산점도(산점도 그래프라고도 함)는 데이터 분석가에게 유용한 도구로, 두 가지 다른 데이터 세트를 시각적으로 탐색하고 분석하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 예를 들어, 여러 영업 팀의 영업 결과를 비교하는 경우 산점도를 사용하면 꺾은선형 차트와 마찬가지로 누가 가장 실적이 좋은(또는 가장 나쁜) 실적을 냈는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
Excel을 사용하여 산점도를 만들(Excel to make a scatter plot) 수 있지만 다른 방법은 무료로 제공되는 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 를 사용하여 산점도를 만드는 것입니다. 이 문서에서는 생성된 후 사용자 지정하는 방법을 포함하여 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 에서 산점도를 만드는 방법을 설명합니다 .

Google 스프레드시트 에서 산점도(Scatter Plot) 를 만드는 방법
산점도는 이름에서 알 수 있듯이 차트 전체에 분산된 점을 사용하여 두 가지 이상의 연결된 데이터 유형을 시각화합니다. 예를 들어, 영업 팀의 매출과 이익을 비교하려는 경우 각 영업 사원의 이익과 매출을 보여주는 분산형 그래프(이익 대 매출 매출 표시)가 완벽할 것입니다.
두 개의 비교 가능한 데이터 세트가 있는 한 산점도를 생성할 수 있으며 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 는 차트 생성 도구를 사용하여 이를 쉽게 만듭니다.
- Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 에서 산점도를 만들려면 스프레드시트 를 열고(open a spreadsheet) 데이터가 포함된 셀을 선택하세요. 데이터를 선택한 상태에서 메뉴에서 Insert > Chart 를 선택 합니다.

- 그러면 오른쪽 패널에 차트 편집기 도구가 열립니다. (Chart editor )Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 는 선택한 데이터와 함께 사용해야 하는 차트 또는 그래프 유형을 자동으로 결정합니다. Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 가 자동으로 산점도를 선택하지 않은 경우 설정(Setup) 탭 아래에 나열된 차트 유형(Chart type) 드롭다운 메뉴 에서 선택합니다. 각 차트가 무엇인지 확실하지 않은 경우 차트 위로 마우스를 가져가서 이름을 나열합니다.

- 차트 편집기는 선택한 셀을 사용하여 플롯 차트의 데이터 범위를 형성합니다. 이를 변경하려면 데이터 범위 선택 버튼( (Select data range )데이터 범위(Data range) 상자 옆에 있음 )을 누릅니다. 또는 데이터 범위(Data range) 상자 에 셀 범위를 수동으로 입력 합니다.

- 삽입된 차트는 새 차트 유형으로 즉시 업데이트됩니다. 기본적으로 산점도 에는 두 가지 형식의 데이터(예: 영업 팀 이름)를 연결하는 X축 데이터 가 있습니다. (X-axis data)시리즈(series ) 에는 비교하려는 두 가지(또는 그 이상) 형식의 데이터가 표시됩니다(예: 이익 및 수익). 추가 계열을 추가하려면 계열 추가(Add Series) 상자를 선택하고 추가 데이터 세트 중 하나를 선택합니다.

- 시리즈 중 하나를 제거해야 하는 경우 햄버거 메뉴 아이콘(hamburger menu icon) 을 선택한 다음 제거(Remove ) 옵션을 선택하십시오.

- Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 에서 맨 위 행을 사용하여 머리글 제목을 만들도록 하려면 행 1을 머리글로 사용(Use row 1 as headers) 확인란을 선택합니다. 첫 번째 열을 레이블로 사용하려면( X축(X-axis) 옆에 표시됨 ) 열 A를 레이블로 사용(Use column A as labels) 확인란을 선택합니다. Switch rows/columns 확인란 을 선택하여 행과 열을 전환할 수도 있습니다 .

산점도 사용자 정의
Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 의 모든 차트 및 그래프와 마찬가지로 차트 편집기는 다양한 추가 맞춤설정 옵션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해 레이블, 축 제목, 색상, 글꼴 등을 변경할 수 있습니다.
- 산점도를 사용자 지정하려면 오른쪽에 차트 편집기 패널이 표시되는지 확인합니다. (chart editor)그렇지 않은 경우 차트를 선택한 다음 오른쪽 상단 의 햄버거 메뉴 아이콘 을 선택합니다. (hamburger menu icon)메뉴에서 차트 편집(Edit the chart) 옵션을 선택합니다.

- 차트 편집기(Chart editor) 메뉴 의 사용자 정의(Customize) 탭에서 차트 변경을 시작할 수 있습니다. 차트 색상과 글꼴을 변경하려면 차트 스타일(Chart style) 범주를 선택하고 옵션(예: 배경색(background colour) ) 중 하나를 선택하여 변경합니다. 변경 사항은 자동으로 나타납니다.

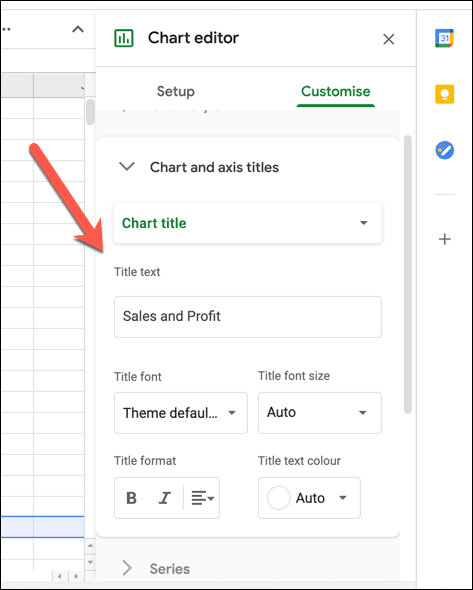
- 차트 및 축 제목(Chart and axis titles) 아래에서 차트 및 차트 축에 대해 표시된 제목을 변경할 수 있습니다. 차트 제목(Chart title) 드롭다운 메뉴 에서 제목 옵션을 선택한 다음 제목 텍스트(Title text) 상자 에 사용하려는 텍스트를 삽입합니다 . 그런 다음 상자 아래의 옵션에서 텍스트(글꼴, 서식 및 색상 포함)의 서식을 지정할 수 있습니다.
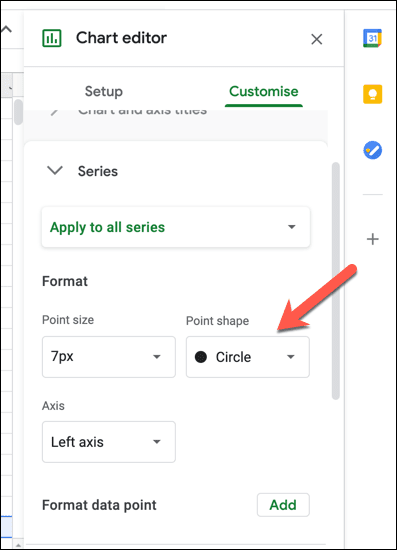
- 기본적으로 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 산점도 의 데이터 요소는 원(circles) 으로 표시됩니다 . 다른 모양(예: 삼각형 또는 X 표시)을 사용하려면 시리즈(Series) 범주를 선택한 다음 점 모양(Point shape) 드롭다운 메뉴에서 새 모양을 선택하십시오. 포인트 크기(Point size) 드롭다운 메뉴 에서 새 포인트 크기를 선택할 수도 있습니다 .
- 범례를 통해 산점도의 점이 속한 데이터 세트를 식별할 수 있습니다. 범례의 글꼴, 서식, 색상 및 위치를 변경하려면 범례(Legend) 범주를 선택하고 제공된 옵션을 사용하여 변경합니다.

- 가로 축(Horizontal axis ) 및 세로 축(Vertical axis) 범주 에서 다양한 축 레이블의 형식을 변경할 수 있습니다. 범주 중 하나를 선택한(Select) 다음 제공된 옵션에서 글꼴, 글꼴 크기, 서식 및 색상을 변경합니다. 축 순서를 반대로 하려면(왼쪽에서 오른쪽 또는 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로) 축 순서 반전(Reverse axis order) 확인란을 선택합니다.

- 산점도를 더 잘 보이게 하기 위해 눈금선과 눈금을 추가할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하려면 눈금선 및 눈금(Gridlines and ticks ) 범주를 선택한 다음 드롭다운 메뉴에서 가로 축(Horizontal axis ) 또는 세로 축을 선택합니다. (Vertical axis )가로 축(Horizontal axis ) 옵션을 선택한 상태에서 주요 눈금(Major ticks) 확인란을 선택 하여 가로 축의 눈금을 활성화한 다음 그 아래의 설정(위치, 길이, 색상 및 두께 포함)을 추가로 변경합니다.

- 눈금선 및 눈금 메뉴에서 (Gridlines and ticks)세로 축(Vertical axis) 옵션을 선택 하면 세로 축에 눈금 선(주요 및 보조)과 눈금을 활성화할 수 있습니다. 주요 눈금선, 보조 눈금선, (Major gridlines, Minor gridlines,)주요 눈금(Major ticks) 또는 보조 눈금(Minor ticks ) 확인란을 선택 하여 이러한 옵션을 활성화한 다음 아래에 있는 설정(색상, 위치, 길이, 두께 및 색상 포함)을 변경합니다.

시각적 스프레드시트 만들기
이제 Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 에서 산점도를 만드는 방법을 알게 되었으며 꺾은선형 차트(line chart) 에서 막대 그래프 에 이르기까지 데이터 분석을 위해 다른 (bar graph)Google 스프레드시트(Google Sheets) 그래프와 차트를 만드는 실험도 할 수 있습니다 . 어려움이 있다면 시작하는 데 사용할 수 있는 Google 스프레드시트 템플릿 이 있습니다. 데이터를 채우고 데이터를 중심으로 자신만의 차트를 만들 수 있습니다.(Google Sheets templates)
Excel 매크로(Excel macros) 와 같은 일부 기능은 지원되지 않지만 숙련된 Excel 사용자는 스프레드시트를 Google 스프레드시트로 쉽게 변환(convert spreadsheets to Google Sheets) 할 수도 있습니다. Google 스프레드시트 스크립트(Google Sheets scripts) 를 사용하여 기능을 확장하고 스프레드시트를 다른 Google 및 타사 서비스 와 통합 하여 작업을 더욱 확장할 수 있습니다 .
How to Make a Scatter Plot in Google Sheets
A sсatter plot (also known as a scatter plot graph) is a useful tool for data analysts, helping to visually explore and anаlyze twо different data sets. For instance, if you’re comparing the sales results aсross different sales teams, a ѕcatter plot woυld allow you to see whо was the best (or worst) performing, much like a line chart woυld.
While you could use Excel to make a scatter plot, another way you can do it is to use the freely-available Google Sheets to make a scatter plot instead. In this article, we’ll explain how to make a scatter plot in Google Sheets, including how to customize it once it’s created.

How to Make a Scatter Plot in Google Sheets
A scatter plot, as the name suggests, uses scattered dots across a chart to visualize two or more types of linked data. For instance, if you wanted to compare the sales and profits of a sales team, a scatter graph (showing the profit vs the sales revenue) would be perfect, showing the profit and revenue for each salesperson.
As long as you have two comparable data sets, it’s possible to create a scatter plot, and Google Sheets makes this easy with its chart creation tool.
- To create a scatter plot in Google Sheets, open a spreadsheet and select the cells containing your data. With the data selected, select Insert > Chart from the menu.

- This will open the Chart editor tool in the right-hand panel. Google Sheets will automatically attempt to determine what type of chart or graph it should use with the selected data. If Google Sheets hasn’t selected a scatter plot automatically, select it from the Chart type drop-down menu, listed under the Setup tab. If you’re unsure what each chart is, hover over it to list the name.

- The chart editor will use the selected cells to form the data range for the plot chart. If you want to change this, press the Select data range button (next to the Data range box). Alternatively, type the cell range into the Data range box manually.

- The inserted chart will immediately update to the new chart type. By default, a scatter plot will have X-axis data that ties the two forms of data together (eg. the names of a sales team). The series will show the two (or more) forms of data that you want to compare (eg. profit and revenue). To add additional series, select the Add Series box and choose one of the additional data sets.

- If you need to remove one of the series, select the hamburger menu icon, then select the Remove option.

- If you want Google Sheets to use the top row to create header titles, select the Use row 1 as headers checkbox. To use the first column as labels (shown alongside the X-axis), select the Use column A as labels checkbox. You can also switch rows and columns by selecting the Switch rows/columns checkbox.

Customizing a Scatter Plot
Like all charts and graphs in Google Sheets, the chart editor offers a number of additional customization options. This allows you to change labels, axis titles, colors, fonts, and more.
- To customize a scatter plot, make sure that the chart editor panel on the right-hand side is visible. If it isn’t, select the chart, then select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select the Edit the chart option.

- In the Customize tab of the Chart editor menu, you can begin to make changes to your chart. To change the chart colors and fonts, select the Chart style category and select one of the options (eg. background colour) to make changes. Any changes you make will appear automatically.

- Under Chart and axis titles, you can change the displayed titles for the chart and chart axes. Select a title option from the Chart title drop-down menu, then insert the text you wish to use in the Title text box. You can then format the text (including font, formatting, and color) in the options below the box.

- By default, data points on a Google Sheets scatter plot are displayed as circles. To use a different shape (for instance, triangles or X marks), select the Series category, then choose a new shape from the Point shape drop-down menu. You can also select a new point size from the Point size drop-down menu.

- The legend allows you to identify what data sets the points on a scatter plot belong to. To change the font, formatting, color, and position of the legend, select the Legend category and make changes using the options provided.

- In the Horizontal axis and Vertical axis categories, you can change how the different axis labels are formatted. Select either category, then make changes to the font, font size, formatting, and color from the options provided. If you want to reverse the axis order (from left to right or right to left), select the Reverse axis order checkbox.

- To help make your scatter plot more visible, you can add gridlines and ticks. To do this, select the Gridlines and ticks category, then select either Horizontal axis or Vertical axis from the drop-down menu. With the Horizontal axis option selected, select the Major ticks checkbox to enable ticks on the horizontal axis, then make further changes to the settings (including position, length, color, and thickness) below it.

- With the Vertical axis option selected in the Gridlines and ticks menu, you can enable gridlines (both major and minor) and ticks for the vertical axis. Select the Major gridlines, Minor gridlines, Major ticks or Minor ticks checkboxes to enable these options, then make changes to the settings (including color, position, length, thickness, and color) below it.

Create Visual Spreadsheets
Now you know how to make a scatter plot in Google Sheets, you can also experiment with creating other Google Sheets graphs and charts for data analysis, from a line chart to a bar graph. If you’re struggling, there are Google Sheets templates you can use to get started, ready for you to fill with data and create your own charts around it.
Experienced Excel users can also convert spreadsheets to Google Sheets with ease, although some features (like Excel macros) won’t be supported. You can take things even further, using Google Sheets scripts to expand functionality and integrate spreadsheets with other Google and third-party services.















