모든 PC를 동기화된 상태로 유지하려면 인터넷 시간을 업데이트하면 시간을 끄는 데 도움이 됩니다. 그리고 그러기 위해서는 먼저 NTP(NTP) ( Network Time Protocol ) 서버 를 찾아야 합니다 .
Windows의 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt ) 가 당신을 거기에 데려다 줄 것입니다. 그리고 어디서부터 시작해야 할지 모르겠다고 걱정하지 마세요.
이 게시물에서는 도메인 의 NTP 서버를 찾는 방법에 대해 설명합니다.(NTP)

등록 및 시작
아직 Windows 시간 서비스(Windows Time Service) 를 등록하지 않은 경우 아래 명령을 통해 등록 방법을 보여줍니다. 또한 컴퓨터 시간을 NTP(NTP) 서버 와 동기화하기 전에 서비스를 시작해야 합니다.
먼저 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 를 실행하는 것 입니다. 관리자 권한으로 실행을(Run as administrator) 선택합니다 .

그런 다음 다음 명령을 입력하여 시스템을 등록하십시오. w32tm
/register

Enter 키를 누르면 등록이 성공했는지 알 수 있습니다.

이제 다음 명령을 실행하여 시작하십시오. sc start w32time

W32tm / 쿼리
이제
Windows 시간 서비스(Windows Time Service) 가 등록되어 실행 중이므로 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다. 다음을 입력하여 이를 수행할 수 있습니다. w32tm /query 및 다음 매개변수와 일치시킵니다.
/상태
그러면 Windows 시간 서비스(Windows Time Service) 의 상태가 표시됩니다 .

/상태 /상세
이렇게 하면 자세한 정보를 표시하도록 자세한 정보 표시 모드가 설정됩니다.

/원천
그러면 시간 소스가 표시됩니다.

/구성
그러면 런타임의 구성 및 설정이 표시됩니다.

/동료
그러면 시스템을 사용하는 사람들의 목록이 표시됩니다.

W32tm /재동기화
명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt ) 를 사용하여 가능한 한 빨리 시계를 재동기화할 수도 있습니다.
다음은 이 명령의 각 매개변수에 대한 설명입니다.
/computer:<다시 동기화할 컴퓨터 이름>
이렇게 하면 재동기화할 컴퓨터를 지정할 수 있습니다. 이 필드를 비워 두면 주제는 로컬 컴퓨터가 됩니다.
/노웨이트
이렇게 하면 재동기화 대기 시간을 제거할 수 있습니다. 이는 결과가 반환되기 전에 프로세스가 완료될 때까지 기다릴 필요가 없음을 의미합니다.
/부드러운
이를 통해 기존 오류를 사용하여 시계를 다시 동기화할 수 있습니다. 물론 이것은 당신에게 아무런 도움이 되지 않을 것입니다. 그러나 호환성을 위해 제공하는 정보를 참조할 수 있습니다.

W32tm / 구성
이 명령을 사용하여 시스템을 구성합니다.
구성 요소를 살펴보겠습니다.
/manualpeerlist:
이를 통해 피어 목록을 설정할 수 있습니다. IP 주소 목록입니다.
비워둘 수 있으며 기본적으로 <peers>로 설정됩니다.
/업데이트
이를 통해 적용해야 하는 새로운 변경 사항이 있음을 서비스에 알릴 수 있습니다.
/localclockdispersion:<초 단위>
이것은 내부(Internal) 시계의 정확도를 구성합니다.
/reliable:<예 또는 아니오>
이를 통해 시스템이 신뢰할 수 있는 시간 소스인지 여부를 지정할 수 있습니다.
/largephaseoffset:<밀리초 단위>
이를 통해 로컬 및 네트워크 시간과 관련된 시차를 설정할 수 있습니다.

W32tm /dumpreg
레지스트리 키에 대한 정보를 얻으려면 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 로 이동할 수도 있습니다 . w32tm /dumpreg 와 함께 다음을 입력하십시오.
/하위 키:<키>
기본 키의 하위 키와 연결된 값을 보여줍니다.
/computer:<컴퓨터 이름>
지정된 컴퓨터에 대한 쿼리 레지스트리 설정이 표시됩니다.

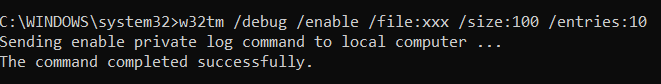
W32tm /디버그
명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt ) 는 컴퓨터의 개인 로그에 액세스할 수 있는 곳이기도 합니다 . 다음은 이 범주의 매개변수에 대한 간략한 설명입니다.
/활성화 또는 /비활성화
이를 통해 개인 로그 를 활성화(enable ) 하거나 비활성화 할 수 있습니다. (disable )이 로그에 액세스하기를 원하기 때문에 활성화하는 것이 좋습니다.
/file:<파일 이름>
이렇게 하면 파일 이름을 지정할 수 있습니다. 아래 예에서 파일 이름이 "xxx"라고 가정해 보겠습니다.
/size:<파일 크기>
이렇게 하면 파일의 크기를 지정할 수 있습니다. 여기에 입력해야 하는 것은 최대 바이트 수입니다. 이 예에서 파일 크기는 100바이트입니다.
/entries:<항목 수>
이렇게 하면 항목 값을 나열할 수 있습니다. 이 필드에 유효한 숫자는 0에서 300 사이입니다. 이 예에서 값은 10입니다.
How to Find NTP Server in a Domain to Sync All PCs
To keep all PCs
synchronized, updating the internet time will help you рull it off. And to do
that, you need to find the NTP (Network Timе Protocol) server first.
Windows’ Command Prompt will get you there. And
if you don’t know where to begin, don’t worry.
In this post,
you’ll learn what you need on how to find the NTP server for the domain.

Register and Start
If you haven’t
registered Windows Time Service yet, the commands below will show you how to do
it. You also need to start the service before you can sync your computer time
with your NTP server.
First up is to
launch the Command Prompt. Choose Run as administrator.

Then enter the
following command to register your system: w32tm
/register

Once you hit
enter, you will find out if the registration was a success.

Now, start things
up by issuing this command: sc start
w32time

W32tm /query
Now that the
Windows Time Service is registered and running, you can get information from
it. You can do this by typing the following: w32tm /query and match it with the following parameters.
/status
This will show
you the status of Windows Time Service.

/status
/verbose
This will set the
verbose mode to show you more information.

/source
This will show
you the time source.

/configuration
This will show
you the run-time’s configuration and settings.

/peers
This will show a
list of people using your system.

W32tm
/resync
You can also use
the Command Prompt to resynchronize
the clock the soonest time possible.
Here’s a
discussion on each parameter of this command:
/computer:<name
of computer to be resynchronized>
This lets you
specify a computer that will be resynchronized. If you leave this blank, the
subject will be the local computer.
/nowait
This lets you
eliminate the wait time for the resynchronization. It means that you will not
have to wait for the process to be completed before the results are returned.
/soft
This lets you
resync the clock using the existing errors. Of course, this wouldn’t do you any
good. But you can refer to the information it provides for compatibility.

W32tm
/config
Use this command
to configure your system.
Let’s look at its
components:
/manualpeerlist:
This lets you set
a list of peers. It’s a list of IP addresses.
You can leave it
blank and by default, it will be set to <peers>.
/update
This allows you
to notify the service that there are new changes that need to take effect.
/localclockdispersion:<in
seconds>
This configures
the Internal clock’s accuracy.
/reliable:<YES
or NO>
This allows you
to specify whether the system is a reliable source for time.
/largephaseoffset:<in
milliseconds>
This lets you set
the time difference involving your local and network time.

W32tm
/dumpreg
To get
information about a registry key, you can also go to the Command Prompt. There, enter the following, along with w32tm /dumpreg
/subkey:<key>
This shows you
the values that are associated with the sub-key of the default key.
/computer:<name
of the computer>
This shows you
the queries registry settings for a specified computer.

W32tm
/debug
The Command Prompt is also where you can
access your computer’s private log. Here’s a short discussion of the parameters
in this category.
/enable
or /disable
This lets you enable or disable the private log. Because you want to access this log,
enabling is the way to go.
/file:<name
of your file>
This lets you
specify the name of your file. In the example below, let’s say the name of our
file is “xxx”.
/size:<size
of your file>
This lets you
specify the size of your file. What you should enter here is the maximum number
of bytes.in the example, the size of our file is 100 bytes.
/entries:<number
of entries>
This allows you
to list down the value for your entries. The valid numbers for this field are
in between 0 to 300. In the example, the value is 10.















