Windows 파일 탐색기(Windows File Explorer) 에서 폴더를 열면 모든 파일, 모든 하위 폴더의 전체 내용이 표시될 것으로 예상합니다. 그러나 반드시 그런 것은 아닙니다. 찾고 있는 폴더에 숨김 파일이나 폴더가 포함되어 있으면 파일 탐색기에서 숨김 파일 보기를 활성화(enabled hidden file view in File Explorer) 하지 않는 한 Windows 에서 해당 파일을 표시하지 않습니다 .
Windows 10 에서 숨겨진 폴더와 그 안에 포함된 모든 숨겨진 파일을 찾는 방법을 알고 싶다면 아래에 나열된 방법 중 일부를 사용해야 합니다. 여기에는 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 및 Windows PowerShell 에서 비밀 검색 도구를 사용하여 이를 찾는 것과 (Windows PowerShell)FreeCommander 와 같은 타사 대안을 사용하는 것이 포함됩니다 .

파일 탐색기를 사용하여 Windows 10에서 숨겨진 파일 및 폴더를 찾는 방법(How to Find Find Hidden Files and Folders on Windows 10 Using File Explorer)
누락된 파일이나 폴더를 찾으려면 가장 좋은 방법은 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 의 검색 도구를 사용하는 것입니다. 고급 검색 매개변수를 사용 하면 열려 있는 (Using)파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 창 을 사용하여 보기에 의해(자동 또는 수동으로) 숨겨진 모든 폴더 또는 파일을 찾을 수 있습니다 .
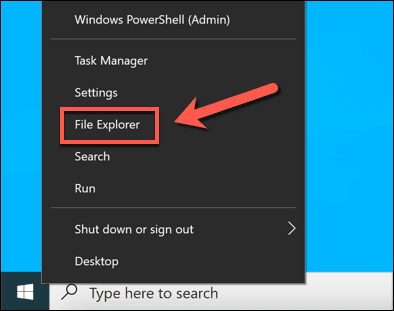
- 이렇게 하려면 작업 표시줄( 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 아이콘이 고정되어 있는 경우)을 사용하거나 시작(Start) 메뉴 를 통해 새 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 창을 엽니다. 시작(Start) 메뉴를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 를 선택 하여 대신 새 창을 열 수도 있습니다.
- 새 파일 탐색기(File Explorer ) 창에서 검색하려는 폴더(또는 드라이브)를 엽니다. 오른쪽 상단의 검색 창을 사용하여 속성:H 를 입력하고 (attributes:H)Enter 키(enter key) 를 선택 하여 검색을 시작합니다. 속성(Properties) 메뉴 에서 숨김 파일 속성이 적용된 폴더 내의 모든 파일과 폴더를 검색 합니다.

- 검색을 추가로 사용자 지정하려면 검색에 파일 또는 폴더 이름(또는 일부 이름)을 추가할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하려면 검색 창에서 속성:H(attributes:H) 매개변수 앞이나 뒤에 파일 또는 폴더 이름을 입력하십시오 (예 : 파일 특성:H(file attributes:H) ). 부분 일치를 검색하려면 와일드카드(예: fil* attributes:H )를 사용하여 검색할 수 있습니다.

- 파일이나 폴더를 찾으면 파일이나 폴더를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 팝업 메뉴에서 파일 위치 열기 를 선택하여 저장된 위치로 다시 추적할 수 있습니다.(Open file location)

Windows Powershell을 사용하여 숨김 파일 및 폴더 검색(Searching for Hidden Files and Folders Using Windows Powershell)
위 의 파일 탐색기 방법은 (File Explorer)Windows 10 에서 숨겨진 파일 및 폴더를 찾는 가장 쉬운 방법을 제공 하지만 반드시 가장 빠른 것은 아닙니다. PC에서 누락된 파일을 빠르게 검색하려면 Windows PowerShell 을 사용하여 검색하는 것이 좋습니다.
최신 Windows 터미널(newer Windows Terminal) 을 사용할 수도 있지만 PowerShell 은 (PowerShell)Windows 10 사용자 의 기본 옵션으로 남아 있습니다 . 아래 명령은 PowerShell 에만 해당되며 이전 명령줄(Command Line) 에서는 작동하지 않습니다 .
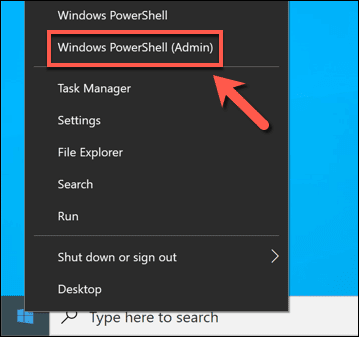
시작하려면 시작(Start) 메뉴 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 Windows PowerShell(관리자(Windows PowerShell (Admin) )을 선택하여 새 PowerShell 창을 엽니다 .
새 PowerShell 창에서 검색하려는 폴더 또는 드라이브로 이동합니다. 예를 들어, cd C:\ 를 입력하면 기본 시스템 드라이브의 루트(첫 번째) 폴더로 이동하여 전체 드라이브를 검색할 수 있습니다.
cd C:\Program Files 를 입력 하면 수행하는 검색이 Program Files 폴더에 포함된 모든 파일 및 하위 폴더에 대해서만 작동함을 의미합니다. 폴더를 이동했으면 ls -Force 를 입력 하여 그 안에 포함된 파일 및 폴더(숨김 파일 또는 폴더 포함) 목록을 봅니다.

폴더로 이동하여 검색을 시작했으면 PowerShell 창에 다음 명령을 입력하고 Enter 키(Enter key) 를 눌러 실행합니다. Get-ChildItem -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”} .
이렇게 하면 현재 폴더 위치에서 모든 숨겨진 파일과 하위 폴더를 검색하여 PowerShell 창에 나열합니다.

검색을 시작할 폴더 디렉터리를 나열하려면 Get-ChildItem 뒤에 (Get-ChildItem)-Path location 을 명령 에 추가하고 location 을 적절한 파일 경로로 바꿉니다 .
예를 들어 Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Folder -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”} C:\Folder 디렉터리 의 모든 숨겨진 파일과 하위 폴더를 검색합니다 . 파일 경로에 공백이나 기타 특수 문자가 포함된 경우 따옴표 안에 포함해야 합니다(예: Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\New Folder” 등).

PowerShell 이 많은 수의 숨겨진 파일과 폴더를 찾는 경우 PowerShell 터미널 출력은 항목을 빠르게 스크롤하여 분석하기 어렵게 만듭니다. 이를 더 쉽게 하기 위해 Get-ChildItem 명령의 출력을 텍스트 파일에 저장하여 여가 시간에 검색하고 검토할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 하려면 명령 끝에 > log.txt Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\New Folder” -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”} > log.txt ). 이렇게 하면 Get-ChildItem(Get-ChildItem) 명령 의 터미널 출력이 포함된 현재 활성 폴더에 log.txt 라는 파일이 생성됩니다 .
필요 에 따라 대체 파일 경로(예: > C:\Folder\log.txt ) 또는 파일 이름(예: hiddenlog.txt )을 설정할 수 있습니다 .

로그 파일을 만든 경우 cat log.txt ( log.txt 를 올바른 파일 경로 및 파일 이름으로 대체 )를 입력하여 PowerShell 창에서 직접 내용을 볼 수 있습니다. 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 와 메모장(Notepad) 을 사용하여 파일을 정상적으로 열 수도 있습니다 .

타사 앱을 사용하여 숨겨진 파일 및 폴더 찾기(Locating Hidden Files and Folders Using Third-Party Apps)
Windows에서 숨김 파일 및 폴더를 찾는 가장 좋은 방법은 위에서 설명한 대로 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 또는 Windows PowerShell 을 사용하는 것입니다. (Windows PowerShell)이러한 방법이 너무 느리거나 필요한 복잡한 검색 기준을 제공하지 않는 경우 대안으로 타사 앱을 사용하여 PC에서 숨겨진 파일을 검색할 수 있습니다.
이를 지원하는 다양한 도구가 있지만 한 가지 좋은 옵션은 프리웨어 FreeCommander 도구를 사용하는 것입니다. 이 파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 대체품에는 PC에서 숨겨진 파일과 폴더를 찾을 수 있는 강력한 검색 도구가 포함되어 있습니다.
시작하려면 PC에 FreeCommander(download and install FreeCommander) 를 다운로드하여 설치하고 설치가 완료되면 실행하십시오. FreeCommander 창 에서 검색을 시작하려면 키보드 에서 Ctrl + F파일(File ) > 검색(Search) 을 선택 하여 새 검색 창을 엽니다.

Search files/folders 창 에서 위치(Location) 탭 에 있는 파일 이름( File name) 상자 에 파일 또는 폴더 이름에 대한 검색 기준을 입력합니다 . 전체 파일 이름을 사용하거나 와일드카드를 사용하여 부분적으로 일치하는 항목을 찾을 수 있습니다(예: file 또는 fil* ).
그 아래의 검색(Search In) 위치 상자에서 검색을 시작할 폴더를 선택합니다. 이것을 수동으로 입력하거나(예 : 전체 시스템 드라이브를 검색하려면 C:\추가 버튼(add button ) > 찾아보기(Browse) 를 선택하여 개별적으로 식별할 수 있습니다.

옆 에 있는 Timestamp/Size/Attr 탭을 선택하고 체크 표시가 보이도록 Hidden 속성 확인란을 선택해야 합니다. 다른 모든 확인란은 검은색 체크 표시가 있는 상태로 두거나(포함되어 있는지 확인) 두 번 선택하여 선택을 취소하고 해당 속성이 포함된 파일을 검색에서 제거합니다.

(Select)사용 가능한 모든 검색 탭에서 필요한 다른 검색 기준을 선택하십시오 . 검색을 시작할 준비가 되면 찾기(Find) 를 선택하여 시작합니다.

검색 결과는 검색 창 하단의 검색 결과 탭에 나타납니다. (Search result )FreeCommander 가 찾은 숨겨진 파일이나 폴더를 열려면 항목을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 열기(Open) 를 선택하십시오 .

Windows 10에서 파일 관리(Managing Your Files on Windows 10)
Windows 10 에서 숨김 파일을 찾는 방법을 아는 것은 쉽습니다. 파일 탐색기(Explorer) , Windows PowerShell 또는 (Windows PowerShell)FileCommander 와 같은 타사 앱 을 사용하여 작업을 수행 하는지 여부 에 관계없이 위의 단계는 이전에 숨겨진 파일 및 폴더를 찾는 데 도움이 될 것입니다.(Whether)
다음 단계는 파일을 적절하게 관리하는 것입니다. 누락된 파일을 찾기 위한 고급 검색 팁(advanced search tips) 이 많이 있지만 장기적으로 더 쉽게 액세스할 수 있도록 중요한 파일을 백업하는(backing up your important files) 것을 고려해야 할 수도 있습니다 . Windows 에서 대용량 파일을 찾아(look for large files on Windows) 다른 파일 및 응용 프로그램을 위한 디스크 공간 을 확보 할 수도 있습니다 .
How to Find Hidden Files and Folders on Windows
When you open a folder in Windows File Exрlorer, you expect to see the full contentѕ — all the files, all the sub-folders. That isn’t necessarily true, however. If the folder you’re looking in contains hidden filеs оr folders, Windows won’t show them unless yоu’ve enabled hidden file view in File Explorer.
If you want to know how to find hidden folders on Windows 10 and any hidden files contained within, you’ll need to use some of the methods we’ve listed below. This includes using secret search tools in File Explorer and Windows PowerShell to locate them, as well as using third-party alternatives like FreeCommander.

How to Find Find Hidden Files and Folders on Windows 10 Using File Explorer
If you’re trying to hunt down a missing file or folder, the best way to do it is to use File Explorer’s search tool. Using advanced search parameters, you can locate any folders or files that have been hidden by view (either automatically or manually) using an open File Explorer window.
- To do this, open a new File Explorer window using your taskbar (if the File Explorer icon is pinned) or via the Start menu. You can also right-click the Start menu and select File Explorer to open a new window instead.

- In the new File Explorer window, open the folder (or drive) that you’re looking to search. Using the search bar in the top right, type attributes:H and select the enter key to begin the search. This searches for all files and folders within that folder that have the hidden file attribute applied to them in the Properties menu.

- If you want to customize the search further, you can add a file or folder name (or partial name) to the search. To do this, type the file or folder name before or after the attributes:H parameter in the search bar (eg. file attributes:H). If you want to search for partial match, you can use a wildcard (eg. fil* attributes:H) to do so.

- Once you’ve located a file or folder, you can trace it back to its saved location by right-clicking the file or folder and selecting Open file location from the pop-up menu.

Searching for Hidden Files and Folders Using Windows Powershell
While the File Explorer method above offers the easiest way to find hidden files and folders on Windows 10, it isn’t necessarily the quickest. If you want to quickly search through your PC for any files you’ve missed, a good alternative is to use the Windows PowerShell to do so.
You can also use the newer Windows Terminal, but PowerShell remains the default option for Windows 10 users. The commands below are PowerShell specific and won’t work with the older Command Line.
To start, open a new PowerShell window by right-clicking the Start menu and selecting Windows PowerShell (Admin).

In the new PowerShell window, move to the folder or drive you wish to search. For instance, typing cd C:\ will move you to the root (first) folder on the main system drive, allowing you to search the entire drive.
Typing cd C:\Program Files means that the search you perform will only work through any files and sub-folders contained in the Program Files folder. Once you’ve moved folders, type ls -Force to view a list of files and folders contained within (including any hidden files or folders).

Once you’ve moved into the folder to begin your search, type the following command into the PowerShell window and press the Enter key to run it: Get-ChildItem -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”}.
This will search for all hidden files and sub-folders in your current folder position and list them in the PowerShell window.

If you’d prefer to list a folder directory to begin the search, add -Path location to your command after Get-ChildItem, replacing location with a suitable file path.
For instance, Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Folder -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”} will search for all hidden files and subfolders in the C:\Folder directory. If the file path contains spaces or other special characters, you’ll need to contain them within quotation marks (eg. Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\New Folder” etc).

If PowerShell locates a large number of hidden files and folders, the PowerShell terminal output will scroll through the entries rapidly, making it difficult to analyze. To make this easier, you can save the output of the Get-ChildItem command to a text file, allowing you to search through and review at your leisure.
To do this, add > log.txt to the end of your command (eg. Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\New Folder” -Filter *.* -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | where { $_.Attributes -match “Hidden”} > log.txt). This will create a file named log.txt in your currently active folder containing the terminal output of the Get-ChildItem command.
You can set an alternative filepath (eg > C:\Folder\log.txt) or filename (eg hiddenlog.txt) as required.

If you’ve created a log file, you can view the contents in the PowerShell window directly by typing cat log.txt (replacing log.txt with the correct file path and file name). You can also open the file as normal using File Explorer and Notepad.

Locating Hidden Files and Folders Using Third-Party Apps
The best methods for finding hidden files and folders on Windows are to use File Explorer or Windows PowerShell as explained above. If these methods are too slow or don’t offer the complex search criteria that you need, you can use third-party apps to search your PC for hidden files as an alternative.
While various tools exist that support this, one good option is to use the freeware FreeCommander tool. This File Explorer replacement includes a powerful search tool that allows you to locate hidden files and folders on your PC.
To start, download and install FreeCommander on your PC and launch it once the installation is complete. To begin a search in the FreeCommander window, select Ctrl + F on your keyboard or select File > Search to open a new search window.

In the Search files/folders window, enter the search criteria for file or folder names in the File name box, located in the Location tab. You can use full file names or find partial matches using a wildcard (eg. file or fil*).
In the Search In box below it, select the folder to begin the search. You can type this manually (eg. C:\ to search the entire system drive) or select the add button > Browse to identify them individually.

Select the Timestamp/Size/Attr tab next and make sure to select the Hidden attribute checkbox so that a tick is visible. Leave all other checkboxes with a solid black check (ensuring that they’re included) or select them twice to uncheck them and remove any files containing those attributes from your search.

Select any other search criteria that you require in all the available search tabs. When you’re ready to begin your search, select Find to begin.

Search results will appear in the Search result tab at the bottom of the search window. To open any of the hidden files or folders that FreeCommander locates, right-click the entries and select Open.

Managing Your Files on Windows 10
Knowing how to find hidden files on Windows 10 is easy — once you know where to look. Whether you use File Explorer, Windows PowerShell, or third-party apps like FileCommander to get the job done, the steps above should help you locate your previously hidden files and folders.
The next step is to manage your files properly. There are plenty of advanced search tips to locate missing files, but you may also need to consider backing up your important files to make them easier to access in the long run. You can also look for large files on Windows to help free up disk space for other files and applications.
















