다. 다시 한번, Round 함수를 사용하여 정수를 얻을 수 있습니다.
=ROUND(STDEV.P(D2:D11),0)

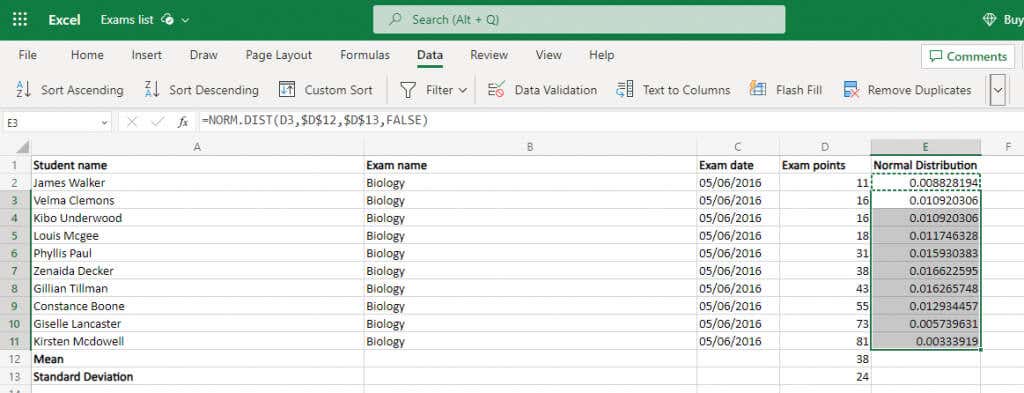
- 이 모든 것은 우리에게 필요한 실제 값, 즉 정규(Normal) 분포를 위한 준비 작업에 불과했습니다. 물론 Excel에는(Excel) 이미 이를 위한 전용 기능도 있습니다.
NORM.DIST 함수는 누적(NORM.DIST) 분포를 활성화하기 위해 데이터 포인트, 평균, 표준 편차 및 부울 플래그의 네 가지 인수를 사용합니다. 마지막 항목( FALSE(FALSE) 입력 )을 안전하게 무시할 수 있으며 이미 평균과 편차를 계산했습니다. 이는 셀 값만 입력하면 결과를 얻을 수 있음을 의미합니다.
=NORM.DIST(D2,$D$12,$D$13,FALSE)
하나의 셀에 대해 수행한 다음 전체 열에 수식을 복사하면 됩니다 . Excel에서는(– Excel) 새 위치와 일치하도록 참조를 자동으로 변경합니다. 하지만 먼저 $ 기호를 사용하여 평균 및 표준 편차 셀 참조를 잠그십시오.
- 원래 값과 함께 이 정규 분포를 선택합니다. 분포는 y축을 형성하고 원래 데이터 포인트는 x축을 형성합니다.

- 삽입(Insert) 메뉴 로 이동하여 분산형 다이어그램으로 이동하세요. 부드러운 선(Smooth Lines) 으로 분산(Scatter) 옵션을 선택합니다 .

MS Excel 에서 종형 곡선 차트를(Bell Curve Chart) 만드는 가장 좋은 방법은 무엇입니까 ?
종형(Bell) 곡선 차트는 복잡해 보이지만 실제로는 만들기가 매우 간단합니다. 필요한 것은 데이터세트의 정규 분포 지점뿐입니다.
먼저 내장된 Excel(Excel) 수식을 사용하여 평균과 표준 편차를 결정합니다 . 그런 다음 이 값을 사용하여 전체 데이터 세트의 정규 분포를 계산합니다.
종형 곡선 차트는 x축에 원래 데이터 포인트를 사용하고 y축에 정규 분포 값을 사용하는 부드러운 선이 있는 분산형 플롯 입니다 . (Smooth Lines)데이터 세트가 정규 분포를 따른다면 Excel(Excel) 에서 부드러운 종형 곡선을 얻을 수 있습니다 .
How to Create a Bell Curve Chart in Microsoft Excel
Graphs and Excel charts are a great way to visualize complex datasets, and Bell curves are no exception. They let you analyze a normal distribution easily and can be easily created in Excel. Let’s find out how.
Keep in mind that the purpose of a bell curve goes beyond simply prettifying the data. There are many forms of data analysis that can be performed on such a chart, revealing many trends and characteristics of the dataset. For this guide, though, we will be only focusing on creating a bell curve, not analyzing it.

Introduction to a Normal Distribution
Bell curves are only useful to visualize datasets that are distributed normally. So before we dive into bell curves, let us take a look into what a normal distribution even means.
Basically, any dataset where the values are largely clustered around the mean can be called a normal distribution (or a Gaussian distribution as it is sometimes called). Most naturally collected datasets tend to be like that, from employee performance numbers to weekly sales figures.
What Is a Bell Curve And Why Is It Useful?
Since the data points of a normal distribution are clustered around the mean, it is more useful to measure the variance of each data point from the central mean rather than its absolute value. And plotting these variances in the form of a graph yields a Bell Curve.
This allows you to spot the outliers at a glance, as well as see the relative performance of the data points with respect to the average. For things like employee appraisals and student scores, this gives you the ability to tell the underperformers apart.
How to Create a Bell Curve
Unlike many simple charts in Excel, you cannot create a bell curve by simply running a wizard on your dataset. The data needs a bit of pre-processing first. Here is what you need to do:
- Begin by sorting the data in ascending order. You can do this easily by selecting the whole column and then heading to Data > Sort Ascending.

- Next, calculate the average value (or Mean) using the Average function. As the result is often in decimals, it is a good idea to pair it with the Round function as well.
For our sample dataset, the function looks something like this:
=ROUND(AVERAGE(D2:D11),0)

- Now we have two functions for calculating the Standard Deviation. STDEV.S is used when you only have a sample of the population (usually in statistical research) while STDEV.P is used when you have the complete dataset.
For most real-life applications (employee appraisal, student marks, etc.) the STDEV.P is ideal. Once again, you can use the Round function to get a whole number.
=ROUND(STDEV.P(D2:D11),0)

- All of this was just prep work for the real values we need – the Normal distribution. Of course, Excel already has a dedicated function for that as well.
The NORM.DIST function takes in four arguments – the data point, the mean, the standard deviation, and a boolean flag to enable cumulative distribution. We can safely ignore the last one (putting in FALSE) and we already calculated the mean and the deviation. This means we just need to feed in the cell values and we will get the result.
=NORM.DIST(D2,$D$12,$D$13,FALSE)
Do it for one cell and then just copy the formula over to the whole column – Excel will automatically change the references to match the new locations. But make sure to lock the mean and standard deviation cell references first by using a $ symbol.

- Select this normal distribution along with the original values. The distribution will form the y-axis while the original data points form the x-axis.

- Head to the Insert menu and navigate to the scatter diagrams. Select the Scatter with Smooth Lines option.

What Is the Best Way of Creating a Bell Curve Chart in MS Excel?
Bell curve charts might seem complicated, but are actually pretty simple to create. All you need is the normal distribution points of your dataset.
First, determine the mean and the standard deviation using built-in Excel formulas. Then use these values to calculate the normal distribution of the entire dataset.
The bell curve chart is just a Scatter with Smooth Lines plot using the original data points for the x-axis and the normal distribution values for the y-axis. If your dataset was normally distributed, you will get a smooth bell curve in Excel.







