우리는 인터넷과 무선 연결(internet and wireless connections) 의 시대에 살고 있으며 대부분의 사람들은 집에 무선 라우터(wireless router) 를 가지고 있습니다. Wi-Fi 는 우리 어휘에서 흔한 용어가 되었지만 무선 네트워킹 표준은 이해하거나 발음하기조차 쉽지 않습니다. 네트워크 엔지니어와 기업이 만들어낸 복잡한 이름 때문입니다. 802.11ax가 무엇인지 아십니까? 802.11ad 또는 802.11ac는 어떻습니까? 이러한 이름이 Wi-Fi 6(Wi-Fi 6) , Wi-Fi 5 또는 Wi-Fi 4 와 같이 더 간단한 용어로 변경되고 있다는 소식을 들으 셨습니까(Did) ? 이 모든 것이 무엇을 의미하고 왜 중요한지 이해하고 싶습니까? 필요한 정보를 찾으려면 이 문서를 읽으십시오.
Wi-Fi Alliance 는 무선 네트워킹 표준 개발을 담당합니다.
Wi-Fi Alliance 는 Wi-Fi 네트워킹 표준을 개발하고 발표하는 전 세계의 컴퓨팅 제조업체 연합입니다. 전체 기술 산업(tech industry) 이 이를 따르고 Wi-Fi 표준의 도움으로 서로 호환되는 무선 장치를 개발합니다.

Wi-Fi Alliance 가 없으면 무선 라우터와 (Alliance)랩톱 및 스마트폰과(laptop and smartphone) 같은 무선 장치 간의 상호 운용성이 좋지 않을 것 입니다. Wi-Fi Alliance 는 이 기사에서 다루는 모든 표준을 게시합니다. 하나씩 논의해 보겠습니다.
Wi-Fi 4라고도 하는 802.11n이란 무엇입니까?
IEEE 802.11n-2009라는 이름으로 802.11n은 2009년(name IEEE 802.11n-2009) 에 발표된 무선 네트워킹 표준입니다. Wi-Fi 802.11n은 Wi-Fi 4라고도 합니다(Wi-Fi 802.11n is also referred to as Wi-Fi 4) . 802.11n은 2.4GHz(GHz) 및 5GHz 의 두 가지 (GHz)무선 주파수(radio frequency) 대역을 사용할 수 있으며 최대 600Mbps(Mbps) 의 데이터 전송 속도를 제공할 수 있습니다 . Wi-Fi 802.11n은 MIMO(MIMO) (다중 입력 다중 출력) 를 지원하는 최초의 무선 표준이기도 합니다 . MIMO 는 여러 안테나를 사용하여 독립적인 데이터 스트림을 결합하여 더 많은 데이터를 전송할 수 있도록 하는 기술입니다.

최신 무선 라우터는 (Modern wireless)2.4GHz 대역(GHz band) 에서 Wi-Fi 4 표준을 사용합니다 . Wi-Fi 4는 구형 장치를 네트워크에 연결하거나 스마트 플러그, 스마트 전구, 센서 등과 같은 스마트 홈 장치를 연결하는 데 사용됩니다.
Wi-Fi 5라고도 하는 802.11ac는 무엇입니까?
802.11ac 또는 IEEE 802.11ac 는 2013년 말에 발표된 무선 네트워킹 표준입니다. Wi-Fi 802.11ac는 Wi-Fi 5라고도(Wi-Fi 802.11ac is also known as Wi-Fi 5) 합니다. 지난 몇 년 동안 판매된 대부분의 라우터가 802.11ac와 호환되므로 802.11ac는 오늘날 가장 일반적인 무선 표준입니다 . (standard today)이 표준은 이전의 802.11n과 마찬가지로 MU-MIMO 를 지원하지만 최대 (MU-MIMO)2.3Gbps(Gbps) 의 최대 데이터 전송 속도를 제공할 수 있습니다 . 802.11ac 표준은 5GHz 주파수(GHz frequency) 대역 에서만 작동 하지만 이를 지원하는 대부분의 무선 라우터는 2.4GHz 주파수(GHz frequency) 대역 에서 802.11n 표준도 지원합니다 .

802.11ac 장치는 802.11ac Wave 1(Wave 1) 및 Wave 2 라는 두 가지 범주로 나뉩니다 . 802.11ac Wave 1(Wave 1) 의 일부로 판매되는 제품은 2013년에 시장에 출시된 반면 Wave 2 의 제품은 2016년에 출시되었습니다. Wave 2 는 표준의 개선된 버전입니다. 802.11ac Wave 2 무선 라우터는 처리량이 더 높으며 MU-MIMO 지원을 추가합니다. (MU-MIMO)Wave 1 라우터는 최대 1.3Gbps의 속도를 제공할 수 있지만(Gbps) Wave 2 의 라우터는 최대 (Wave 2)2.3Gbps(Gbps) 의 속도 를 제공할 수 있습니다 . 따라서 오늘 무선 라우터(wireless router today) 를 구입하면, 향상된 무선 속도 및 적용 범위 의 이점을 얻으려면 802.11ac (wireless speed and coverage)Wave 2 를 지원하는지 확인하는 것이 좋습니다 .
802.11ax는 무엇입니까?
802.11ax 또는 IEEE802.11ax 는 아직 작업 중이며 아직 승인되지 않은 무선 네트워킹 표준입니다. ZDNet: Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, 지연된(Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, delayed) .
802.11ax는 Wi-Fi 6이라고도 합니다(802.11ax is also referred to as Wi-Fi 6) . HEW ( 고효율 무선(High-Efficiency Wireless) ) 라고도 하며 지금까지 언급한 표준 과 동일한 2.4GHz(GHz) 및 5GHz 주파수(GHz frequency) 대역 에서 작동하도록 설계되었습니다 . 1 ~ 7GHz(GHz) 사이의 추가 대역 이 출시되면 이 대역도 사용할 수 있을 것으로 보입니다 . 802.11ax 무선 네트워킹 표준은 평균 데이터 전송 속도를 802.11ac 표준보다 최대 4배 향상시키는 것을 목표로 합니다. 특히 공항, 기차역, 레스토랑 또는 커피숍과 같이 붐비는 장소에서 상당히 향상된 속도를 제공해야 합니다.

Wi-Fi 6을 지원하는 무선 라우터 및 메시 Wi-Fi 시스템은 이미 시장에 등장했습니다. 그러나 그들은 프리미엄 가격을 갖는 경향이 있으며 대부분의 사람들은 그것을 감당할 수 없습니다. 표준이 승인되고 확정되는 대로 더 저렴한 Wi-Fi 장비가 출시될 것으로 기대합니다.
802.11ad는 무엇입니까?
IEEE 802.11ad 는 (IEEE 802.11ad)WiGig 또는 60GHz Wi-Fi(WiGig or 60 GHz Wi-Fi) 라고도 하는 무선 네트워킹 표준입니다 . 2.4GHz(GHz) 또는 5GHz(GHz) 와 같은 기존 무선 주파수 대역을 사용하는 대신 약 (wireless frequency)60GHz(GHz) 에서 실행되는 무선 스펙트럼(radio spectrum) 의 마이크로웨이브 섹션을 사용하는 Wi-Fi 의 한 형태입니다 . 그것은 최대 7Gbps의 믿을 수 없을 정도로 빠른 데이터 전송 속도를 허용 합니다(Gbps) . 그러나 마이크로파 범위 주파수(microwave range frequency) 에서 작동하기 때문에, 벽을 통과할 수 없다는 심각한 단점이 있으며 범위가 1~10미터에 불과합니다. 번개처럼 빠르지만 방해가 되는 벽이나 장애물이 없을 때 한 방만 덮도록 설계되었습니다.
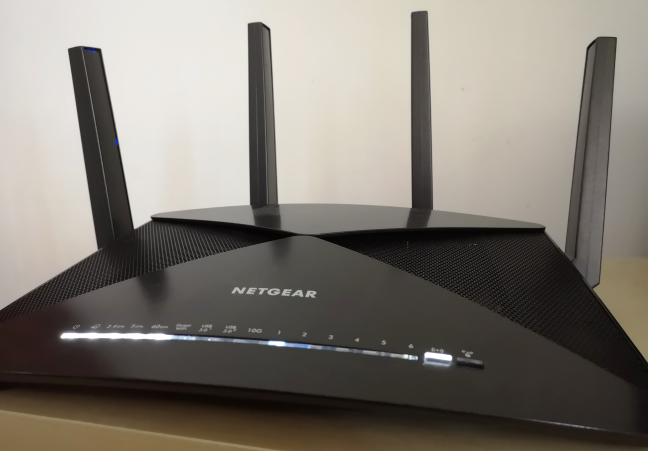

시장에는 802.11ad를 지원하는 무선 라우터가 거의 없으며 이를 지원하는 네트워크 장치도 거의 없습니다. 802.11ad로 테스트한 라우터 중 하나는 Netgear Nighthawk X10 입니다.
Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 4 등이란 무엇입니까?
2018 년 10월 3(October 3) 일 Wi-Fi Alliance 는 사람들이 더 쉽게 식별할 수 있도록 무선 네트워킹 표준에 (wireless networking)새로운 이름(new naming) 을 추가했다고 발표했습니다 . 결국 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, 802.11n 및 기타 유사한 이름은 모두 기억하기 쉽지 않으며 대부분의 사람들은 그 이름이 무엇을 의미하는지 모릅니다. 그들의 생각은 Wi-Fi 다음에 숫자가 붙으면 기억하기 쉽다는 것입니다. 규칙은 숫자가 높을수록 더 새롭고 더 나은 표준입니다. Wi-Fi 6 , Wi-Fi 5 및 Wi-Fi 4 가 무엇을 의미하는지 이미 알고 계실 것 입니다. 그러나 요약하자면 다음과 같습니다.
- Wi-Fi 6 은 (Wi-Fi 6)802.11ax 무선 네트워킹 표준 을 지원하는 장치를 식별합니다.
- Wi-Fi 5 는 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5)Wave 2 를 포함하여 (Wave 2)802.11ac 무선 네트워킹 표준 을 지원하는 장치를 식별합니다.
- Wi-Fi 4 는 (Wi-Fi 4)802.11n 무선 네트워킹 표준 을 지원하는 장치를 식별합니다.
각 최신 Wi-Fi 네트워킹(Wi-Fi networking) 표준이 제공 하는 것을 이해하는 데 도움이 되도록 해당 주파수 대역과 최대 이론 속도를 비교하는 표를 만들었습니다.

Wi-Fi 1, Wi-Fi 2 및 Wi-Fi 3에는 브랜드가 없습니다. Wi-Fi Alliance 가 이전 Wi-Fi 표준을 많이 사용하는 것으로 간주하지 않았기 때문일 수 있습니다. 그러나 완성을 위해 올바른 브랜딩은 다음과 같았습니다.
- Wi-Fi 1은 802.11b여야 합니다. 이 표준은 1999년에 발표되었으며 2.4GHz 대역(GHz band) 을 사용하며 최대 11Mbps 의 (Mbps)데이터 전송률(data rate) 을 가지고 있습니다.
- Wi-Fi 2는 802.11a여야 합니다. 1999년에 출시되었으며 5GHz 대역(GHz band) 을 사용하며 최대 54Mbps 의 (Mbps)데이터 전송률(data rate) 을 가지고 있습니다.
- Wi-Fi 3는 802.11g여야 합니다. 이 표준은 2003년에 발표되었으며 2.4GHz 대역(GHz band) 을 사용하며 최대 54Mbps 의 (Mbps)데이터 전송률(data rate) 을 가지고 있습니다.
802.11ax 대 802.11ac 대 802.11n(vs 802.11n) 또는 Wi-Fi 6 대 Wi-Fi 5 대 Wi-Fi 5 및 실제 속도
각 Wi-Fi 표준(Wi-Fi standard) 의 사양과 각각이 달성할 수 있는 이론상 최대 속도를 읽으면 감동할 것입니다. 그러나 실제 생활에서 얻는 속도는 훨씬 더 낮습니다. AC1200 , AC1750 , AC1900 또는 그 이상은 무엇을 의미하고 차이점은 무엇입니까? 에서 이 주제에 대해 자세히 알아볼 수 있습니다 .
사용 가능한 다양한 표준에서 얻을 수 있는 실제 속도에 대한 현실적인 관점을 제공하기 위해 가장 강력한 무선 라우터 중 하나인 ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000 을 사용하여 (ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000)SpeedTest 로 몇 가지 측정을 수행 했습니다. Intel Wi-Fi 6 (Intel Wi-Fi 6) AX200 네트워크(AX200 network) 카드. 우리의 인터넷 연결은 1Gbps의 다운로드 속도 와 (download speed)500Mbps(Mbps) 의 업로드 속도를 제공(Gbps) 합니다 .
먼저 라우터에서 방출되는 Wi-Fi 에 (Wi-Fi)2.4GHz 대역(GHz band) 에서 802.11n( Wi-Fi 4 ) 표준을 사용하여 연결했으며 측정한 최대 다운로드 속도 (download speed)는(Mbps) 221.28Mbps 입니다.
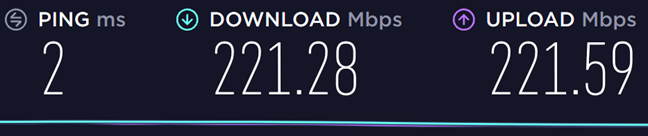
그런 다음 802.11ac( Wi-Fi 5 ) 표준 을 사용하여 라우터에서 방출하는 두 대역 중 첫 번째 5GHz 대역 으로 전환했습니다. (GHz band)도달 한 최대 다운로드 속도(download speed) 는 630.10Mbps 입니다(Mbps) . 이 무선 라우터 를 사용할 때 (wireless router)Wi-Fi 5 표준은 Wi-Fi 4 표준보다 2.8배 빠릅니다 .
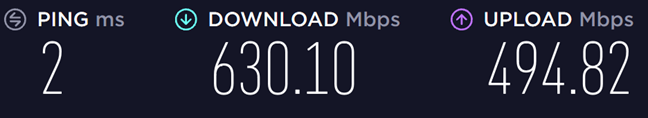
마지막으로 802.11ax( Wi-Fi 6 ) 표준 을 사용하는 두 번째 5GHz 대역 으로 전환했습니다. (GHz band)이번에는 최대 다운로드 속도 (download speed)762.03Mbps(Mbps) 에 도달했습니다 . 이는 Wi-Fi 5보다 20% 빠르며 상당한 개선이지만 Wi-Fi 6 표준이 약속하는 최대 이론 속도와는 거리가 있습니다.

이 빠른 비교를 통해 다양한 Wi-Fi 표준을 사용할 때 실제 생활에서 달성할 수 있는 속도에 대한 보다 현실적인 관점을 얻을 수 있기를 바랍니다.
무선(Do wireless) 라우터는 하나 이상의 Wi-Fi 표준을 사용합니까?
예, 대부분이 그렇습니다! 제조업체는 각 대역에서 서로 다른 무선 표준을 지원하면서 동시에 1개, 2개 또는 3개의 대역에서 작동할 수 있는 무선 라우터를 만듭니다. 오늘날 대부분의 무선 라우터는 더 빠른 속도 와 다양한 장치 와의 호환성(speed and compatibility) 을 제공하기 때문에 듀얼 밴드 또는 트라이 밴드 라우터 입니다. 현재 판매되는 모든 무선 라우터는 802.11n 표준(보통 2.4GHz 대역(GHz band) )을 지원하며 802.11ac 표준( 5GHz 대역(GHz band) )에 대한 지원도 추가합니다. 고급형 무선 라우터는 이 모든 작업을 수행하지만 802.11ac Wave 2 , 802.11ax 또는 802.11ad 와 같은 최신 표준에 사용되는 세 번째 대역( 5GHz(GHz) 또는 60GHz )도 포함할 수 있습니다.(GHz)
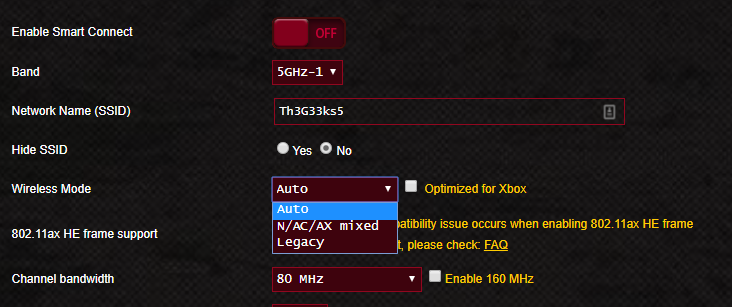
단일 대역, 이중 대역 또는 삼중 대역 라우터 가 있는지 여부에 관계없이 펌웨어에서 활성화하고 사용하려는 (tri-band router)Wi-Fi 표준 및 대역을 선택할 수 있어야 합니다 . 2.4GHz 대역(GHz band) 및 지원되는 무선 표준 만 활성화할지 여부를 선택 하거나, 5GHz 대역(GHz band) 및 지원되는 무선 표준 만 활성화하도록 선택할 수 있습니다 . 또한 라우터에서 사용할 수 있는 모든 대역과 모든 무선 표준을 활성화하고 모든 것을 혼합하여 네트워크에서 원하는 결과를 얻을 수도 있습니다.
새로운 Wi-Fi 표준을 지원하는 새로운 장치를 구입할 계획입니까?
Wi-Fi 5 호환 장치를 사용하고 있습니까(Are) ? 최신 Wi-Fi 6 표준으로 업그레이드할 가치가 있다고 생각하십니까, 아니면 투자하기에는 너무 이르다고 생각하십니까? 아래에 댓글(Comment) 을 달고 모든 무선 네트워킹(wireless networking) 표준, 명명 규칙 및 기능 에 대한 의견 을 공유 하십시오.(below and share)
What is 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, and 802.11n? What is Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5 and so on?
We arе living in the age of the internet and wireless connections, and most people have a wireless router in their homes. Wi-Fi has become a common term in our vocabulary, but wireless networking standards are not eaѕy to understand or even pronounce. Thаt is beсauѕe they have complicated names, invented by network engineers and сorрorations. Do you know what 802.11ax is? What about 802.11ad, or 802.11ac? Did you hear the news that these names аre changing into simpler terms like Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, or Wi-Fi 4? Do you want to understand what all that means and why it matters? Read thіs article to find the information you need:
The Wi-Fi Alliance is in charge of developing wireless networking standards
The Wi-Fi Alliance is an alliance of computing manufacturers from all over the world that develops and publishes the Wi-Fi networking standards. The entire tech industry follows them and develops wireless devices that are compatible with each other, with the help of Wi-Fi standards.

Without the Wi-Fi Alliance, we would not have good interoperability between wireless routers and wireless devices, such as your laptop and smartphone. The Wi-Fi Alliance publishes all the standards covered in this article. Let's discuss them one by one:
What is 802.11n, also known as Wi-Fi 4?
802.11n, under its full name IEEE 802.11n-2009, is a wireless networking standard that was published in 2009. Wi-Fi 802.11n is also referred to as Wi-Fi 4. 802.11n allows the use of two radio frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and can deliver data transfer speeds of up to 600 Mbps. Wi-Fi 802.11n was also the first wireless standard that offered support for MIMO (multiple-input-multiple-output). MIMO is a technology that allows the use of multiple antennas to transmit more data by combining independent data streams.

Modern wireless routers use the Wi-Fi 4 standard on the 2.4 GHz band. Wi-Fi 4 is used to connect older devices to the network, or smart home devices like smart plugs, smart bulbs, sensors, and so on.
What is 802.11ac, also known as Wi-Fi 5?
802.11ac or IEEE 802.11ac is a wireless networking standard that was published in late 2013. Wi-Fi 802.11ac is also known as Wi-Fi 5. The 802.11ac is the most common wireless standard today, as most routers sold during the last few years are 802.11ac-compatible. This standard, just like the 802.11n before it, supports MU-MIMO, but it can offer maximum data transfer speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. The 802.11ac standard works only on the 5 GHz frequency band but most of the wireless routers that support it also offer support for the 802.11n standard on the 2.4 GHz frequency band.

802.11ac devices are split into two categories, called 802.11ac Wave 1 and Wave 2. The products that are sold as part of the 802.11ac Wave 1 were introduced to the market in 2013, while the ones in Wave 2 were introduced in 2016. Wave 2 is an improved version of the standard. The 802.11ac Wave 2 wireless routers have higher throughput and add support for MU-MIMO: while the Wave 1 routers can provide speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps, the ones in Wave 2 can deliver speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. Therefore, if you buy a wireless router today, it is a good idea to check whether it offers support for 802.11ac Wave 2, to benefit from improved wireless speed and coverage.
What is 802.11ax?
802.11ax or IEEE802.11ax is a wireless networking standard that is still in the works and has not yet been approved. It is expected that it will be finalized and approved sometime during late 2019, as shared by ZDNet: Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, delayed.
802.11ax is also referred to as Wi-Fi 6. It is also known as High-Efficiency Wireless (HEW) and is designed to work in the same 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands as the standards that we mentioned so far. It appears that it will also be capable of working with additional bands between 1 and 7 GHz, when they become available. The 802.11ax wireless networking standard aims to improve the average data transfer speeds by up to four times more than the 802.11ac standard. It should offer significantly improved speeds, especially in crowded places such as airports, train stations, restaurants, or coffee shops.

Wireless routers and mesh Wi-Fi systems with Wi-Fi 6 have already shown up on the market. However, they tend to have a premium price, and most people can't afford them. As soon as the standard is approved and finalized, expect more affordable Wi-Fi equipment to be launched.
What is 802.11ad?
IEEE 802.11ad is a wireless networking standard that is also known as WiGig or 60 GHz Wi-Fi. It is a form of Wi-Fi that, instead of using traditional wireless frequency bands such as 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, uses a microwave section of the radio spectrum, running at about 60 GHz. It allows for incredibly fast data transfer speeds of up to 7 Gbps. However, because it works on a microwave range frequency, it has the significant disadvantage of not being able to pass through walls and has a range of only 3 to 32 feet (1 to 10 meters). It is "lightning fast," but it is designed to cover only one room when no walls or obstacles stand in the way.

There are few wireless routers on the market with support for 802.11ad, and few network devices that have support for it. One of the routers that we tested with 802.11ad is Netgear Nighthawk X10.
What is Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 4, and so on?
On October 3, 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced that it added a new naming for the wireless networking standards, to make it easier for people to identify them. After all, 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, 802.11n, and all the other similar names are not easy to remember, and most people have no idea what they mean. Their thinking is that Wi-Fi, followed by a number, is easy to remember. The rule is that the higher the number, the newer and the better the standard. You already know by now what Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, and Wi-Fi 4 mean. However, to summarize, here is what they are:
- Wi-Fi 6 identifies devices that support the 802.11ax wireless networking standard
- Wi-Fi 5 identifies devices that support the 802.11ac wireless networking standard, including 802.11ac Wave 2
- Wi-Fi 4 identifies devices that support the 802.11n wireless networking standard
To help you understand what each of the modern Wi-Fi networking standards offers, we made a table which compares their frequency bands and maximum theoretical speed:

Wi-Fi 1, Wi-Fi 2, and Wi-Fi 3 are not branded. That is likely because the Wi-Fi Alliance did not consider older Wi-Fi standards to be used much. However, for the sake of completion, we believe that the correct branding would have been:
- Wi-Fi 1 should have been 802.11b. This standard was released in 1999, it uses the 2.4 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 11 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 2 should have been 802.11a. It was released in 1999, it uses the 5 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 54 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 3 should have been 802.11g. This standard was released in 2003, it uses the 2.4 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 54 Mbps.
802.11ax vs 802.11ac vs 802.11n or Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 5, and real-life speeds
If you read the specifications of each Wi-Fi standard, and the maximum theoretical speed that each can achieve, you are going to be impressed. However, in real life, the speeds you get are much lower. You can find out more about this subject, in this article: What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 or more, mean and what's the difference?
To give you a realistic perspective on the real-life speed you get from the different standards that are available, we took one of the most powerful wireless routers - ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000 - and made some measurements with SpeedTest, on a laptop with an Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200 network card. Our internet connection offers a download speed of 1 Gbps, and an upload speed of 500 Mbps.
We first connected to the Wi-Fi emitted by the router, on the 2.4 GHz band, using the 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) standard, and the maximum download speed we measured is of 221.28 Mbps.

We then switched to the first 5 GHz band of the two emitted by the router, using the 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) standard. The maximum download speed that we reached is 630.10 Mbps. The Wi-Fi 5 standard is 2.8 times faster than the Wi-Fi 4 standard when using this wireless router.

Lastly, we switched to the second 5 GHz band, which used the 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) standard. This time we reached a maximum download speed of 762.03 Mbps. That is 20% faster than Wi-Fi 5, which is a substantial improvement, but far from the maximum theoretical speeds that are promised by the Wi-Fi 6 standard.

Hopefully, this quick comparison has given you a more realistic perspective of the speeds you can achieve, in real life, when using different Wi-Fi standards.
Do wireless routers use one or more Wi-Fi standards?
Yes, most of them do! Manufacturers make wireless routers that can work on one, two, or even three bands simultaneously, while supporting different wireless standards on each band. Most wireless routers today are dual-band or tri-band routers because they offer more speed and compatibility with various devices. All the wireless routers sold today have support for the 802.11n standard (usually on the 2.4 GHz band), and also add support for the 802.11ac standard (on the 5 GHz band). High-end wireless routers do all that, but can also include a third band (5 GHz or even 60 GHz), that is used for newer standards such as 802.11ac Wave 2, 802.11ax or 802.11ad.

Whether you have a single-band, dual-band, or tri-band router, the good thing is that the firmware should let you choose what Wi-Fi standards and bands you want to enable and use. You can select whether to activate only the 2.4 GHz band and the wireless standards supported on it, or you can choose to activate only the 5 GHz band and the wireless standards supported on it. Furthermore, you can also enable all the bands and all the wireless standards available on your router, mixing everything to get the desired results for your network.
Do you plan on getting new devices that support newer Wi-Fi standards?
Are you using Wi-Fi 5 compatible devices? Do you believe that it is worth upgrading to the latest Wi-Fi 6 standard, or is it too soon to invest in it? Comment below and share your opinion about all the wireless networking standards, their naming conventions, and features.










