막대(Bar) 그래프는 데이터를 시각화할 때 매우 유용할 수 있습니다. 하나의 데이터 세트를 표시하거나 여러 데이터 세트를 비교할 수 있습니다.
이 기사에서는 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 에서 다양한 유형의 막대 그래프를 만드는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다 .

Google 스프레드시트 에서 막대 그래프(Bar Graph) 를 만드는 방법
간단한 2열 스프레드시트로 시작하겠습니다. 스프레드시트의 첫 번째 열에서 시리즈의 각 행에 대한 레이블을 추가합니다. 원하는 경우 상단 셀에 범주를 추가할 수 있으며 해당 범주는 그래프의 수평 y축 제목으로 표시됩니다. 해당 범주 이름 아래의 레이블은 차트의 가로 축을 따라 나타납니다.
(Add)데이터 열을 하나 이상 추가하십시오 . 두 번째 열의 첫 번째 셀에 레이블을 입력하고 그 아래 셀에 데이터를 추가합니다.

다음으로, 다음 단계에 따라 데이터를 나타내는 막대 그래프를 삽입하십시오.
- (Select)데이터가 있는 모든 셀을 선택 합니다.
- 메뉴에서 삽입(Insert ) > 차트(Chart) 를 선택하거나 차트 삽입(Insert Chart) 아이콘을 선택합니다.

어떤 방법을 선택하든 Google 은 시트에 막대 그래프를 삽입합니다. ( 구글 에서는 이것을 (Google)세로 막대형 차트(column chart) 라고 부릅니다 . 이것은 같은 것입니다.)

Google Sheets에서 여러 데이터로 막대 그래프 만들기(Making a Bar Graph with Multiple Data in Google Sheets)
여러 데이터 세트를 포함하는 막대 그래프를 만들려면 데이터 열을 더 추가하기만 하면 됩니다.

위와 동일한 단계에 따라 데이터의 막대 그래프 표현을 삽입하십시오.
- (Select)데이터가 있는 모든 셀을 선택 합니다.
- 메뉴에서 삽입(Insert ) > 차트(Chart) 를 선택하거나 차트 삽입(Insert Chart) 아이콘을 선택합니다.
다음은 위 스프레드시트의 여러 데이터 열을 사용하는 막대 그래프입니다.
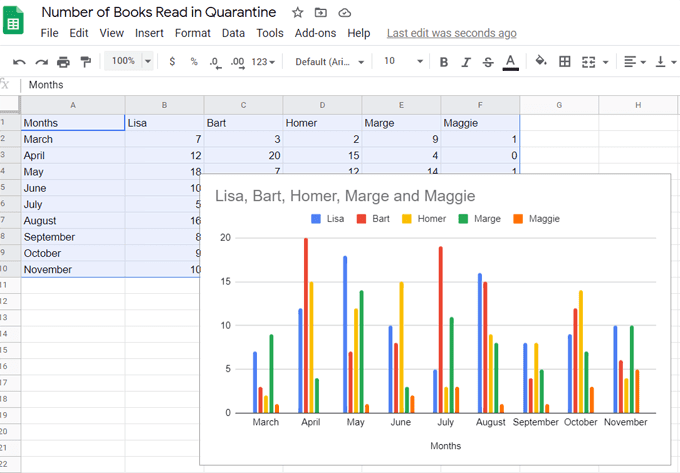
이 경우 Google 은 데이터의 첫 번째 행에 있는 카테고리를 차트 제목으로 사용합니다.
Google 스프레드시트에서 누적 막대 그래프 만들기(Making a Stacked Bar Graph in Google Sheets)
여러 데이터 세트를 사용하는 경우 누적 막대 차트(stacked bar chart) 를 선택하여 데이터의 부분 대 전체 관계를 표시할 수 있습니다 . 위의 예에서 차트는 각 사람이 특정 달에 읽은 책의 수를 보여줍니다. 막대 그래프를 누적 막대 차트로 전환하면 모든 사람이 그 달에 읽은 총 책 수와 비교하여 그 달에 각 사람이 읽은 책의 수를 볼 수 있습니다.
누적 막대 차트에는 몇 가지 다른 유형이 있습니다. 먼저 (First)표준 누적 막대 차트(Standard stacked bar chart.) 를 살펴보겠습니다 .
막대 차트를 삽입한 후 내부를 두 번 클릭하면 차트 편집기(Chart Editor) 패널이 오른쪽에 나타납니다.
참고 : (Note)차트 편집기(Chart Editor) 내에서 또는 차트 제목 자체를 두 번 클릭하여 언제든지 차트 제목을 변경할 수 있습니다 .

스태킹(Stacking) 에서 표준(Standard) 을 선택합니다 .
이제 단일 막대에 쌓인 각 범주의 값을 볼 수 있습니다.

또는 표준(Standard) 대신 100% 를 선택 하여 전체에 대한 개별 데이터의 비율을 나타내는 누적 막대 차트를 만들 수 있습니다. 누적 합계가 중요하지 않을 때 사용합니다.
따라서 우리의 예에서 우리는 한 달에 총 몇 권의 책을 읽었는지는 신경 쓰지 않을 수 있습니다.

위(Notice) 의 100% 누적 가로 막대형 차트(Stacked Bar Chart) 에서 x축의 레이블은 이제 백분율입니다.
차트에서 열과 행을 바꾸는 방법(How to Swap Columns & Rows in a Chart)
이 예를 사용하여 각 사람의 독서 습관이 월별로 어떻게 변했는지 쉽게 시각화하고 싶다고 가정해 보겠습니다. Google 스프레드시트(Sheets) 를 사용하면 열을 행으로 또는 그 반대로 쉽게 바꿀 수 있습니다.
- 차트 또는 그래프를 두 번 클릭합니다.
- 오른쪽에서 설정(Setup ) 을 선택 합니다.
- Switch rows/columns 옆의 확인란을 선택합니다 .
이제 일반 막대 그래프는 다음과 같습니다.

누적 막대 차트에서 행과 열을 전환하면 다음과 같이 표시됩니다.

이러한 다양한 옵션 각각이 우리 데이터에 대한 특정 이야기를 전달하는 데 이상적이라는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 어떤 이야기 를(you) 하고 싶은지 생각하고 어떤 종류의 막대 그래프가 당신의 요점을 가장 명확하게 설명하는지 결정하십시오.
Google 스프레드시트에서 막대 그래프 사용자 정의(Customizing Bar Graphs in Google Sheets)
차트 편집기 의 사용자 정의(Customize ) 탭을 보셨을 것 입니다.

차트의 모양과 느낌을 변경하려면 해당 탭을 선택하십시오. 다음으로 사용자 정의(Customize ) 탭 의 각 섹션을 살펴보겠습니다 .
차트 스타일(Chart style) 을 사용하면 차트의 배경색, 테두리 색상 및 글꼴을 선택할 수 있습니다. 변경 사항이 마음에 들지 않으면 언제든지 레이아웃 재설정(Reset layout) 버튼을 선택하여 다시 시작할 수 있습니다.
최대화 상자를 선택(Maximize) 하면 차트의 공백이 줄어듭니다. 그것을 시도하고 당신이 보는 것이 마음에 드는지 확인하십시오.
3D 상자를 선택하면 막대가 다음과 같이 3차원이 됩니다.

비교 모드(Compare mode) 는 차트의 다른 요소 위로 마우스를 가져가면 비교 가능한 데이터를 강조 표시합니다. 아래 차트에서 11월(November) 데이터(각 누적 막대의 맨 위 섹션)가 어떻게 강조 표시되는지 확인하십시오.

차트 및 축 제목(Chart & axis titles) 섹션 은 차트 제목과 글꼴, 글꼴 크기, 형식(기울임꼴, 굵게 등) 및 텍스트 색상을 변경할 수 있는 또 다른 위치입니다.
시리즈(Series) 섹션 에서 시리즈 레이블의 모양을 변경할 수 있습니다. 우리의 경우 그것은 월과 막대 그래프의 해당 부분입니다. 예를 들어 11월(November) 데이터를 노란색에서 회색으로 변경할 수 있습니다 .
예를 들어 Lisa 가 (Lisa)10월(October) 에 읽은 책 수를 나타내는 데이터와 같은 특정 데이터 요소의 형식을 지정할 수도 있습니다 . 데이터 요소 서식(Format data point) 옆에 있는 추가 버튼을 (Add)클릭(Click) 하면 단일 데이터 요소의 색상을 변경할 수 있습니다.
범례(Legend) 섹션 에서 범례 글꼴, 글꼴 크기, 형식 및 텍스트 색상을 변경할 수 있습니다.
가로 축(Horizontal axis) 및 세로 축(Vertical axis) 섹션 은 차트의 각 축에 레이블 서식을 지정하기 위한 유사한 옵션을 제공합니다.
마지막으로 눈금선 및 눈금(Gridlines and ticks) 은 눈금 표시를 삽입하고 서식을 지정하고 축 사이의 간격을 설정하여 축의 일부를 강조할 수 있는 비교적 새로운 기능( 2020년 6월 기준)입니다.(June 2020)

막대 그래프를 쉽게 만드는 Google 스프레드시트
이제 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 에서 막대 그래프를 만드는 방법에 대해 알아야 할 거의 모든 것을 알게 되었습니다 . Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 를 사용하는 더 많은 방법을 알고 싶다면 알아야 할 5가지 Google 스프레드시트 스크립트 기능(5 Google Sheets Script Functions You Need to Know)(5 Google Sheets Script Functions You Need to Know) 에 대해 읽어 보세요.
How to Make a Bar Graph in Google Sheets
Bar graphs can be extremely helpful when it comes to visuаlizing data. They can displaу one set of data or cоmpare multiple data sets.
In this article, we’ll go over how to make various types of bar graphs in Google Sheets.

How to Create a Bar Graph in Google Sheets
We’ll start with a simple, two-column spreadsheet. In the first column of your spreadsheet, add a label for each row in your series. If you like, you can add a category in the top cell and that category will appear as the title of your graph’s horizontal y-axis. The labels under that category name will appear along the horizontal axis of your chart.
Add at least one column of data. Enter a label in the first cell of the second column, and add the data in the cells beneath it.

Next, follow these steps to insert a bar graph to represent your data.
- Select all the cells that have data in them.
- From the menu, select Insert > Chart or select the Insert Chart icon.

Whichever method you choose, Google will insert a bar graph into your sheet. (Google calls it a column chart. This is the same thing.)

Making a Bar Graph with Multiple Data in Google Sheets
To make a bar graph that includes multiple sets of data, just add more columns of data.

Follow the same steps as above to insert a bar graph representation of your data.
- Select all the cells that have data in them.
- From the menu, select Insert > Chart or select the Insert Chart icon.
Here’s a bar graph that uses multiple columns of data from the spreadsheet above.

In this case, Google uses the categories in the first row of data as the chart title.
Making a Stacked Bar Graph in Google Sheets
When you use multiple data sets, you can show the part-to-whole relationships in your data by opting for what’s called a stacked bar chart. In our example above, the chart showed how many books each person read in a particular month. If we switch the bar graph to a stacked bar chart, we’ll see how many books each person read that month compared to the total number of books everyone read that month.
There are a couple different flavors of stacked bar charts. First we’ll look at the Standard stacked bar chart.
After you’ve inserted your bar chart, double-click inside it and the Chart Editor panel will appear to the right.
Note: You can always change the chart’s title inside the Chart Editor or by double-clicking on the chart title itself.

Under Stacking, choose Standard.
Now you’ll see the values of each category stacked into single bars.

Alternatively, instead of Standard, you can choose 100% to make a stacked bar chart that depicts the ratio of individual data to the whole. Use this when the cumulative total isn’t important.
So for our example, we might not care how many books were read in total each month—only how many books each person read relative to other people.

Notice that in the 100% Stacked Bar Chart above, the labels along the x axis are now percentages.
How to Swap Columns & Rows in a Chart
Using our example, let’s say you want to make it easy to visualize how each person’s reading habits changed from month to month. Google Sheets makes it easy to turn your columns into rows and vice versa.
- Double-click the chart or graph.
- Select Setup on the right.
- Check the box next to Switch rows/columns.
Our regular bar graph now looks like this:

If we switch rows and columns on our stacked bar chart, it will look like this:

You can see that each of these different options is ideal for telling a particular story about our data. Think about what story you want to tell, and determine which kind of bar graph most clearly makes your point.
Customizing Bar Graphs in Google Sheets
You may have noticed the Customize tab in the Chart Editor.

Select that tab to change the look and feel of your chart. Next we’ll go through each section of the Customize tab.
Chart style allows you to choose the background color, border color, and font for your chart. If you don’t like the changes you made, you can always select the Reset layout button to start over.
Checking the Maximize box will decrease the white space in your chart. Try it and see if you like what you see.
Selecting the 3D box will make your bars three-dimensional, like this:

Compare mode will highlight comparable data when you hover your mouse over different elements of your chart. In the chart below, notice how the November data (the top-most section of each stacked bar) is highlighted.

The Chart & axis titles section is another place you can change the chart title as well as its font, font size, format (italics, bold, etc.), and text color.
In the Series section, you can change the appearance of your series labels. In our case, that’s the months and their corresponding parts of the bar graph. For example, you could change the November data from yellow to gray.
You can also format a specific data point like, for example, the data representing the number of books Lisa read in October. Click the Add button next to Format data point, and from there you can change the color of that single data point.
In the Legend section, you can change the legend font, font size, format, and text color.
The Horizontal axis and Vertical axis sections offer similar options for formatting labels on each of your chart’s axes.
Finally, Gridlines and ticks is a relatively new feature (as of June 2020) allowing you to emphasize parts of your axes by inserting tick marks, formatting them, and setting the spacing between them.

Google Sheets Makes Bar Graphs Easy
Now you know almost all there is to know about making a bar graph in Google Sheets. If you’d like to learn more ways to use Google Sheets, read about the 5 Google Sheets Script Functions You Need to Know.















