인터넷을 검색할 때 종종 "쿠키"라는 용어를 접하게 됩니다. ("cookies.")많은 웹사이트에서 쿠키 사용에 대해 알려주고 승인을 요청합니다. 웹 브라우저에는 쿠키를 관리하기 위한 많은 설정이 있으며 브라우저 추가 기능에도 모든 종류의 쿠키 차단이 언급되어 있습니다. 이러한 "쿠키"("cookies") 가 정확히 달콤한 디저트가 아니라는 것을 알고 있더라도 인터넷에서 쿠키가 무엇이며 목적이 무엇인지 정확히 알지 못할 수 있습니다. 그렇기 때문에 이 기사에서는 쿠키가 무엇인지, 어떤 역할을 하며 어떻게 작동하는지, 인터넷에서 가장 많이 사용되는 쿠키의 종류에 대해 설명합니다. 시작하자:
인터넷에서 쿠키란 무엇입니까?
쿠키는 귀하, 귀하의 웹 브라우저 및 인터넷에서의 귀하의 행동에 대한 정보를 담고 있는 파일입니다. PC 또는 장치(PC or device) 에 저장된 작은 파일로 , 웹사이트나 웹 앱에서 온라인 경험을 맞춤화하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
쿠키는 어떤 역할을 하나요?
쿠키는 발신자(일반적으로 웹사이트 또는 웹 앱)와 수신자(귀하의 기기) 간에 전송됩니다. 쿠키는 발신자에 의해 생성되고 해석되는 반면 수신자는 쿠키를 보유하고 발신자가 요청할 경우 다시 보냅니다.
웹을 검색할 때 발신자는 웹사이트가 실행되는 서버이고 수신자는 해당 웹사이트를 방문하는 사용자의 웹 브라우저입니다. 그들의 목적은 사용자를 식별하고 웹사이트에서의 과거 활동을 확인하며 이 데이터를 기반으로 적절한 콘텐츠를 제공하는 것입니다.

사용자가 웹사이트를 처음 방문할 때 서버는 해당 사용자의 웹 브라우저(web browser) 에 특정 쿠키를 저장합니다. 이후에 웹사이트를 방문할 때 서버는 쿠키를 요청하고 쿠키를 읽고 해당 특정 사용자에 대한 웹사이트의 특정 구성을 로드합니다. 쿠키는 웹 서버가 모든 사용자에게 적용하는 태그로 생각할 수 있으며, 웹 서버는 사용자를 식별하기 위해 이를 읽습니다.
이 식별은 실시간 사용자 데이터가 중요한 웹사이트에서 유용합니다. 예를 들어, 온라인 상점(online shop) 을 사용할 때 쿠키의 도움 없이는 아무것도 살 수 없습니다. 상점은 웹 페이지를 로드할 때마다 상점에서 당신을 새로운 사용자로 보고 처음부터 방문을 시작하기 때문에 상점에서 당신을 식별하고 쇼핑 카트를 만들 수 없습니다.
쿠키 안에는 무엇이 들어 있습니까?
모든 최신 웹 브라우저(web browser) 는 쿠키를 지원하며 약 4KB의 작은 크기를 가지고 있습니다. 쿠키의 구조를 이해하는 데 도움이 되도록 당사 웹사이트인 Digital Citizen 에서 보낸 (Digital Citizen)"cfduid" 쿠키 를 예로 들어 보겠습니다 . Google 크롬(Google Chrome) 을 사용하여 분석했습니다 .
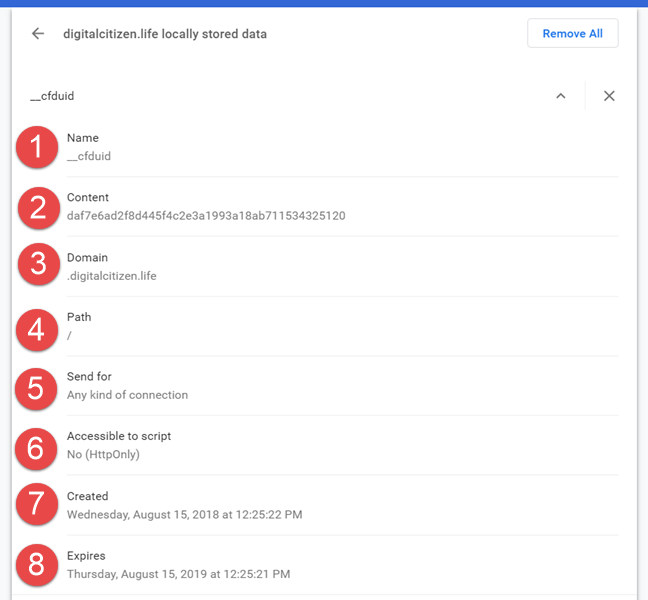
구조는 다음과 같습니다.
- 이름(Name) - 쿠키의 이름입니다.
- 콘텐츠(Content) - 쿠키에 포함된 정보입니다.
- 도메인(Domain) - 이 쿠키를 사용하는 도메인.
- 경로(Path) - 쿠키가 사용되는 도메인의 페이지입니다. 경로가 "/"이면 전체 웹사이트에서 쿠키가 사용됨을 의미합니다.
- 보내기 대상(Send for) - 연결에서 쿠키를 사용해야 하는 보안 수준입니다.
- 스크립트에 액세스 가능 - 쿠키가 (Accessible to script)HTML 이외의 다른 방법을 통해 액세스될 수 있는지 여부를 보여줍니다 .
- 만든(Created) 날짜 - 사용자의 웹 브라우저(web browser) 에서 쿠키가 만들어진 날짜 입니다.
- 만료(Expires) - 쿠키가 만료되고 브라우저가 쿠키를 삭제하는 순간입니다.
쿠키의 종류는 몇 가지입니까?
쿠키라는 용어(term cookie) 는 다소 일반적이지만 쿠키를 사용할 수 있는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다 . 이것이 인터넷에 다양한 유형의 쿠키가 있는 이유입니다. 가장 일반적인 유형은 다음과 같습니다.
- 세션 쿠키(Session cookies) - 가장 일반적인 것 중 하나입니다. 웹 브라우저(web browser) 가 닫힐 때까지 임시 메모리에 존재합니다 . 브라우징 세션(browsing session) 이 끝나면 모든 정보가 삭제되기 때문에 유해하지 않습니다 .
- 영구 쿠키(Persistent cookies) - 추적 쿠키라고도 합니다. 삭제되거나 만료일(expiry date) 에 도달할 때까지 사용자의 기기에서 지속됩니다 . 사용자에 대한 정보를 수집하고 일정 기간 동안 특정 웹사이트에서 사용자의 행동을 기록하는 데 사용됩니다.
- 보안 쿠키 - 보안 (Secure cookies)HTTPS 연결(HTTPS connection) 을 사용할 때만 작동하는 암호화된 쿠키입니다 . 이러한 쿠키는 사용자와 동일한 네트워크에 연결된 잠재적인 해커가 자신의 정보를 도용하지 못하도록 하는 데 사용됩니다. 사용자에 대한 필수 정보를 유지하며 사용자가 금융 거래를 수행하는 웹 사이트에서 주로 사용됩니다. 암호화되어 있기 때문에 다른 유형의 쿠키보다 훨씬 안전합니다.
- HttpOnly 쿠키 - (HttpOnly cookies)HTTP 이외의 프로토콜에서는 사용할 수 없습니다 . 이러한 쿠키는 쿠키를 생성한 웹사이트에서만 쿠키를 사용할 수 있도록 합니다. 세션 쿠키만 HttpOnly일 수 있으며 일반적으로 사용자의 개인 정보 또는 보안 위험(privacy or security risks) 을 암시하지 않습니다 .
- 타사 쿠키(Third-party cookies) - 이러한 쿠키는 쿠키를 보낸 도메인이 아닌 다른 도메인에 속합니다. 일반적으로 광고를 통해 전송되며 동일한 광고 네트워크(advertising network) 를 사용하는 여러 웹사이트에서 사용자의 검색 기록을 저장할 수 있습니다 . 이러한 쿠키는 일부 광고 네트워크에서 타겟 광고를 표시하기 위해 너무 많은 데이터를 추적하는 데 사용하기 때문에 개인 정보를 손상시킬 수 있습니다.
- 좀비 쿠키(Zombie cookie) - 삭제된 후 다시 생성되는 쿠키입니다. 일반적으로 웹 분석 서비스에서 사용되며 동일한 컴퓨터에 설치된 브라우저에서 사용할 수 있기 때문에 브라우저 외부에 저장됩니다. 스스로 재생성하는 이유는 사용자가 쿠키를 삭제한 후 데이터가 단편화되는 것을 방지하기 위함입니다. 웹 브라우저(web browser) 가 존재를 제어할 수 없기 때문에 악의적인 목적으로 사용될 수도 있습니다 . 보안 제품만이 좀비 쿠키를 식별하고 제거할 수 있습니다.
쿠키는 언제 발명되었습니까( 간결한 역사(concise history) )?
1994(July 1994) 년 7월 Netscape Communications 의 직원 은 전자 상거래 응용 프로그램을 개발해야 했습니다. 그는 서버에 과부하가 걸리지 않고 모든 사용자를 위해 장바구니(shopping cart) 를 보관할 수 있는 쉬운 방법을 찾아야 했기 때문에 이를 수행하는 가장 좋은 방법은 이 정보를 모든 사용자 의 웹 브라우저 에 저장하는 것이라고 결정했습니다. (web browser)쿠키는 이미 IT 산업(IT industry) 의 다른 분야에서 사용되었기 때문에 웹 브라우징에도 사용할 수 있다고 결정했습니다.
쿠키를 사용하고 지원하는 최초의 브라우저는 1994년 10월(October 1994) Mosaic Netscape(Mosaic Netscape) 였습니다 . 1년 후 Internet Explorer 2 도 쿠키를 지원했습니다. 그 이후로 모든 웹 브라우저는 쿠키에 대한 지원을 제공했습니다. 쿠키가 만들어진 이유는 긍정적이지만 현재 쿠키는 윤리적이거나 합법적이지 않은 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다.
모든 웹사이트에서 쿠키에 대한 메시지가 표시되는 이유는 무엇입니까?
유럽(Europe) 에 거주 하거나 유럽 (Europe)IP 주소(IP address) 를 사용하여 웹을 탐색하는 경우 방문하는 많은 웹사이트에서 쿠키 사용에 대한 메시지가 표시됩니다. 이러한 프롬프트는 유럽 연합(European union) 을 구성하는 모든 국가와 유럽 사용자가 있는 모든 웹 사이트 및 온라인 서비스(website and online services) 에 적용되는 GDPR(일반 데이터 보호 규정) 법률 때문에 표시됩니다.(General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR))
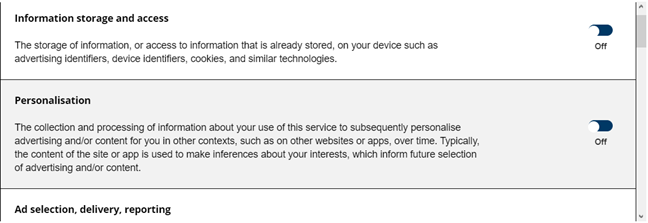
이러한 프롬프트의 목적은 모든 유럽 사용자에게 쿠키, 쿠키 사용 방법 및 이유를 알리고 명시적 동의를 요청하는 것입니다. 이 프롬프트를 읽고 귀하에게 적합한 용도만 허용할 것을 권장합니다.
웹사이트에서 귀하의 웹 브라우저에 저장된 쿠키를 확인하고 관리하는 방법
웹 브라우저가 장치에 저장하는 쿠키를 보고 관리하는 방법을 알고 싶다면 모든 주요 웹 브라우저를 다루는 가이드가 있습니다. 여기 있습니다:
- Chrome(Google Chrome) 에 저장된 쿠키를 보고 제거하는 2가지 방법
- Mozilla Firefox 에 저장된 쿠키를 보고 제거하는 방법
- Microsoft Edge 에 저장된 쿠키를 보고 제거하는 방법
- Opera에 저장된 쿠키를 보고 제거하는 2가지 방법
- Chrome , Firefox , Edge , Opera 및 Internet Explorer(Opera and Internet Explorer) 에서 타사 쿠키 비활성화
결론
쿠키는 모든 사용자에게 가장 유용한 콘텐츠를 제공함으로써 웹사이트를 더욱 강력하게 만들기 때문에 인터넷에서 널리 사용됩니다. 경우에 따라 웹 사이트는 쿠키를 사용하지 않고 작동할 수 없습니다. 또한 웹 사이트에서 사용자와 방문하는 페이지에 대해 알 수 있습니다. 그러나 다른 기술과 마찬가지로 비윤리적인 목적으로도 사용될 수 있습니다. 그렇기 때문에 쿠키의 작동 방식과 사용 방식을 아는 것은 웹을 검색하는 모든 디지털 시민에게 유용한 기술입니다. 쿠키에 대해 궁금한 점이 있으면 주저하지 말고 아래에 의견을 남겨주세요.
Simple questions: What are cookies and what do they do?
When browsing the internet, you often encounter the term "cookies." Many websites inform you about using cookies, and ask for your approval. Web browsers have many settings for managing cookies and even browser add-ons mention blocking cookies of all kinds. Even though you know that these "cookies" are not exactly a sweet dessert, you may not know precisely what they are and what their purpose is on the internet. This is why, in this article, we explain what cookies are, what they do and how they work, and what kind of cookies are most frequently used on the internet. Let's get started:
What are cookies on the internet?
Cookies are files that hold information about you, your web browser and your behavior on the internet. They are tiny files stored on your PC or device, which can be used by websites or web apps to tailor your online experience.
What do cookies do?
Cookies are sent between a sender (usually a website or a web app) and a receiver (your device). A cookie is created and interpreted by the sender, while the receiver only holds it and sends it back if the sender asks for it.
When browsing the web, the sender is the server on which a website runs, and the receiver is the web browser of the user who visits that website. Their purpose is to identify the user, check for his or her past activity on the website and provide appropriate content based on this data.

The first time a user visits a website, the server stores a particular cookie in the web browser of that user. On subsequent visits to the website, the server asks for its cookie, reads it and loads a particular configuration of the website for that specific user. You can think of cookies like a tag applied by web servers to every user, which is read by web servers to identify users.
This identification is beneficial on websites where real-time user data is critical. For example, when using an online shop, you cannot buy anything without the help of cookies. Shops would not be able to identify you and build your shopping cart without them because each time you load a web page, the shop would see you as a new user and start your visit from scratch.
What is inside of a cookie?
Every modern web browser supports cookies, and they have a small size, of roughly 4 KB. To help you understand the structure of a cookie, let's use as an example the "cfduid" cookie sent by our website - Digital Citizen. We analyzed it using Google Chrome.

Here is its structure:
- Name - the name of the cookie.
- Content - the information the cookie contains.
- Domain - the domain using this cookie.
- Path - the page of the domain where the cookie is used. If the path is "/" it means that the cookie is used across the whole website.
- Send for - the level of security the connection needs to have to use the cookie.
- Accessible to script - it shows whether or not the cookie can be accessed through other ways than HTML.
- Created - the date the cookie was created on the user's web browser.
- Expires - the moment when the cookie expires and the browser deletes it.
How many types of cookies are there?
Even though the term cookie is rather general, there are many ways a cookie can be used. This is why there are different types of cookies on the internet. The most common types are the following:
- Session cookies - one of the most common. They exist in temporary memory until the web browser is closed. They are not harmful because all their information is deleted when your browsing session is over.
- Persistent cookies - also called tracking cookies. They last on the user's device until they are deleted or reach their expiry date. They are used to gather information about the user, recording his or her behavior on a specific website over a period of time.
- Secure cookies - an encrypted cookie that works only when using a secure HTTPS connection. These cookies are used to ensure that their information cannot be stolen by potential hackers connected to the same network as the user. They keep essential information about the user and are used mostly on websites where users perform financial transactions. Because they are encrypted, they are a lot more secure than other types of cookies.
- HttpOnly cookies - they cannot be used by any protocol other than HTTP. Such cookies ensure that only the website that created them can use them. Only session cookies can be HttpOnly, and they generally do not imply any privacy or security risks for users.
- Third-party cookies - these cookies belong to a different domain, other than the one that sent them. They are usually sent by ads and can store the browsing history of a user across multiple websites that use the same advertising network. These cookies may hurt your privacy because some ad networks use them to track way too much data about you, to display targeted ads.
- Zombie cookie - cookies that recreate themselves after they are deleted. They are generally used by web analytics services and stored outside of the browser because they are available across browsers installed on the same computer. The reason they recreate themselves is to prevent data from becoming fragmented after the user deletes the cookies. They can also be used for malicious purposes because the web browser cannot control their existence. Only security products can identify zombie cookies and remove them.
When were cookies invented (a concise history)?
In July 1994, an employee at Netscape Communications had to develop an e-commerce application. He had to find an easy way to keep the shopping cart for every user, without overloading the server, so he decided that the best way to do this was to store this information in the web browser of every user. Because cookies were already used in different fields of the IT industry, he decided they could also be used for web browsing.
The first browser to use and support cookies was Mosaic Netscape, in October 1994. One year later, Internet Explorer 2 also supported cookies. Since then, all web browsers have offered support for cookies. Even though the reason why they were created is a positive one, cookies are now used for all kinds of purposes, some of which are not ethical or legal.
Why am I seeing messages about cookies on every website?
If you live in Europe, or you are browsing the web using a European IP address, you see prompts about the use of cookies on many websites that you visit. These prompts are shown because of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) legislation that is applied in all the countries that form the European union, and to all the website and online services that have European users.

The purpose of these prompts is to inform all European users about cookies, how they are used and why, and ask for their explicit consent. We recommend that you read these prompts and permit only the uses that you are OK with.
How to see and manage the cookies stored in your web browser by websites
If you want to know how to see and manage the cookies your web browser stores on your device, we have guides that cover all the major web browsers. Here they are:
Conclusion
Cookies are widely used on the internet because they allow websites to be more powerful by providing the most useful content to every user. In some cases, websites cannot function without using cookies. They also allow websites to learn about their users and the pages they are visiting. However, just like any other technology, they can also be used for unethical purposes. That is why knowing how cookies work and how they are used is a useful skill for any digital citizen browsing the web. If you have any questions about cookies, do not hesitate to leave a comment below.



