Microsoft Excel 의 VLOOKUP 함수는 말 그대로 수직 조회(vertical lookup) 를 의미 합니다. 열의 셀에 있는 값을 조회하는 검색 기능입니다. 이 함수는 왼쪽에서 첫 번째 열의 항목을 기준으로 데이터를 검색합니다.
수직 데이터 검색은 수많은 열과 행이 있는 테이블을 다룰 때 가장 중요합니다. 수백 개의 셀을 스크롤하여 분석하는 대신 Excel의 VLOOKUP 기능을 사용하면 위에서 아래로 값을 조회하여 원하는 데이터를 찾을 수 있습니다.
(Create)Excel의 VLOOKUP 기능 만들기 , 빌드 및 사용
이 예에서는 7명의 직원 급여에 대한 정보를 검색 하는 VLOOKUP 함수로 작업합니다. (VLOOKUP)이 섹션에서는 다음과 같은 방법으로 VLOOKUP 기능을 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
- Excel VLOOKUP 함수를 작성합니다.
- Excel에서 VLOOKUP 함수를 작성하십시오.
더 이상 고민하지 않고 시작하겠습니다. 첫 번째 방법에서는 함수를 수동으로 만듭니다. 다음으로 Excel의 내장 함수 인수(Functions Arguments) 마법사에서 사용합니다.
1] 엑셀 VLOOKUP 함수 작성
Microsoft Excel 을 시작 하고 고유 식별자 역할을 하는 값에 대한 열을 만듭니다. 이것을 참조 열(reference column) 이라고 부를 것 입니다.
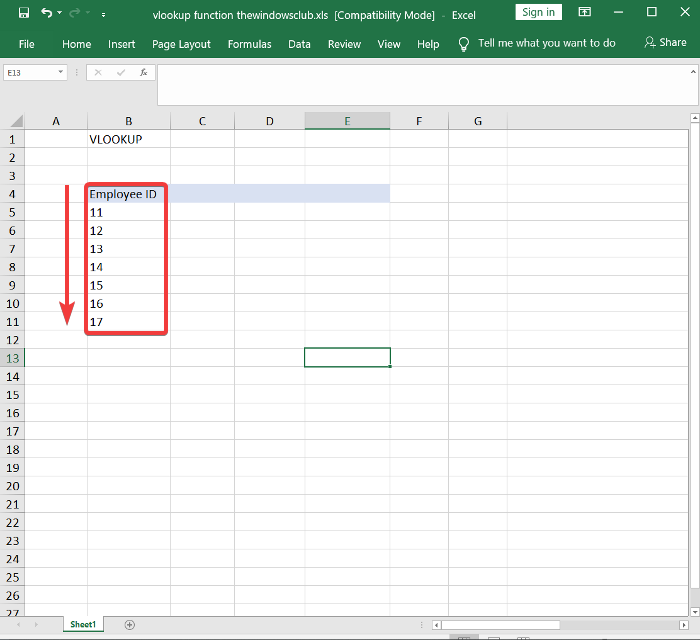
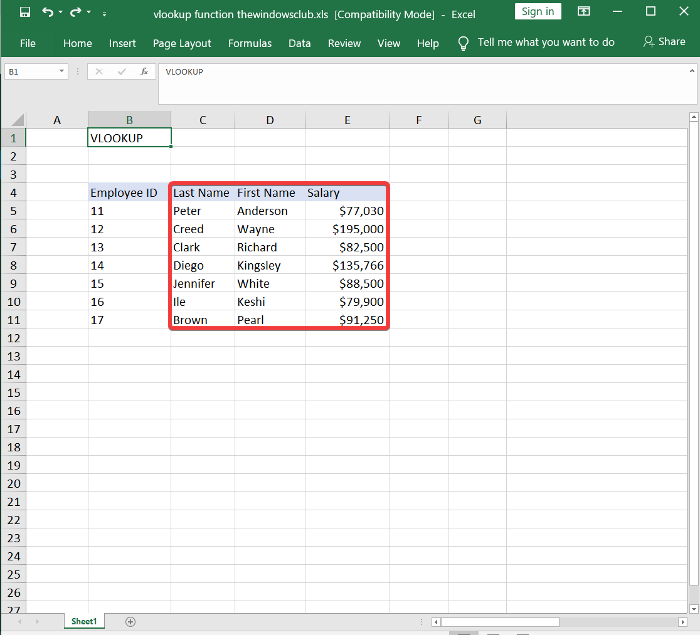
첫 번째 단계에서 만든 첫 번째 열의 오른쪽에 열을 더 추가하고 이 열에 셀 값을 삽입합니다.
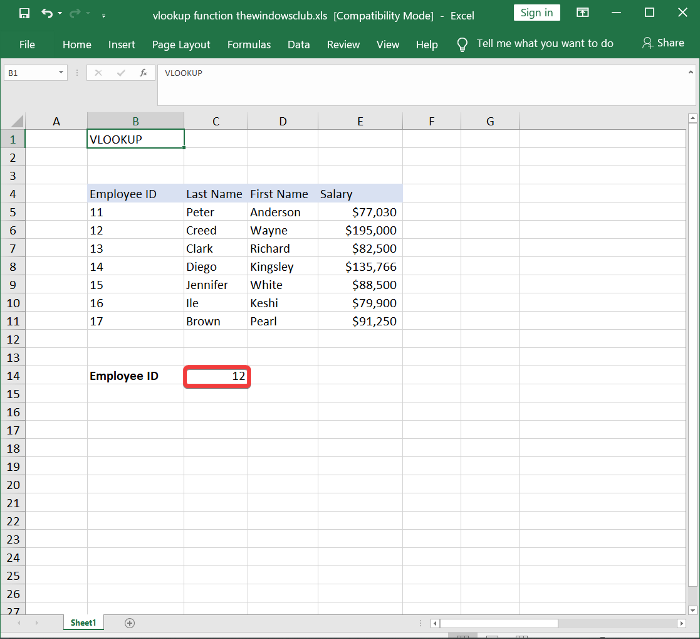
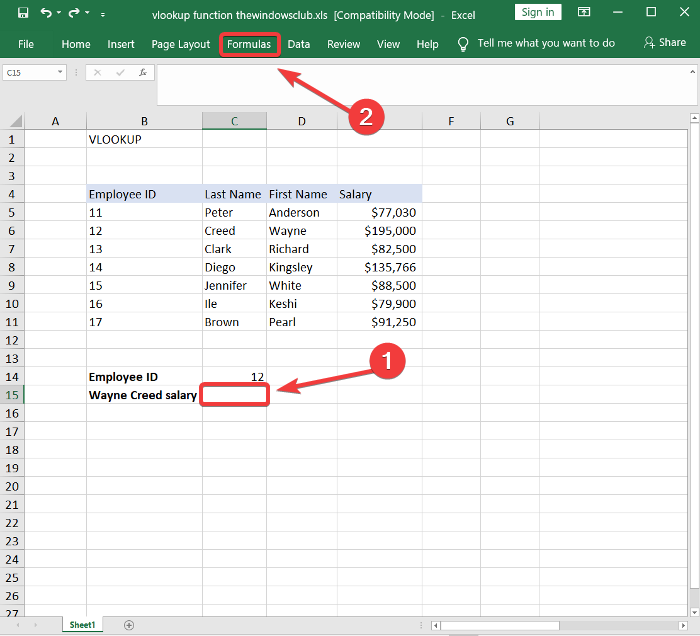
(Click)스프레드시트에서 빈 셀을 클릭 하고 데이터를 검색하려는 직원의 참조 열에서 직원 ID 를 입력합니다.(Employee ID)
(Select)Excel 에서 수식을 저장하여 반환된 값을 표시할 스프레드시트에서 다른 빈 셀을 선택 합니다. 여기에 다음 수식을 입력합니다.
=VLOOKUP()
위의 수식을 입력하면 Excel 에서 (Excel)VLOOKUP 구문 을 제안 합니다.
=VLOOKUP(vlookup_value,table_array,col_index_num,range_lookup)
인수 또는 매개변수
다음은 위의 인수가 구문에서 정의한 내용입니다.
- lookup_value: 참조 열의 제품 식별자가 있는 셀.
- table_array: with에서 검색까지의 데이터 범위. 여기에는 참조 열과 찾고 있는 값이 포함된 열이 포함되어야 합니다. 대부분의 경우 전체 워크시트를 사용할 수 있습니다. 테이블 값 위로 마우스를 끌어 데이터 범위를 선택할 수 있습니다.
- col_index_num: 값을 조회할 열의 번호입니다. 이것을 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 넣습니다.
- range_lookup: 근사 일치의 경우 TRUE , 정확한 일치의 경우 FALSE 입니다. (FALSE )값은 기본적으로 TRUE 이지만 일반적으로 (TRUE )FALSE를 사용합니다.(FALSE.)
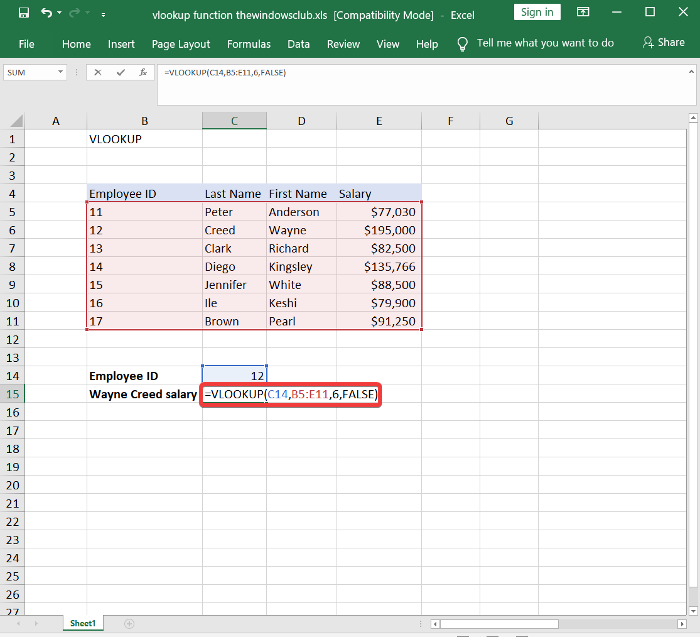
이 정보를 사용하여 이제 괄호 안의 매개변수를 조회하려는 정보로 교체합니다. 예를 들어 Wayne Creed 의 급여를 반환하려면 다음 공식을 입력하십시오.
=VLOOKUP(C14,B5:E11,6,FALSE)
VLOOKUP 수식 을 사용하여 셀에서 다른 곳으로 이동할 때 쿼리한 값을 반환합니다. #N/A 오류가 발생하면 이 Microsoft 가이드를 읽고 수정 방법을 알아(Microsoft guide to learn how to correct it) 보세요.
2] Excel 에서 VLOOKUP 함수 빌드(Build)
첫 번째 부분에서는 VLOOKUP(VLOOKUP) 함수를 수동으로 만드는 방법을 보여주었습니다 . 위의 방법이 쉽다고 생각하셨다면 이 글을 읽을 때까지 기다리세요. 여기에서는 사용자 친화적인 함수 인수 (Functions Arguments ) 마법사 를 사용하여 VLOOKUP 함수를 빠르게 구축하는 방법을 배웁니다.(VLOOKUP)
먼저 Microsoft Excel(Microsoft Excel) 을 열고 고유 식별자를 포함할 참조 열을 만듭니다.

다음으로, 참조 열의 오른쪽에 열을 추가로 생성합니다. 여기에서 참조 열의 항목에 대한 관련 값을 삽입합니다.

빈 셀을 선택(Select) 하고 참조 셀의 값을 입력합니다. 이것은 속성을 조회할 값입니다.

(Click)다른 빈 셀을 클릭 합니다. 선택한 상태에서 수식(Formulas) 탭을 클릭합니다.
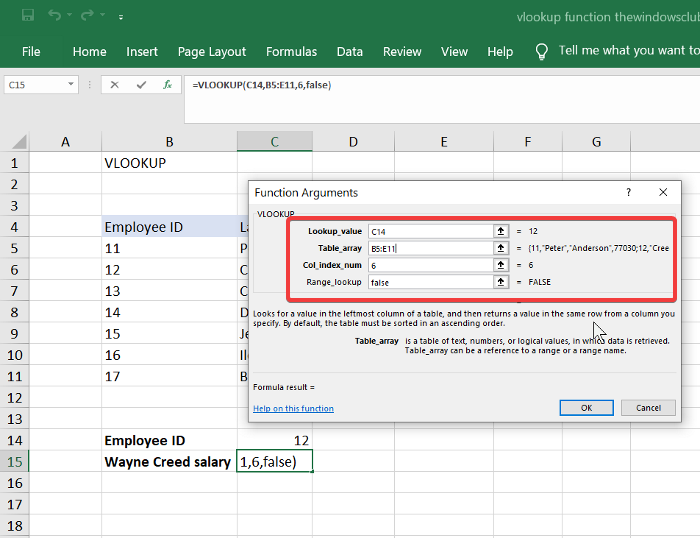
함수 라이브러리 에서 (Functions Library)조회 및 참조 (Lookup & Reference ) 도구를 선택 하고 드롭다운 메뉴에서 VLOOKUP 을 선택 합니다. 함수 인수(Functions Arguments) 마법사 가 열립니다 .
첫 번째 방법에서 지정한 함수 인수(Functions Arguments) 마법사 의 Lookup_value , Table_array , Col_index_num 및 Range_lookup 필드를 채우십시오.
완료 되면 확인(OK) 버튼을 누르면 VLOOKUP 함수가 입력한 인수의 결과를 반환합니다.
이 가이드는 Excel 공식이 자동으로 업데이트되지 않는 경우에 도움이 될 것 입니다.
두 방법 모두 첫 번째 열을 참조하여 필요한 데이터를 성공적으로 쿼리합니다. 수식 인수(Formulas Argument) 마법사를 사용 하면 VLOOKUP 함수가 작동 하도록 변수를 쉽게 입력할 수 있습니다.
그러나 VLOOKUP 기능은 웹 버전의 Excel 에서도 작동합니다 . 함수 인수(Functions Argument) 마법사 를 사용 하거나 웹 버전에서 수동으로 VLOOKUP 함수를 만들 수도 있습니다.(VLOOKUP)
이제 Excel의 HLOOKUP 함수를(HLOOKUP function in Excel) 살펴보겠습니다 .
How to write, build, and use VLOOKUP function in Excel
The VLOOKUP function in Microsoft Excel literally means vertical lookup. It’s a search function for querying values in the cell of a column. This function searches for the data relative to the entries in the first column from the left.
A vertical data search is most vital when dealing with tables with numerous columns and rows. Instead of scrolling through and analyzing hundreds of cells, Excel’s VLOOKUP function helps you find the data you’re looking for by looking up the values from top to bottom.
Create, build & use Excel’s VLOOKUP function
In our example, we’ll work with a VLOOKUP function that searches for information about seven employees’ salaries. This section shows you how to use the VLOOKUP function in the following ways:
- Write the Excel VLOOKUP function.
- Build a VLOOKUP function in Excel.
Without further ado, let’s get to it. In the first method, we’ll create the function manually. Next, we’ll use it from Excel’s inbuilt Functions Arguments wizard.
1] Write the Excel VLOOKUP function
Launch Microsoft Excel and make a column for the values that act as unique identifiers. We’ll call this the reference column.

Add some more columns to the right-hand side of the first one you created in the first step and insert values for the cells in these columns.

Click on an empty cell in the spreadsheet and type in an Employee ID from the reference column of an employee for whom you wish to search for data.

Select another empty cell on the spreadsheet in which Excel will store the formula and hence display the returned value. Here, enter the following formula:
=VLOOKUP()
On entering the above formula, Excel suggests the VLOOKUP syntax:
=VLOOKUP(vlookup_value,table_array,col_index_num,range_lookup)
Arguments or parameters
Here are what the above arguments define in the syntax:
- lookup_value: the cell with the product identifier from the reference column.
- table_array: the data range from with to search. It must contain the reference column and the column containing the value you’re looking up. In most cases, you can use the entire worksheet. You can drag your mouse over the values of the table to select a data range.
- col_index_num: the number of the column from which to look up a value. You put this in from left to right.
- range_lookup: TRUE for an approximate match, FALSE for an exact match. The value is TRUE by default, but you generally use FALSE.
With this information, we’ll now replace the parameters in the parenthesis with the information we wish to look up. For example, to return Wayne Creed‘s salary, enter the following formula:
=VLOOKUP(C14,B5:E11,6,FALSE)

On navigating away from the cell with the VLOOKUP formula, it returns the value for which you queried. If you get a #N/A error, read this Microsoft guide to learn how to correct it.
2] Build a VLOOKUP function in Excel
The first part showed you how to create a VLOOKUP function manually. If you thought the above method was easy, wait till you read this. Here, you’ll learn how to build a VLOOKUP function quickly using the user-friendly Functions Arguments wizard.
Open Microsoft Excel first, and create a reference column that will contain unique identifiers.

Next, create some more columns on the right-hand side of the reference column. Here, we’ll insert the relevant values for the items on the reference column.

Select an empty cell and type in a value from the reference cell. This is the value whose properties we’ll lookup.

Click on another empty cell. With that selected, click on the Formulas tab.

Select the Lookup & Reference tool from the Functions Library and choose VLOOKUP from the dropdown menu. This opens the Functions Arguments wizard.
Fill in the Lookup_value, Table_array, Col_index_num, and Range_lookup fields in the Functions Arguments wizard specified in the first method.
Hit the OK button when you’re done, and the VLOOKUP function will return the results from the arguments you entered.
This guide will help you if the Excel formula fails to update automatically.

Both methods will successfully query the data you need in reference to the first column. The Formulas Argument wizard makes it easy to input the variables to make the VLOOKUP function work.
However, the VLOOKUP function also works on the web version of Excel. You also get to use the Functions Argument wizard or create the VLOOKUP function manually on the web version.
Let us take a look at the HLOOKUP function in Excel now.









