Windows 10 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 는 시스템 리소스 모니터링과 관련하여 많은 기능을 제공합니다. 프로세스(Processes) 탭은 그 어느 때보다 많은 정보를 공유하므로 필요에 따라 표시되는 데이터를 사용자 정의할 수 있습니다. 다음은 Windows 10 에서 (Windows 10)작업 관리자의 (Task Manager's) 프로세스(Processes) 탭 을 조정하고 사용자 와 관련된 데이터 가 (data relevant)기본 보기(default view) 보다 필요에 더 잘 맞는 방식으로 표시 되도록 하여 보다 효율적으로 만드는 방법입니다 .
프로세스 탭(Processes tab) 이란 무엇이며 액세스하는 방법은 무엇입니까?
프로세스(Processes) 탭에는 주어진 시간에 실행되는 모든 앱, 백그라운드 프로세스 및 Windows 프로세스가 나열되어 각각에 대한 유용한 데이터를 제공 합니다 . (Windows)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 정식 버전에서 사용할 수 있습니다 . 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 여는 데 사용할 수 있는 몇 가지 옵션이 있지만 가장 편안한 것은 바로 가기 (keyboard shortcut) "Ctrl + Shift + Esc" 입니다. Windows 8 을 건너뛰고 도구에 처음 액세스하는 경우 다음 위치에서 열립니다. Windows 10 장치에서 현재 실행 중인 모든 앱 목록을 표시하는 압축 보기라고 합니다. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 정식 버전을 열려면 을 클릭하거나 누릅니다.자세한 내용(More details) 은 컴팩트 보기 하단에 있습니다.

작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 정식 버전이 열리고 프로세스(Processes) 탭이 기본 탭입니다.

팁: (TIP:)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 는 원하는 탭에서 열리도록 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 Windows 10 작업 관리자의 기본 보기/탭을 설정하는 방법 을 (Windows 10)참조 (Task Manager)default view/tab .
1. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 프로세스 탭(Processes tab) 에서 데이터 열을 추가하거나 제거하는 방법
프로세스(Processes) 탭 에서는 현재 컴퓨터에서 실행 중인 모든 앱, 백그라운드 프로세스(background process) 및 Windows 프로세스 에 대한 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다. (Windows process)이 데이터는 구조화되어 열에 표시됩니다. 열의 머리글을 클릭(Click) 하거나 탭하고 끌어서 원하는 순서로 열을 재정렬합니다. 열을 추가 및 제거하여 프로세스(Processes) 탭에 표시된 정보를 선택하고 선택할 수 있습니다 . 기존 열의 헤더(header and select) 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 14개의 선택적 열 중 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)프로세스(Processes) 탭에 표시할 열을 선택 합니다. 이름 이(Name)열은 숨길 수 없는 유일한 열입니다.

선택한 열이 관련 데이터를 제공할 수 있도록 제공해야 하는 항목에 대한 요약은 다음과 같습니다.
-
유형(Type) - 프로세스가 앱인지, 백그라운드 프로세스인지, Windows 프로세스인지 표시합니다. "유형별 그룹화"("Group by type") 를 선택 하면 이 열이 중복됩니다.
-
상태(Status) - 프로세스가 일시 중단되었는지 여부를 표시합니다. 무언가가 일시 중단되면 백그라운드에서 실행되지만 CPU 주기에 액세스할 수 없고 메모리를 거의 사용하지 않습니다.
- 게시자 - 프로세스 게시자의 이름을 표시합니다.
-
PID - 실행 중인 각 프로세스에 대해 고유한 프로세스 식별자를 표시합니다. 이 숫자는 실행 중인 프로세스를 PID를 나열하는 오류 또는 이벤트와 일치시키는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
-
프로세스 이름(Process name) - 프로세스의 실행 파일 이름을 표시합니다. 예: 7-Zip 파일 관리자(7-Zip File Manager) 용 7zFM.exe .
-
명령줄(Command line) - 각 프로세스에 대해 실행되는 명령줄 구문을 표시합니다. 이를 통해 특별한 명령줄 매개변수를 사용하여 앱이나 프로세스가 실행되었는지 확인할 수 있으며 각 프로세스의 실행 파일 위치도 알 수 있습니다.
-
CPU - 각 프로세스의 프로세서 사용량을 표시합니다.
-
메모리 -(Memory -) 각 프로세스의 RAM 사용량을 표시합니다.
-
디스크(Disk) - 각 프로세스의 하드 디스크 사용량을 표시합니다.
-
네트워크(Network) - 각 프로세스의 네트워크 사용량을 표시합니다.
-
GPU - 각 프로세스의 비디오 카드 사용량을 표시합니다.
-
GPU 엔진(GPU engine) - 각 프로세스에서 사용되는 GPU 엔진을 공유합니다. Microsoft에 따르면 GPU 엔진은 그래픽 카드의 독립적인 실리콘 단위를 나타내며 다른 것과 병렬로 예약 및 작동할 수 있습니다. 이 개념에 대한 자세한 내용은 여기 에서(here) 확인할 수 있습니다 .
-
전력 사용량(Power usage) - 각 프로세스에서 사용하는 전력을 표시합니다.
-
전력사용량 추이(Power usage trend) - 프로세스별 전력사용량의 전반적인 추이를 보여줍니다.
2. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 프로세스 탭(Processes tab) 에서 실행 중인 앱 및 프로세스(apps and processes) 를 정렬하는 방법
기본적으로 작업 관리자의 프로세스 목록은 (Task Manager's Processes)프로세스 유형(process type) 에 따라 논리적으로 정렬됩니다 . 즉, 모든 앱, 백그라운드 프로세스 및 Windows 10 프로세스는 이름(Name) 이라는 탭의 첫 번째 열에서 함께 그룹화되고 해당 그룹 내에서 정렬됩니다 . 우리는 이 시스템의 열렬한 팬이지만 목록을 알파벳순으로 정렬하고 싶을 수도 있습니다. 모든 활성 앱과 프로세스를 알파벳 목록으로 표시 하려면 보기 를 (View)클릭(Click) 하거나 탭 하고 "유형별 그룹화"("Group by type") 를 선택 취소 합니다.

열 헤더를 클릭하거나 탭하면 해당 열에 표시된 값을 기반으로 실행 중인 앱과 프로세스 를 정렬할 수 있습니다. (running apps and processes)예를 들어, 메모리(Memory) 를 클릭하면 프로세스가 사용 중인 RAM 의 양에 따라 목록이 정렬 됩니다. 이것은 어떤 프로세스가 컴퓨터에서 가장 많은 리소스를 사용하거나 가장 적게 사용하는지 궁금할 때 유용할 수 있습니다. 사용 중인 정렬 방법에 관계없이(Regardless) 언제든지 기본 정렬로 돌아가려면 보기 메뉴에서 (View)"유형별 그룹화"("Group by type") 옵션을 선택하십시오.
3. 프로세스 탭(Processes tab) 에서 데이터 값이 표시되는 방식을 변경하는 방법
표시되는 정보를 사용자 정의할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 프로세스(Processes) 탭에서 해당 데이터의 일부가 표시되는 방식을 결정할 수도 있습니다. 메모리(Memory) , 디스크(Disk) 및 네트워크(Network) 열의 경우 값(MB 메모리, MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage )을 사용하여 데이터를 표시할지 또는 사용 가능한 총 리소스의 백분율로 표시할지 선택할 수 있습니다. 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)프로세스(Processes) 탭 에서 열 헤더 또는 프로세스(header or process) 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 리소스 값(Resource values) 으로 이동 합니다 . 리소스 중 하나를 선택한 다음 백분율(Percents) 또는 값 을 선택합니다.(Values)귀하의 필요와 선호도에 따라 데이터가 표시되도록 합니다.

4. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에서 실행 중인 프로세스를 확장 및 축소하는 방법
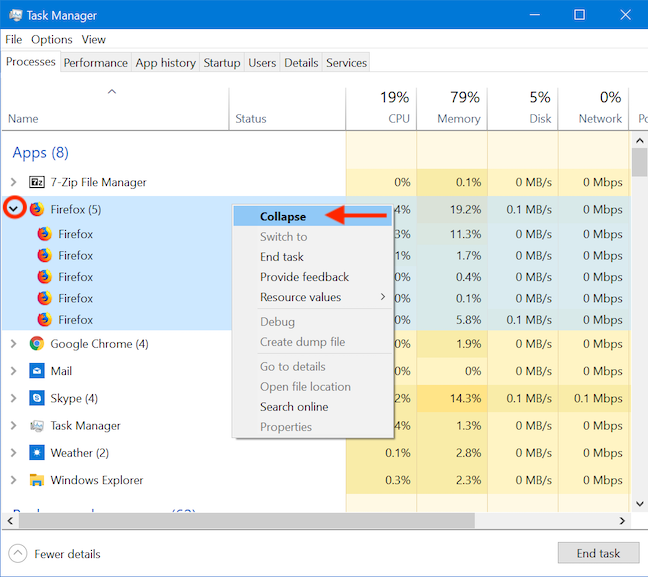
일부 프로세스는 주요 프로세스 이상을 포함하여 다른 프로세스보다 더 복잡합니다. 작업 관리자의(Task Manager's) 프로세스 탭(Processes) 을 사용하면 나열된 프로세스를 확장하고 해당 프로세스에서 실행 중인 하위 프로세스에 대한 자세한 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다. 하위 프로세스의 수는 각 프로세스 다음에 괄호 안에 숫자로 표시됩니다. 단일 프로세스를 확장하려면 해당 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 확장 을 (Expand)클릭하거나 탭(click or tap) 합니다. 이를 수행하는 더 쉬운 방법은 프로세스 왼쪽에 있는 화살표를 클릭하거나 탭하는 것입니다.

화살표를 다시 클릭하거나 해당 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 하위 프로세스를 다시 숨기려면 축소 로 이동할 수 있습니다.(Collapse)
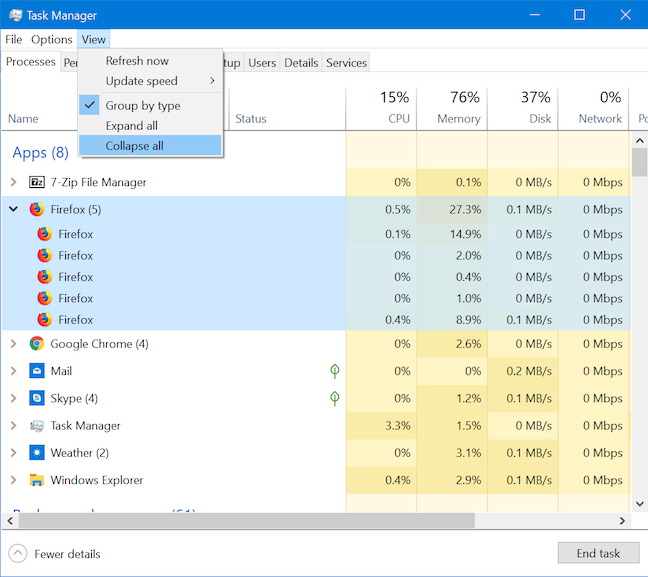
보기(View) 를 클릭하거나 탭한 다음 모두 확장(Expand all) 을 눌러 축소된 항목을 확장할 수도 있습니다 .

확장된 모든 항목을 즉시 축소하려면 보기(View) 메뉴 에서 모두 축소 를 (Collapse all)클릭하거나 탭 합니다.(click or tap)
팁:(TIP:) 다중 프로세스 응용 프로그램의 경우 기본(상위) 프로세스 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르면 상황에 맞는 메뉴가 회색으로 표시된 옵션을 표시합니다. (right-clicking or pressing-and-holding)상호 작용하려면 각 하위 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누릅니다.

5. 작업 관리자 를 사용하여 실행 중인 프로세스를 종료하는 방법(Task Manager)
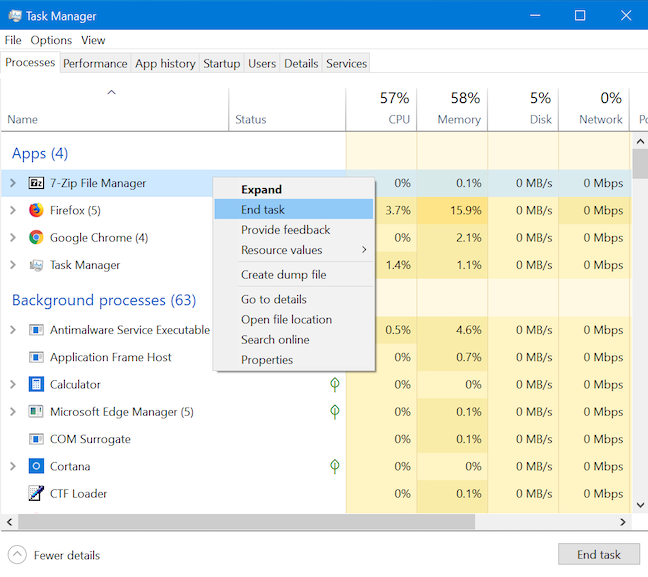
작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 주요 용도 는 더 이상 응답하지 않는 실행 중인 프로세스를 닫는 것입니다. 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르면 상황에 맞는 메뉴가 열립니다. 작업 끝내기 를 (End task)클릭(Click) 하거나 탭 하여 프로세스를 닫습니다.
앱(app and click) 을 선택 하고 프로세스(Processes) 탭 의 오른쪽 하단 모서리에 있는 작업 끝내기(End task) 버튼을 클릭 하거나 탭 하여 프로세스 를 닫을 수도 있습니다.
6. 실행 중인 프로세스에 대한 피드백을 Microsoft 에 제공하는 방법(Microsoft)
피드백 허브(Feedback Hub) 는 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에서 쉽게 액세스할 수 있으므로 실행 중인 프로세스에 대한 피드백을 제공할 수 있습니다. 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 피드백 제공(Provide feedback) 을 선택합니다 .

피드백 허브(Feedback Hub) 가 열리면 Microsoft 계정으로 로그인 하고(Microsoft account) 이를 사용하여 문제, 비판 또는 제안을 Microsoft 에 보낼 수 있습니다 .

7. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 사용하여 실행 중인 프로세스에 대한 덤프 파일 을 만드는 방법(dump file)
덤프 파일 은 (dump file)DMP 형식(DMP format) 을 사용 하는 큰 파일이며 덤프 파일(dump file) 이 생성된 정확한 시간에 특정 프로세스 또는 응용 프로그램 이 수행하는 작업에 대한 세부 정보를 제공합니다. (process or application)이는 일반적으로 해당 프로세스의 버그나 문제를 해결하려는 소프트웨어 개발자에게 유용합니다. 덤프 파일(dump file) 을 만들려면 프로세스를(process and click) 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "덤프 파일 만들기"("Create dump file.") 를 클릭 하거나 탭 합니다.

8. 작업 관리자 에서 실행 중인 프로세스에 대한 세부 정보를 보는 방법(Task Manager)
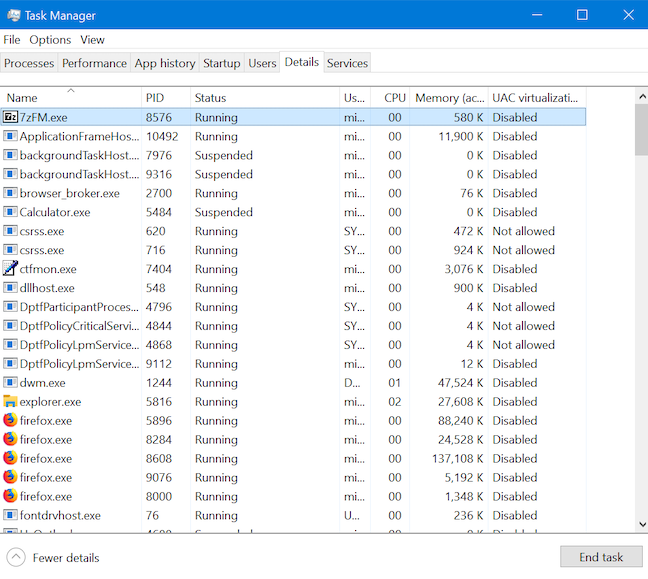
작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보(Details) 탭은 당연히 실행 중인 프로세스에 대한 정확한 세부 정보를 제공합니다. 그러나 이 탭의 정렬 옵션은 제한적이므로 특히 컴퓨터에서 실행 중인 프로세스가 많은 경우 특정 프로세스에 대해 더 많이 찾는 것이 보물 찾기 로 바뀔 수 있습니다. (treasure hunt)운 좋게도 프로세스 탭은 (Processes)세부 정보(Details) 탭 에서 해당 프로세스를 강조 표시하는 옵션을 제공하여 이를 보완합니다 . 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 "세부 정보로 이동"을 클릭하거나 탭 (")합니다("Go to details) .

포커스가 해당 실행 파일이 강조 표시된 세부 정보 탭으로 이동합니다.(Details)
9. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에서 실행 중인 프로세스의 위치를 찾는 방법
앱 또는 프로세스에 해당하는 실행 파일의 하드 드라이브에서 정확한 위치를 찾는 것도 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 사용하면 더 쉬워집니다 . 프로세스(Processes) 탭 에서 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 (Right-click or press-and-hold)"파일 위치 열기" 를 클릭하거나 탭합니다.("Open file location.")

파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 는 응용 프로그램의 실행 파일이 저장된 폴더에서 열립니다. 폴더가 열리면 해당 파일이 선택됩니다.

10. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 사용하여 알려지지 않은 프로세스 또는 앱 을 조사하는 방법(process or app)
작업 관리자의 프로세스 (Task Manager's Processes) 탭(tab show) 에는 현재 열려 있는 앱이 표시될 뿐만 아니라 고급 사용자가 주로 사용하는 백그라운드 프로세스도 표시됩니다. 알 수 없는 앱이나 프로세스 를 조사하려면 (app or process)프로세스(Processes) 탭 에서 해당 앱이나 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 온라인 검색(Search online) 을 클릭하거나 탭합니다 .
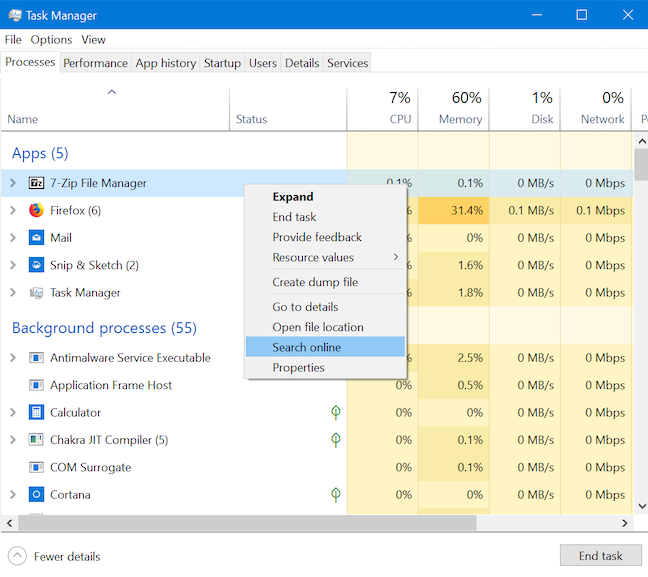
새 탭에서 기본 웹 브라우저는 기본 검색 엔진(default search engine) 에 관계없이 Bing 에서 프로세스 또는 앱의 실행 파일 이름으로 웹 검색을 실행하여 추가 정보를 얻는 데 도움이 됩니다.

11. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에서 실행 중인 앱의 속성을 보는 방법
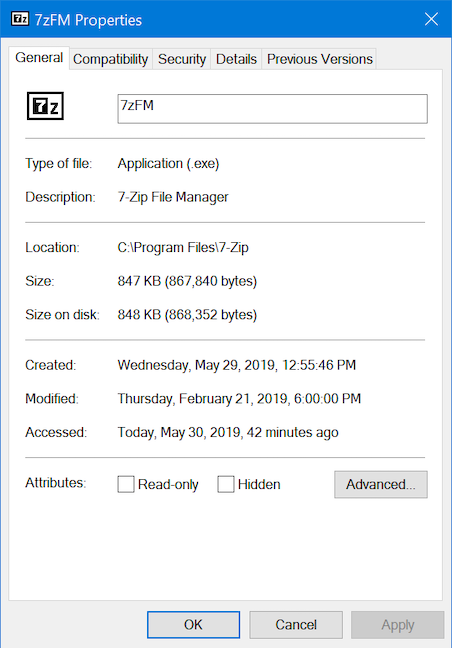
프로세스 또는 응용 프로그램의 속성은 이를 실행하는 실행 파일에 대한 많은 정보를 제공합니다. 파일의 크기, 위치, 액세스 날짜 및 보안 설정이 표시되며 호환성 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다. 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)프로세스(Processes) 목록 에서 앱 또는 프로세스(app or process) 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 속성(Properties) 을 선택합니다 .
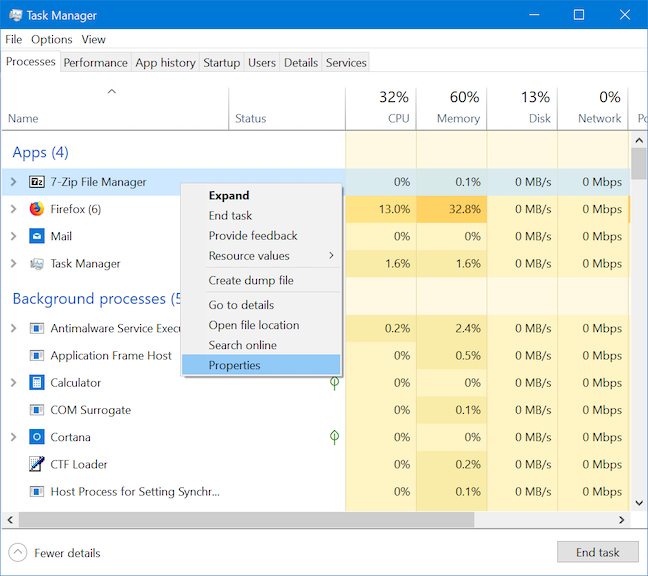
속성(Properties) 창이 열리고 앱에 대한 유용한 정보에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 프로세스 탭(Processes tab) 이 얼마나 혼잡 합니까?
이 탭을 사용자화할 수 있는 다양한 방법을 살펴보았으므로 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에서 무엇을 보려고 선택했는지 알려주십시오 . 대다수의 사용자처럼 기본을 유지하시겠습니까, 아니면 더 자세한 보기를 선호하십니까? 아래에 댓글(Comment) 을 달고 토론해 봅시다.
11 ways to manage running processes with the Task Manager in Windows 10
The Windows 10 Task Manager gives you a lot of power when it comes to monitoring system resources. The Processes tab shares more information than ever before, allowing you to customize the data it shows according to your needs. Here is how to tweak the Task Manager's Processes tab in Windows 10 and become more efficient, by ensuring the data relevant to you is displayed in a way that suits your needs better than the default view:
What is the Processes tab and how to access it?
The Processes tab lists all the apps, background processes, and Windows processes running at any given time, providing useful data about each of them. It is available in the full version of the Task Manager. There are several options available to open the Task Manager, but we think the most comfortable is the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." If you skipped Windows 8, and if this is your first time accessing the tool, it opens in what we call the compact view, showing you a list of all the apps currently running on your Windows 10 device. To open the full version of the Task Manager, click or tap More details at the bottom of the compact view.

The full version of the Task Manager opens, and the Processes tab is the default tab.

TIP: The Task Manager can be customized to open in any tab you want. To find out more, read How to set the default view/tab for the Windows 10 Task Manager.
1. How to add or remove data columns in Task Manager's Processes tab
In the Processes tab, you get information on every app, background process, and Windows process currently running on your computer. This data is structured and displayed in columns. Click or tap on a column's header, and drag it to reorder the columns in the order you prefer. You can pick and choose the information shown in the Processes tab by adding and removing columns. Right-click or press-and-hold on an existing column's header and select which of the fourteen optional columns are displayed in the Processes tab of the Task Manager. Keep in mind that the Name column is the only column that you cannot hide.

To ensure that the columns you select provide you with relevant data, here is a run-down of what they have to offer:
-
Type - Displays whether the process is an app, a background process, or a Windows process. If "Group by type" is selected, this column becomes redundant
-
Status - Displays whether or not a process is suspended. When something is suspended, it is running in the background, but it has no access to CPU cycles and uses little memory.
- Publisher - Displays the name of the process's publisher.
-
PID - Displays a unique Process Identifier for each running process. These numbers can be used to match a running process with an error or event that lists the PID.
-
Process name - Displays the name of the process's executable. E.g., 7zFM.exe for 7-Zip File Manager.
-
Command line - Displays the command-line syntax run for each process. This lets you see if any apps or processes have been launched with special command-line parameters and also gives you the location of each process's executable file.
-
CPU - Shows each process's processor usage.
-
Memory - Shows each process's RAM usage.
-
Disk - Shows each process's hard disk usage.
-
Network - Shows each process's network usage.
-
GPU - Shows each process's usage of the video card.
-
GPU engine - Shares which GPU engine is utilized by each process. According to Microsoft: a GPU engine represents an independent unit of silicon on the graphics card, that can be scheduled and can operate in parallel with another. You can find our more about this concept, here.
-
Power usage - Displays the power used by each process.
-
Power usage trend - Shows the overall trend in power usage for each process.
2. How to sort running apps and processes in Task Manager's Processes tab
By default, the Task Manager's Processes list is sorted logically by process type. This means that all apps, background processes, and Windows 10 processes are grouped together and sorted within their group in this first column of the tab, called Name. While we are big fans of this system, you may wish to sort the list alphabetically instead. Click or tap View and deselect "Group by type" if you want all the active apps and processes to be displayed in an alphabetical list.

Clicking or tapping on a column's header allows you to sort the running apps and processes based on the values displayed in that column. E.g., clicking on Memory sorts the list by how much RAM the processes are using. This can come in handy if you are wondering what processes consume the most or the least resources on your computer. Regardless of the sorting method you are using, select the "Group by type" option in the View menu if you wish to return to the default sorting at any point.
3. How to change the way data values are displayed in the Processes tab
On top of allowing you to customize which information is shown, the Processes tab also lets you decide how some of that data is displayed. For the Memory, Disk and Network columns you can choose whether to display the data using values - MB of memory, MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage - or as a percentage of the total available resource. Right-click or press-and-hold on any column's header or process in the Processes tab of theTask Manager, and go to Resource values. Choose one of the resources and then select either Percents or Values to have the data displayed according to your needs and preferences.

4. How to expand and collapse running processes in the Task Manager
Some processes are more complex than others, involving more than just the main process. The Task Manager's Processes tab allows you to expand listed processes and get more details about the subprocesses running under them. The number of subprocesses is indicated by a number in brackets following each process. To expand a single process, right-click or press-and-hold on it, and click or tap Expand. An easier way to do this is by clicking or tapping the arrow to the left of the process.

You can click the arrow again, or you can right-click or press-and-hold on that process, and go to Collapse if you want to hide the subprocesses again.

You can also expand any collapsed entries by clicking or tapping View and then Expand all.

To instantly collapse all expanded entries, click or tap Collapse all from the View menu.

TIP: For multi-process applications, the contextual menu displays greyed out options when right-clicking or pressing-and-holding the main (parent) process. Right-click or press-and-hold on each subprocess to interact with it.

5. How to end running processes using the Task Manager
The primary use of the Task Manager is to close running processes that are no longer responding. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process and a contextual menu opens. Click or tap End task to close the process.
You can also select the app and click or tap the End task button on the bottom-right corner of the Processes tab to close the process.

6. How to provide feedback on a running process to Microsoft
The Feedback Hub is easily accessible from the Task Manager, allowing you to offer feedback on a running process. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then choose to Provide feedback.

When the Feedback Hub opens, you can sign in with your Microsoft account and use it to send your issue, criticism, or suggestion to Microsoft.

7. How to create a dump file for a running process using the Task Manager
A dump file is a large file that uses the DMP format and provides details on what a particular process or application is doing at the exact time the dump file is created. This usually comes in handy to software developers trying to solve a bug or a problem with that process. To create a dump file, right-click or press-and-hold on any process and click or tap "Create dump file."

8. How to see details for a running process in the Task Manager
The Details tab of the Task Manager unsurprisingly provides precise details about running processes. However, this tab's sorting options are limited, so finding more about a certain process can turn into a bit of a treasure hunt, especially if you have many processes running on your computer. Luckily, the Processes tab makes up for that by providing an option to highlight the corresponding process in the Details tab. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then click or tap "Go to details."

The focus moves to the Details tab, where the corresponding executable file is highlighted.

9. How to find the location of a running process in the Task Manager
Finding the exact location on your hard drive of the executable file corresponding to an app or a process is also made easier with the Task Manager. Right-click or press-and-hold on the process in the Processes tab and click or tap on "Open file location."

The File Explorer opens at the folder where your application's executable file is stored. The corresponding file is selected when the folder opens.

10. How to research an unknown process or app using the Task Manager
Not only does the Task Manager's Processes tab show apps that are currently open, but it also displays background processes, which are mostly of interest to more advanced users. To research an unknown app or process, right-click or press-and-hold on it in the Processes tab, and then click or tap Search online.

In a new tab, your default web browser runs a web search with the name of the process's or app's executable file on Bing (regardless of your default search engine), helping you get more information.

11. How to view the properties of a running app from the Task Manager
The properties of a process or an application offer a lot of information about the executable that runs it. They show the file's size, location, access dates, and security settings, and let you troubleshoot compatibility issues. Right-click or press-and-hold on an app or process from the Processes list of the Task Manager and choose Properties.

The Properties window opens, providing you access to useful information about the app.

How crowded is your Task Manager's Processes tab?
Since we went over the different ways you can customize this tab, let us know what you choose to see in your Task Manager. Do you keep it basic like the majority of users or prefer a more detailed view? Comment below and let's discuss.






















