PerfMon.exe 또는 PerfMon.msc 라고도 하는 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 에 대해 들어 보셨습니까 ? Windows 컴퓨터 또는 장치(Windows computer or device) 의 성능을 모니터링하는 데 사용할 수 있는 정교한 도구입니다 . 그것을 사용하여 컴퓨터가 리소스를 관리하는 방법을 볼 수 있습니다. 여기에서 제공하는 정보는 특히 컴퓨터 성능이 기대 이하일 때 소프트웨어 및 하드웨어 선택(software and hardware choices) 에 대한 결정을 내리는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다 . 문제 해결을 수행하려는 경우에도 유용합니다. 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 사용하여 전문가처럼 시스템 성능을 분석 하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다 .
참고:(NOTE:) 이 가이드는 Windows 10 , Windows 7 및 Windows 8.1 에서 작동 합니다.
Windows 에서 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 시작하는 방법
성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 시작하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다. 모든 Windows(Windows) 버전에서 작동 하는 것은 검색을 사용하는 것입니다. 예를 들어 Windows 10 에서 작업 표시줄 의 검색 상자 에 (search box)"성능 모니터"("performance monitor") 를 입력 한 다음 적절한 결과를 클릭하거나 탭합니다.

모든 Windows 버전 에서 (Windows version)성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 여는 다른 방법 은 Windows (모든 버전) 에서 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 시작하는 11가지 방법 문서를 확인하십시오 .
성능 모니터 로 (Performance Monitor)시스템 성능(system performance) 을 분석하는 방법
컴퓨터의 현재 성능 분석을 시작하려면 아래와 같이 프로그램의 메인 패널에 있는 모니터링 도구(Monitoring Tools) 아래 에 있는 성능 모니터 를 (Performance Monitor)클릭하거나 누릅니다 .(click or tap)

참고: 특정 (NOTE:)앱 및 프로그램(apps and programs) 세트를 사용하는 동안 컴퓨터가 어떻게 작동 하는지 확인하려면 그래프가 시스템 리소스에 미치는 영향을 기록할 수 있도록 지금 열어야 합니다.
기본적으로 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 에 표시되는 그래프 는 프로세서가 실행 중인 활성 프로그램(백분율으로 표시)에서 작업 중인 시간인 프로세서(Processor) 시간을 측정 합니다. 이것은 프로세서가 얼마나 열심히 작동하는지에 대한 기본적인 측정을 제공합니다.

이 그래프는 추가 열 및 기타 여러 옵션으로 사용자 정의할 수 있습니다. 보다 심층적인 분석을 위해 다른 데이터를 자세히 설명할 수 있는 카운터를 그래프에 추가할 수도 있습니다. 이렇게 하려면 그래프 위의 녹색 더하기 기호를 누르십시오.

열리는 카운터 추가(Add Counters) 창에서 실시간으로 모니터링할 카운터를 선택할 수 있습니다. 종류별로 정리되어 있고 많습니다. 카운터 이름을 두 번 클릭(두 번 탭)하면 여러 개별 개체가 표시되어야 하며 모든 개체뿐 아니라 그 중 하나라도 모니터링하도록 선택할 수 있습니다.
모니터링할 카운터와 개체를 모두 선택했으면 추가(Add) 버튼을 클릭하거나 탭합니다. 추가된 카운터는 창 오른쪽에 표시됩니다. 확인(OK) 을 클릭하거나 탭 하면 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 에서 그래프에 추가됩니다 .

예를 들어 아래 그래프에서는 프로세서 (Processor) 카운터 세트(counter set) 를 사용했습니다 . Interrupts/sec (프로세서가 응답하도록 요청받은 인터럽트 수 . 하드 디스크 컨트롤러(disk controller) 어댑터 및 네트워크 인터페이스(network interface) 카드 와 같은 하드웨어 구성 요소에 의해 생성됨 ) 또는 % (total amount)%User Time ( 비 -사용자 모드 작업에 소요된 유휴 시간).

이제 선택한 카운터를 사용하여 모니터링하려는 활동을 수행하고 실시간으로 어떻게 변경되는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 에 데이터가 표시되는 방식을 사용자 지정하는 방법
"그래프 유형 변경"("Change graph type") 버튼을 클릭하거나 탭하고(또는 키보드에서 CTRL + G히스토그램 막대(Histogram bar) 또는 보고서(Report) 옵션을 선택 하여 다른 형식의 데이터를 볼 수도 있습니다.

이 그림은 히스토그램(Histogram) 형식의 데이터를 보여줍니다.

여기에 보고서(Report) 옵션 에 대한 데이터 표시의 예가 있습니다.
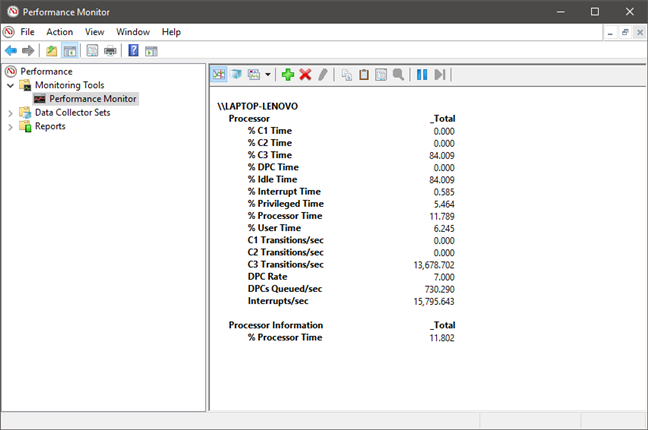
아래에 강조 표시된 속성(Properties) 버튼을 클릭하거나 키보드에서 CTRL + Q 를 눌러 데이터가 표시되는 방식을 추가로 변경할 수 있습니다 .

그러면 각 카운터가 표시되는 방법, 색상, 선 유형 등을 사용자 지정할 수 있는 성능 모니터 속성 창이 열립니다. (Performance Monitor Properties)이러한 유형의 개인화에는 데이터(Data) 및 그래프(Graph) 탭을 모두 사용할 수 있습니다 .
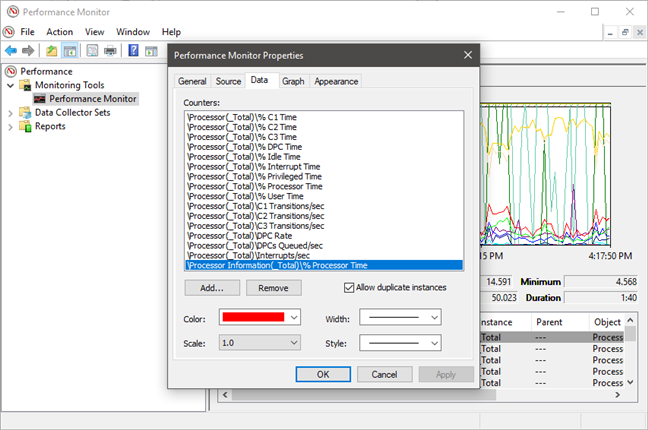
모든 것을 원하는 대로 개인화 했으면 OK(OK) 버튼 을 누르는 것을 잊지 마십시오 .
가장 유용한 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 카운터는 무엇입니까?
성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 의 그래픽 보고서 에 포함된 데이터 는 고도로 기술적인 것이며 일반 사용자가 이해하기 어렵습니다. 그러나 적어도 책상에 Windows 컴퓨터 가 있는 일반 사용자에게는 다른 것보다 더 유용한 몇 가지 카운터가 있습니다. (Windows computer)다음은 제대로 작동하지 않는지 여부를 확인하는 데 도움이 되는 성능 카운터 모음입니다.
-
Processor -> % Processor Time프로세서(Processor) 목록 에서 찾을 수 있습니다 . 다양한 작업에서 프로세서가 소비한 시간을 보여줍니다. 값이 지속적으로 80%를 초과하면 프로세서가 컴퓨터에서 수행하는 모든 작업을 유지할 만큼 강력하지 않아 병목 현상이 발생한다는 의미입니다. 이 문제에 대한 해결책은 컴퓨터에서 덜 까다로운 앱을 사용하는 것이지만 유일한 장기적 해결책은 프로세서를 업그레이드하는 것입니다.
-
Memory -> Available MBytes : 카운터의 메모리(Memory) 목록에서 찾을 수 있습니다. 이 카운터를 그래프에 추가하여 시스템에 사용할 수 있는 메모리가 충분한지 확인할 수 있습니다. 그래프에 사용 가능한 메모리가 총 용량의 10% 미만이라고 표시되면 RAM 이 충분하지 않다는 의미일 수 있습니다 . 이 경우 더 추가하는 것을 고려하십시오.
-
PhysicalDisk -> Current Disk Queue Length 및 PhysicalDisk -> % Disk Time : 이 두 카운터는 모두 PhysicalDisk 목록에서 찾을 수 있습니다. 현재 디스크 대기열 길이(Current Disk Queue Length) 가 2보다 크고 디스크 시간(Disk Time) 이 100%로 닫히면 보고 있는 하드 드라이브가 너무 느리거나 결함이 있을 수 있습니다. 이 경우 하드 드라이브 업그레이드를 고려할 수 있습니다.

성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 에서 사용할 수 있는 모든 데이터를 이해하는 방법
유감스럽게도 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 에서 사용할 수 있는 카운터 목록 은 매우 길어서 한 문서에서 모든 것을 다룰 수 없습니다. %DPC Time 또는 Page Faults/sec 와 같은 모든 횡설수설한 용어를 설명 하는 좋은 지식 기반(knowledge base) 을 찾고 있다면 Microsoft 의 TechNet: Performance Monitor Counters 에서 이 항목을 읽으십시오 . 여기에서 표준 보고서 목록에 있는 각 카운터에 대한 완전한 정보를 찾을 수 있습니다.
성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 사용 하여 시스템의 병목 현상을 찾으십니까?
이 문서에서는 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 보고서 를 열고 필수 판독값을 얻는 방법과 시스템 활동을 추가로 모니터링하기 위해 카운터 세트를 적용하는 방법을 보여주었습니다. 또한 Windows 컴퓨터(Windows computer) 의 주요 하드웨어 부분을 분석하는 데 도움이 되는 몇 가지 유용한 카운터도 표시했습니다 . PC 문제 해결을 위해 성능 모니터(Performance Monitor) 를 사용 하셨습니까 ? (Did)이 도구를 사용하는 방법과 목적에 도움이 되었는지 알려주십시오.
How to work with the Performance Monitor in Windows
Have you heard about the Performance Monitor, also known as PerfMon.exe or PerfMon.msc? It is a sophisticated tool that can be used to monitor the performance of your Windows computer or device. Using it, you can see how your computer manages its resources. The information it gives you can help you make decisions about software and hardware choices, especially when your computer's performance is below expectations. It is also useful when you want to do some troubleshooting. Here is how to use the Performance Monitor to analyze your system's performance like a pro:
NOTE: This guide works in Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
How to start the Performance Monitor in Windows
The are many ways to start the Performance Monitor. One that works in all versions of Windows is to use the search. For example, in Windows 10, type "performance monitor" in the search box on the taskbar and then click or tap the appropriate result.

For other ways to open the Performance Monitor in any Windows version, check this article: 11 ways to start Performance Monitor in Windows (all versions).
How to analyze system performance with Performance Monitor
To begin an analysis of your computer's current performance, click or tap on Performance Monitor under Monitoring Tools on the program's main panel, as indicated below.

NOTE: If you want to see how your computer performs while using a particular set of apps and programs, make sure to open them now so that the graphs can take note of their impact on your system's resources.
By default, the graph shown by Performance Monitor measures Processor time, which is the amount of time that the processor is busy working on running active programs (shown in percentages). This gives you a basic measure of how hard your processor is working.

This graph can be customized with additional columns and several other options. For a more in-depth analysis, you can also add counters to the graph that can detail other data. To do this, hit the green plus sign above the graph.

In the Add Counters window that opens, you can select the counters that you want to monitor in real time. They are organized by type and they are many. If you double-click (double-tap) on the name of a counter, you should see several individual objects and you can select to monitor any of them, as well as all of them.
When you are done selecting the counters and the objects that you want to monitor, click or tap the Add button. The added counters are shown on the right side of the window. When you click or tap OK, they are added to the graph from the Performance Monitor.

For example, in the graph below, we used the Processor counter set. It shows technical but useful data such as Interrupts/sec (the numbers of interrupts your processor was asked to respond to. They are generated by hardware components like hard disk controller adapters and network interface cards) or %User Time (the total amount of non-idle time that was spent on user mode operations).

Now you can go ahead and perform the activities that you want to be monitored, using the selected counters and see how they change in real time.
How to customize the way data is displayed in Performance Monitor
You can also look at the data in other formats by clicking or tapping on the "Change graph type" button (or by hitting CTRL + G on your keyboard) and choosing the Histogram bar or Report options.

This picture shows the data in Histogram format.

And here we have an example of the data display for the Report option.

You can further change how the data is displayed, by clicking the Properties button highlighted below or by pressing CTRL + Q on your keyboard.

This opens the Performance Monitor Properties window, where you can customize how each counter is displayed, in what color, using which type of lines and so on. You can use both the Data and the Graph tabs for this type of personalization.

When you are done personalizing everything as you wish, do not forget to press the OK button.
Which are the most useful Performance Monitor counters?
The data included in the Performance Monitor's graphical reports are highly technical and difficult to understand by casual users. However, there are a few counters that are more useful than others, at least for the regular user with a Windows computer in his or her desk. Here is a selection of performance counters that can help you see whether something is not working right:
-
Processor -> % Processor Time: you can find it in the Processor list of counters. It shows you the time spent by the processor on various tasks. If its value is consistently above 80%, it means that your processor is not powerful enough to sustain everything you do on your computer, so it becomes a bottleneck. Although a solution to this issue would be to use less demanding apps on your computer, the only long-term solution is to upgrade your processor.
-
Memory -> Available MBytes: is found in the Memory list of counters. You can add this counter to your graph to see whether your system has enough memory available to use. If the graph shows you that the available memory is somewhere less than 10 percent of your total amount, it could mean that you do not have enough RAM installed. In that case, consider adding some more.
-
PhysicalDisk -> Current Disk Queue Length and PhysicalDisk -> % Disk Time: these two counters are found both in the PhysicalDisk list. If the Current Disk Queue Length is higher than 2 and the Disk Time is closing on 100%, it is likely that the hard drive that you are watching is too slow or even faulty. In that case, you might want to consider upgrading your hard drive.

How to make sense of all the data that is available in Performance Monitor
Unfortunately, the list of counters available in Performance Monitor is exceptionally long and we cannot cover everything in just one article. However, if you are looking for a good knowledge base, explaining all the gibberish terms like %DPC Time or Page Faults/sec, read this entry on Microsoft's TechNet: Performance Monitor Counters. There you will find complete information about each counter found in the standard list of reports.
Do you use the Performance Monitor to find the bottlenecks in your system?
This article has shown you how to open and get an essential reading of Performance Monitor reports and how to apply counter sets to monitor the activity of your system further. We have also shown a few useful counters that can help you perform an analysis of the main hardware parts in your Windows computer. Did you use the Performance Monitor for troubleshooting your PC? Let us know how you use this tool and whether it was helpful for your purposes.












