새로운 Windows 계산기(Windows Calculator) 는 그 어느 때보다 정확한 계산을 제공하며 새롭고 강력한 인터페이스도 갖추고 있습니다. 이제 기본 표준 계산을 프로그래밍, 과학 계산 및 통계와 통합합니다. 이 외에도 매우 유용한 다른 기능이 있습니다. 모기지 계산(mortgage calculation) , 다기능 변환기 및 주의를 기울여야 하는 몇 가지 옵션과 같은 기능이 있습니다. 이 기사에서는 그것들을 하나씩 제시하고 몇 가지 가능한 사용 시나리오도 공유할 것입니다.
Windows 7 및 Windows 8 에서 계산기(Calculator) 를 찾을 수 있는 위치
Windows 7 에서는 Start Menu - > Accessories -> Calculator 로 이동하여 액세스할 수 있습니다 .
계산기(Calculator) 는 시작 메뉴 (Start Menu)검색 상자(search box) ( Windows 7 의 경우) 또는 시작(Start) 화면( Windows 8 의 경우)에 계산기(calculator) 또는 calc 를 입력 하고 적절한 검색 결과(search result) 를 열어도 열 수 있습니다 .
실행 파일은 다음 위치에서 찾을 수 있습니다 "C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe".
계산 모드
Windows 8 의 버전은 다르지만 Windows 7 과 비교 하여 계산기(Calculator) 는 두 운영 체제에서 동일합니다. 인터페이스는 똑같이 생겼고 기능도 동일합니다.
계산기(Calculator) 에는 계산 을 수행할 수 있는 4가지 주요 모드가 있습니다.
- 표준 모드.
- 과학 모드.
- 프로그래밍 모드.
- 통계 모드.
아래 섹션에서 각각에 대해 설명하고 기능과 사용 방법을 설명합니다.
표준 모드
계산기(Calculator) 를 처음 열면 기본적으로 표준(Standard) 모드가 선택됩니다. 이 모드는 일반 포켓 계산기(pocket calculator) 와 더 비슷합니다 . 키보드 숫자(keyboard number) 값, 키패드( Num 키가 활성화된 상태) 또는 마우스를 사용 하여 계산할 수 있습니다.
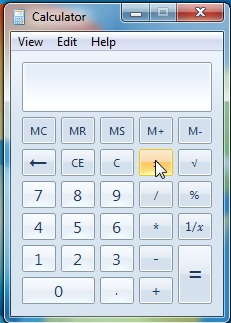
예:(Example:) 계산에 사용할 숫자와 해당 숫자에 대한 연산을 선택해야 합니다. 따라서 간단한 곱셈을 수행하려면 첫 번째 숫자, 연산( * 곱하기 기호 ) 및 두 번째 숫자를 클릭합니다. 계산 프로세스(calculation process) 가 끝나면 해당 결과(result or click) 에 새 연산을 계속 추가 하거나 등호를 클릭하여 최종 결과(end result) 를 얻을 수 있습니다 .
프로그래머 모드
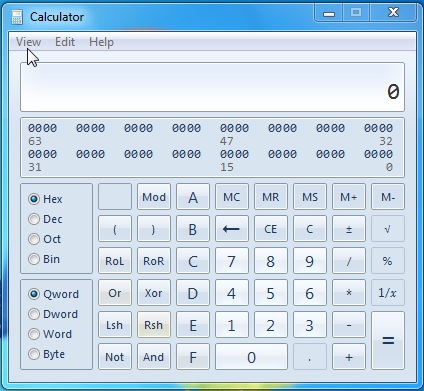
이 모드는 기수(bases) (2진수, 8진수, 16진수, 10진수)로 연산을 수행할 수 있는 가능성을 제공합니다. 한 기준에서 다른 기준으로 값을 변환할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 2 진법 (base two) 숫자 체계(number system) (2진법 - 0, 1)에서 10진법 숫자 체계(base ten number system) (10진법 0-9)로 변환할 수 있습니다. 또한 이 모드는 논리 비트 연산( XOR , OR, AND 등(AND etc) )을 지원합니다.
이 모드에 액세스하려면 보기(View) 메뉴를 클릭하고 프로그래머(Programmer) 옵션을 선택하십시오.

이전 버전과 마찬가지로 사용하는 키는 기본과 관련이 있습니다. 예를 들어 A - F 버튼은 16진수 값으로 작업하도록 선택한 경우에만 액세스할 수 있습니다. 다른 버튼은 프로그래머에게 이미 공통적이거나 공통적이어야 합니다. 팔레트 XOR 테이블(XOR table) 을 통한 범위 , % - 모듈러스, 10진수에서 16진수 또는 2진수 결과로 이동 및 변경. 또한 얻은 값은 정수로 표시됩니다(16/3은 5와 같음을 의미하는 자연수).
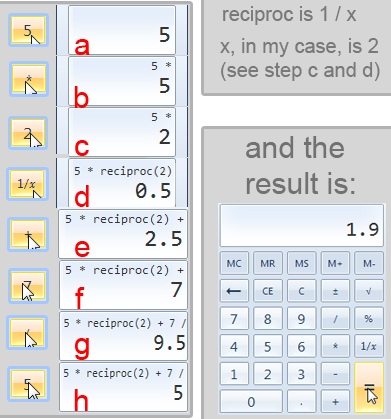
예:(Example:) 1011과 같은 2진 값을 10진수 값으로 변환해야 하는 경우 숫자를 입력하고 10진수 라디오 상자(radio box) 를 클릭하기만 하면 됩니다. 수동으로 이 프로세스는 다소 시간이 걸리고 개념을 완전히 이해하지 못하면 오류 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.

과학 모드
이 모드는 수학 또는 기타 과학적 계산을 추구하는 모든 사람에게 약간의 미소를 제공합니다. 기본 X(X to the power of) 에서 더 유용한 cos , sin 또는 pi 함수의 거듭제곱에 이르기까지 다양한 제품이 제공됩니다.
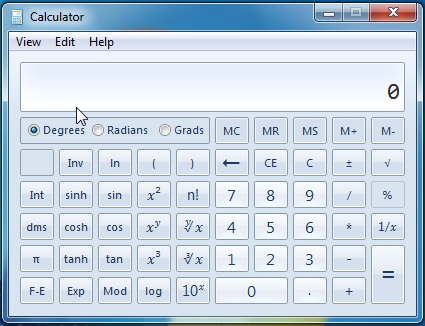
예:(Example:) 이전에 표준 모드에서 했던 것처럼 작업을 수행하려면 숫자를 클릭한 다음 작업을 클릭한 다음 두 번째 숫자를 입력합니다.
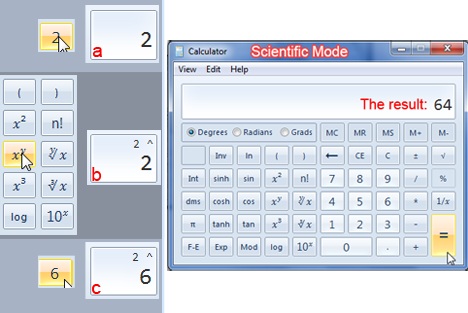
통계 모드
이 모드는 통계와 관련된 옵션을 제공합니다. 다른 모드와 같이 기능이 많지는 않지만 환영할 만한 기능입니다. 숫자의 합, 숫자의 합과 같은 함수를 사용하여 통계를 계산할 수 있습니다.
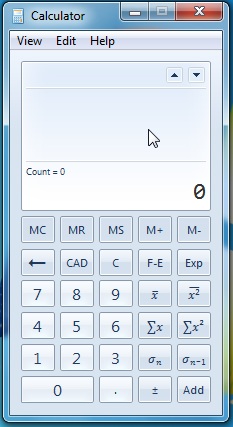
통계 모드의 유일한 경우 C(C) 를 누르면 표시된 현재 값이 삭제됩니다. CAD 는 데이터세트에서 모든 값을 지웁니다. 데이터 세트는 추가된 숫자의 목록입니다. 데이터 세트는 다양한 작업을 수행할 목록입니다.
예:(Example:) 통계 모드에서 작업을 수행하려면 값을 배치해야 합니다. 입력한 후의 각 값은 ADD(ADD) 버튼 을 클릭하여 데이터세트에 배치됩니다 . 데이터 세트 목록(dataset list) 에 필요한 모든 값을 배치한 후 원하는 작업을 클릭할 수 있습니다.

계산 모드(Calculation Modes) 에서 기록(History) 사용
이 옵션은 메모리에 보관된 유용한 값 이상입니다. File -> History 으로 이동하여 사용할 수 있으며 통계 모드를 제외한 모든 모드에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 이름이 모든 것을 말하지만, 그것은 들리는 것보다 더 강력합니다. 복잡한 공식을 가지고 노는 것이 간단해집니다. 계산을 수행하고 완료되면 같음을 클릭하여 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 결과가 기록(History) 목록에 입력됩니다. 다른 계산을 수행하고 해당 결과의 이전 결과 또는 값(result or values) 이 필요한 경우 목록을 찾아 해당 값을 확인하기만 하면 됩니다. 이것은 이전 계산을 빠르게 다시 편집할 수 있다는 사실과 함께 계산기가 온라인 계산기 제공을 (calculator offering)능가 합니다.(calculator surpass)상품으로 사용할 수 있는 것. 이 옵션에 액세스하려면 유효한 모드인지 확인하십시오(통계 모드 제외).

계산기의 기타 옵션
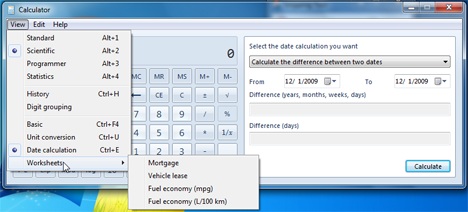
계산기(Calculator) 계산기에는 이제 계산 모드의 범위를 벗어나는 다른 도구가 포함됩니다. 그들은 일상 필수품과 더 관련이 있습니다. 경량 변환 또는 지정된 날짜에서 다른 날짜까지의 거리 계산과 같은 것. 계산기에서 일반적으로 필요한 것보다 조금 더 나아가 모기지 가치, 차량 리스 및 자동차 소비(vehicle lease and car consumption) 를 계산하는 데 도움이 됩니다 .
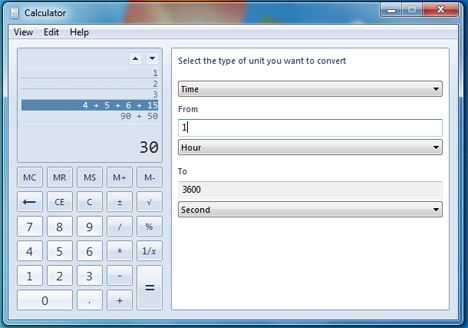
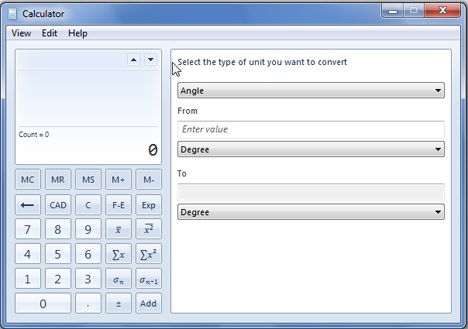
변환 유형(예: 시간), 시작 (From) 단위 측정(unit measurement) ( 예: 시간(Hour) ) 및 종료 측정 단위(예: 초) 를(To) 선택해야 합니다.
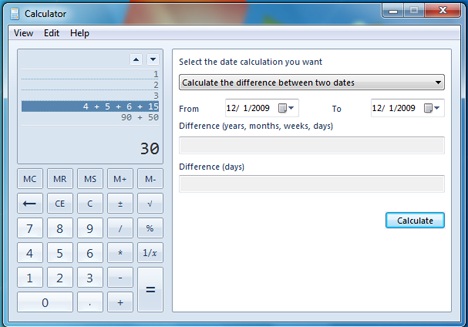
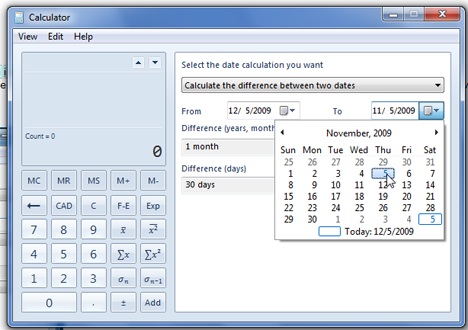
날짜(시작 및 종료)를 선택하여 둘 사이의 차이를 확인합니다. 날짜에서 빼거나 더하기 위해 일, 월 등을 수동으로 입력하고 최종 결과를 볼 수도 있습니다. 이것은 '두 날짜 간의 차이 계산'('Calculate the difference between two dates') 을 클릭 하고 주어진 두 번째 옵션을 선택하여 수행됩니다.
Worksheets - These are options offered for real life calculations. Whether you want to calculate mortgage, vehicle lease or car consummation (American or European measurement), the calculator offers it all in the worksheets place.
팁과 요령
나는 종종 일반 계산기의 일부 유틸리티가 얼마나 사용되지 않는지 놀라곤 합니다. 제가 언급하는 주제는 계산기에 포함된 메모리 및 기타 유용한 기능입니다.
MC (Memory Clear or Clean) - clears the memory of any stored number leaving only the null or zero number in memory.
MR (Memory Reminder or Recalled) - tells the calculator to show the number present in memory.
MS (Memory Store or Set) - this takes the number present in the results and stores it in the memory. Previous calculation stored in memory will be deleted.
M+ (Add to memory) - formula> value stored in memory + current value = new value stored.
M- (Subtract from memory) - formula> value stored in memory - current value = new value stored.
C - Clear all calculations that are currently made.

The Back Arrow or Backspace - present on Windows Calculator but not present on a pocket calculator. This option deletes the last typed number from the current value. This option can be used by clicking on the Back Arrow or by pressing the Backspace key.
Using numerical values from the keyboard makes the calculation faster. You can also use the * key to quickly multiple, the minus key "-", the plus key "+", the divisible by "/" or the equal key "=".
Although this has nothing to do with notations, you can click on the Edit-> Copy to copy the value to clipboard.
Going to the help page for calculator reveals useful keyboard shortcuts for use with functions or options.
결론
모양과 옵션의 변화로 인해 계산기(Calculator) 는 빠르고 가벼운 기능을 염두에 두고 만들어진 것처럼 느껴집니다. 모든 기능이 함께 잘 작동하며 옵션 간 전환이 매우 쉽게 수행됩니다. 결국, 문제가 있거나 질문이 있거나 이 도구에 대한 몇 가지 훌륭한 팁과 트릭을 알고 있다면 주저하지 말고 댓글로 공유해 주세요.
The Calculator in Windows 7 & Windows 8 - A Tool for the Geek in You!
The new Windows Calculator offers more precise calculations than ever and it also has a new and powerful interface. It now integrates the basic standard calculations with programming, scientific calculations and statistics. Beyond this, there are also other features which are very useful: things like mortgage calculation, a multifunctional converter and a few more options which deserve their share of attention. In this article I will present them one by one and also share some possible usage scenarios.
Where to Find the Calculator in Windows 7 & Windows 8
In Windows 7 you can access it by going to Start Menu - > Accessories -> Calculator.

The Calculator can be opened also by typing calculator or calc in the Start Menu search box (in Windows 7) or in the Start screen (in Windows 8) and opening the appropriate search result.
Its executable can be found in this location: "C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe".
Calculation Modes
Even though it has a different version in Windows 8, compared to Windows 7, the Calculator is the same in both operating systems. The interface looks just the same and its features are identical.
The Calculator has 4 main modes with which you can do calculations:
- The Standard Mode.
- The Scientific Mode.
- The Programming Mode.
- The Statistics Mode.
In the sections below I will describe each of them and explain what they do and how to use them.
The Standard Mode
When you first open the Calculator, the Standard mode will be selected by default. This mode is the better equivalent of the normal pocket calculator. You can use the keyboard number values, the keypad (with the Num key activated) or the mouse to make calculations.

Example: You need to choose the numbers with which you want to do calculations and the operation on those numbers. So, if you were to do a simple multiplication you would click on the first number, the operation ( * multiply sign ) and the second number. At the end of the calculation process you can either continue to add a new operation to that result or click on the equal sign to get the end result.

The Programmer Mode
This mode offers the possibility to do operations with bases (binary, octal, hexadecimal, decimal). You can convert values from one base to another. For example, you can convert from a base two number system (binary - 0, 1) to a base ten number system (decimal 0-9). Also, this mode offers to help with logical bit operations (XOR, OR, AND etc).
To access this mode click on the View menu and select the Programmer option.

Like previous versions, the keys you use are related to the base. For example, the A - F buttons are only accessible if you check to work in hexadecimal values. The other buttons are or should be already common for a programmer. Ranging through the palette XOR table, % - modulus, shifting and changing from decimal to hexadecimal or binary results. Also, the values you get are shown as integers (natural numbers, meaning 16/3 will equal to 5).

Example: If you have to transform a binary value like 1011 to its decimal value you would type the number and simply click on the decimal radio box. Manually, this process would be rather lengthy and probably bring error problems if you don't fully grasp the concept.

The Scientific Mode
This mode offers a bit of a smile to any person who pursues mathematical or other scientific calculations. The offering ranges from your basic X to the power of to the more useful cos, sin or pi functions.

Example: Like you did before in the standard mode, to do an operation, click on a number, followed by an operation then put the second number.

The Statistics Mode
This mode presents options related to the statistics. Although it doesn't have many functions like other modes, they are more than welcomed. You can use functions like sum of numbers, sum of numbers to the power to make statistics calculus.

Pressing the C, in the sole case of statistics mode, deletes the current value expressed. The CAD clears all the values from the dataset. The dataset is the list of added numbers. The dataset is the list with which you will perform different operations.
Example:To do an operation in the statistics mode, you have to place the values. Each value after has been typed will be placed in the dataset by clicking the ADD button. After you have placed all the needed values in the dataset list, you can click on the wanted operation.

Using History with Calculation Modes
This option goes beyond the useful values kept in memory. It can be used by going to File -> History and it is available for all the modes except the statistics one. The name says it all, however it is more powerful than it sounds. Playing around with complex formulas is made simple. You can do a calculation and, when done, click on the equal to have the result. This will make the result to enter into the History list. If you do another calculation and need the previous result or values from that result you just look up into the list and see those values. This coupled with the fact that you can quickly reedit former calculations makes the calculator surpass any online calculator offering that one might use for commodity. To access this option, make sure you are in a valid mode (all except statistics mode).

Other Options in the Calculator
The Calculator calculator now includes other tools that are beyond the scope of the calculation modes. They are more related to everyday necessities. Things like light weight conversion or calculating the distance from one specified day to another one. Going a little further than what you would normally need from a calculator, it also offers to help you with calculating mortgage values, vehicle lease and car consumption.




You have to select the type of transformation (example: Time), the From unit measurement (like Hour), and the To measurement unit (like Second).

Select the dates (from and to) to see the difference between them. You can also manually type a number of days, months (etc.) to subtract (or add) from a date and to see the final result. This is done by clicking on the 'Calculate the difference between two dates' and selecting the second given option.
Worksheets - These are options offered for real life calculations. Whether you want to calculate mortgage, vehicle lease or car consummation (American or European measurement), the calculator offers it all in the worksheets place.
Tips and tricks
I am often surprised of how unused some utilities are from a regular calculator. The subject I am referring to is the memory and other useful functions included in a calculator.
MC (Memory Clear or Clean) - clears the memory of any stored number leaving only the null or zero number in memory.
MR (Memory Reminder or Recalled) - tells the calculator to show the number present in memory.
MS (Memory Store or Set) - this takes the number present in the results and stores it in the memory. Previous calculation stored in memory will be deleted.
M+ (Add to memory) - formula> value stored in memory + current value = new value stored.
M- (Subtract from memory) - formula> value stored in memory - current value = new value stored.
C - Clear all calculations that are currently made.

The Back Arrow or Backspace - present on Windows Calculator but not present on a pocket calculator. This option deletes the last typed number from the current value. This option can be used by clicking on the Back Arrow or by pressing the Backspace key.
Using numerical values from the keyboard makes the calculation faster. You can also use the * key to quickly multiple, the minus key "-", the plus key "+", the divisible by "/" or the equal key "=".
Although this has nothing to do with notations, you can click on the Edit-> Copy to copy the value to clipboard.
Going to the help page for calculator reveals useful keyboard shortcuts for use with functions or options.
Conclusion
The changes in the way it looks and the options it has, make the Calculator feel like it has been built with quick lightweight functionality in mind. All features work well together and the transitions between options are done very easily. In the end, if you have problems, questions or you just know some great tips and tricks about this tool, don't hesitate to share them with us in a comment.

















