Linux 를 사용해 본 적이 있거나 Linux 를 사용하는 사람을 알고 있다면 아마도 sudo 명령에 대해 들어본 적이 있을 것입니다. 이 명령은 거의 모든 Linux 배포판에서 중요한 구성 요소이며 이 명령을 사용하면 다른 사용자, 특히 루트 사용자로 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다. 특정 Linux 배포판에서는 (Linux)su 명령 을 사용하여 루트 사용자로 로그인할 수 있지만 이는 매우 위험한 것으로 간주되며 아무도 하지 않습니다.
사실, Ubuntu 와 같은 (Ubuntu)Linux 배포판에서는 기본적으로 비활성화되어 있으므로 매우 위험합니다 . 대신 루트 사용자로 명령을 실행하려면 sudo 명령 을 사용해야 합니다 . 그렇다면 Windows 는 어떻습니까? 불행히도(Well) 대부분의 사람들은 Linux 의 루트 사용자와 동일한 관리자 로 (Administrators)Windows 에 로그인 합니다. 그러나 Microsoft 는 (Microsoft)사용자 계정 컨트롤(User Account Control) 또는 UAC 를 활성화하여 관리자로 로그인하는 위험한 영향을 줄이려고 했습니다.
이렇게 하면 사용자에게 관리 권한이 있더라도 해당 계정으로 실행되는 응용 프로그램은 사용자가 수동으로 승인하지 않는 한 해당 권한을 상속하지 않습니다. 이는 맬웨어 및 스파이웨어가 관리자(Administrator) 로 로그인 한 Windows 사용자를 감염시키는 것을 방지하는 데 도움이 됩니다 .
따라서 Linux 사용자는 sudo 명령을 가지고 있지만 Windows 사용자는 무엇을 가지고 있습니까? Windows 사용자가 상승된 권한으로 명령을 실행하는 데 사용할 수 있는 대안이 있습니까 ? (Are)Windows 용 sudo 명령이 있습니까? 이 기사에서는 Windows(Windows) 사용자 를 위한 sudo 명령에 대한 5가지 대안에 대해 설명 합니다.
참고: 이러한 도구 중 일부는 현재 상당히 오래된 것이므로 최신 버전의 Windows에서 작동하거나 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다. (Note: Some of these tools are quite old now, so they may or may not work with the latest versions of Windows. )
Windows Runas 명령
Windows에는 Linux 의 sudo 에 직접 대응하는 runas 명령이 있습니다. runas 명령을 사용하여 스크립트, 프로그램 또는 명령을 다른 사용자 또는 관리자로 실행할 수 있습니다. runas 명령의 전체 구문은 다음과 같습니다.
runas [{/profile|/noprofile}] [/env] [/netonly] [/smartcard] [/showtrustlevels] [/trustlevel] /user:UserAccountName program
관리 명령 프롬프트를 열려면 다음을 입력할 수 있습니다.
runas /noprofile /user:Administrator cmd

/noprofile은 현재 사용자 프로필을 로드하지 않습니다. 사용자 환경 변수에 액세스해야 하는 경우 제거할 수 있습니다. 관리자 권한으로 메모장(Notepad) 을 사용하여 텍스트 파일을 열려면 다음 명령을 사용할 수 있습니다.
runas /user:Administrator "notepad my_file.txt"
사용 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 runas의 Technet 페이지를 확인 하십시오 .(Technet page)
runas 명령어를 사용할 때 프로그램을 설치하거나 설정 등을 변경하면 명령어를 실행하고 있는 사용자 계정이 변경된다는 점에 유의하세요. 예를 들어 일반 사용자인 사용자 X와 관리자인 사용자 Y가 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다. X에 로그인한 다음 관리자(Administrator) 자격 증명을 사용하여 runas를 수행하면 사용자 X가 아닌 관리자(Administrator) 의 설정 이 변경됩니다.
따라서 EXE 파일 을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 관리자 권한으로 (Administrator)실행(Run) 을 선택하여 응용 프로그램을 설치 하면 로그인한 사용자 프로필이 아닌 기본 제공 관리자 사용자 프로필에 설치됩니다. (Administrator)프로필 문제 없이 sudo와 같은 진정한 상승된 권한을 원한다면 아래의 다음 대안을 확인하십시오.
Windows용 Sudo – Sourceforge
Windows용 Sudo는 Windows (Sudo for Windows)용(Windows) Linux 에서(Linux) sudo 명령과 동일한 경험을 제공하는 설치할 수 있는 무료 프로그램입니다 . 유일한 차이점은 Windows 용 Sudo 는 개발자가 설명한 대로 "생성된 개체의 사용자 프로필과 소유권을 보존" 한다는 것입니다. (“preserves the user’s profile and ownership of created objects”)이것은 앱을 설치하거나 내 문서(My Documents) 등과 같은 사용자 위치를 변경하기 위해 높은 권한을 사용하려는 경우에 정말 편리합니다 .
관리자 권한을 부여하지만 명령을 실행하는 데 사용하는 계정 대신 현재 프로필의 모든 변경 사항을 유지합니다. 이 프로그램에는 .NET 버전 2.0이 필요하며 개별적으로 다운로드할 수 없습니다. 2.0을 얻으려면 2.0 이 포함된 .NET Framework 3.5 를 설치해야 합니다.
Windows 용 (Windows)Sudo 를 설치한 후에 는 S udoers 라는 프로그램에 의해 생성된 특정 그룹에 대해 상승된 권한을 갖도록 허용할 사용자 계정을 추가해야 합니다 . 내 컴퓨터(My Computer) 또는 내 PC 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭 하고 관리(Manage) 를 클릭합니다 . 그런 다음 사용자 및 그룹(Users and Groups) 을 확장 하고 그룹(Groups) 을 클릭합니다 . Sudoers 라는 이름이 표시되어야 합니다 .

Sudoers 를 두 번 클릭 하고 추가(Add) 버튼을 클릭합니다.
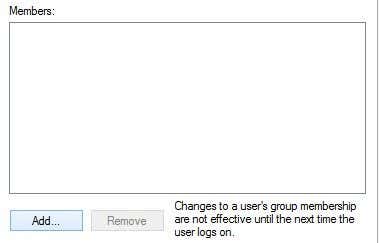
다음 대화 상자에서 고급(Advanced) 버튼을 클릭한 다음 지금 찾기(Find Now) 를 클릭합니다 . 그러면 시스템의 모든 사용자와 그룹이 나열됩니다. 추가하려는 사용자를 두 번 클릭 합니다.(Double-click)

추가하려는 사용자 수에 대해 이 단계를 반복합니다. 그런 다음 확인을 클릭하면 위에 표시된 구성원(Members) 목록 상자 에 나열된 구성원이 표시되어야 합니다 . 확인을 클릭 하면 이제 sudo (Click OK)GUI 및 명령 을 사용할 수 있습니다 . 프로그램을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하면 Sudo 옵션이 표시됩니다.
명령 프롬프트를 열고 sudo를 입력하여 상승된 권한으로 명령을 실행할 수도 있습니다.

전반적으로 꽤 멋지고 잘 작동합니다. 그러나 이 특정 프로그램은 마우스 오른쪽 버튼을 클릭하거나 명령 프롬프트를 통해 프로그램이나 프로세스 를 시작하는 데 정말 유용하지만 명령줄 앱을 실행하기 위한 것은 아닙니다. (launching)예를 들어 sudo mkdir "c:Program Files ew"를 수행하려는 경우 Windows 용 Sudo 에서는 작동하지 않습니다 . 그 기능을 위해 같은 이름이지만 다른 개발자가 만든 다른 프로그램이 있습니다. 아래를 읽으(Read) 십시오.
Windows용 Sudo – Luke Sampson
명령줄 앱도 실행할 수 있는 다른 Windows용 Sudo를(Sudo for Windows) 작성한 또 다른 개발자가 있습니다. C:Program Files에 새 폴더를 만드는 방법에 대한 예제로 돌아가 보겠습니다. 기본적으로 이 작업을 수행할 수 없습니다.

위에서 저는 PowerShell 을 사용하고 있지만 명령 프롬프트를 사용해도 동일한 오류가 발생합니다. 그러나 Windows 용 (Windows)Sudo 를 설치한 후에 는 명령 앞에 sudo라는 단어를 추가하기만 하면 오류 없이 완벽하게 작동합니다!
설치하려면 PowerShell 을 열고 다음 명령을 순서대로 입력해야 합니다.
iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('https://get.scoop.sh')
set-executionpolicy unrestricted -s cu -f
scoop install sudo
모든 것이 제대로 작동하면 각 명령 후에 PowerShell 에서 다음 출력이 표시되어야 합니다 .

그게 다야! 이제 명령을 입력하고 앞에 sudo를 추가할 수 있습니다. 이 프로그램의 유일한 성가신 점은 UAC 창이 계속 뜨고 예(Yes) 를 클릭하면 작동한다는 것입니다. 약간의 성가심에도 불구하고 이점은 그만한 가치가 있습니다.
올리다
Elevate 는 (Elevate)UAC 와 함께 작동하는 프로그램이며 sudo처럼 정확하게 작동하지 않습니다. Elevate 를 사용 하면 runas 명령처럼 실행 중인 사용자를 관리자 로 변경합니다. (Administrator)그러나 명령줄 또는 배치 파일 작업에 유용합니다.

elevate의 주요 목적은 UAC 를 우회하는 것이 아니라 상승되지 않은 셸에서 상승된 상태로 프로세스를 시작한 다음 명령이 완료된 후에도 정상적으로 계속하는 것입니다. Elevate 는 전체 마우스 오른쪽 버튼을 클릭하고 명령 프롬프트를 (Elevate)관리자(Administrator) 프로세스 로 실행하는 스크립팅에 대해 걱정할 필요가 없기 때문에 스크립팅에 유용합니다 .
Windows용 Elevation PowerToys
명령줄에서 많은 작업을 수행하거나 스크립트 및 배치 파일로 작업하는 사용자를 위해 Windows용 Elevation PowerToys(Elevation PowerToys for Windows) 페이지에는 몇 가지 유용한 도구와 스크립트가 있습니다.

스크립트 권한 상승 파워 토이(script elevation power toys) 는 명령줄에서 프로그램 권한을 높이거나 스크립트를 관리자로 실행할 때 UAC 의 좌절감을 극복하기 위해 만들어졌습니다 .
(Hopefully)Windows 에서 실제로 sudo를 사용하고 있다는 느낌을 주기에 충분한 도구와 프로그램이기를 바랍니다 . 이를 완벽하게 대체할 수는 없지만 거의 근접한 몇 가지 옵션이 있습니다. Windows 에서 프로그램, 명령 또는 스크립트를 향상시키기 위해 다른 것을 사용하는 경우 의견에 알려주십시오. 즐기다!
5 Windows Alternatives to the Linux sudo Command
If you’ve ever used Linux or knоw someone who uses Linux, then you’ve probably heard of the sudo command. The command is a critical сomponent to just about every Linux distribution and what it does is let уou run a command as a different user, most nоtably the root user. On certain Linυx distributions, you cаn log in as the root user by using the su command, but this is considered highly risky and no one ever does it.
Actually, it’s so dangerous that it’s disabled by default on Linux distributions like Ubuntu. Instead, you have to use the sudo command if you want to run a command as the root user. So what about Windows? Well, unfortunately, most people are logged into Windows as Administrators, which is the same as root user in Linux. However, Microsoft has tried to lessen the dangerous effects of being logged in as an Administrator by enabling User Account Control or UAC.
That way, even if the user has Administrative privileges, applications running under that account will not inherit those privileges unless it’s manually authorized by the user. This helps prevent malware and spyware from infecting a Windows user who is logged in as an Administrator.
So while Linux users have the sudo command, what do Windows user have? Are there alternatives that Windows users can use to run commands with elevated privileges? Is there a sudo command for Windows? In this article, I’ll talk about five alternatives to the sudo command for Windows users.
Note: Some of these tools are quite old now, so they may or may not work with the latest versions of Windows.
Windows Runas Command
Windows has the runas command, which is the direct counterpart to sudo on Linux. Using the runas command, you can execute a script, program or command as a different user or as an administrator. The full syntax for the runas command is:
runas [{/profile|/noprofile}] [/env] [/netonly] [/smartcard] [/showtrustlevels] [/trustlevel] /user:UserAccountName program
If you wanted to open an administrative command prompt, you could type the following:
runas /noprofile /user:Administrator cmd

/noprofile will not load the current user profile. You can remove that if you need access to the user environment variables. If you wanted to open a text file using Notepad with administrator privileges, you could use this command:
runas /user:Administrator "notepad my_file.txt"
You can checkout the Technet page on runas for more information on how to use it.
Note that when using runas command, if you install a program or make changes to settings, etc., the changes will be made to the user account that you are running the command on. For example, let’s say you have user X who is a normal user and user Y, who is an administrator. If you log into X and then do a runas using the Administrator credentials, changes will be made to the Administrator’s settings, not user X.
So if you install an application by right-clicking on the EXE file and choosing Run as Administrator, it’ll get installed to the built-in Administrator user profile, not the one you are logged into. If you want true elevated privileges like sudo without the profile issues, check out the next alternative below.
Sudo for Windows – Sourceforge
Sudo for Windows is a free program you can install that will give you the same experience of the sudo command on Linux for Windows. The only difference is that Sudo for Windows “preserves the user’s profile and ownership of created objects” as stated by the developer. This is really handy if you like to use elevated permissions for installing apps or making changes to user locations like My Documents, etc.
It’ll give you Administrative privileges, but will keep all the changes in the current profile instead of the account you’re using to run the command with. The program requires .NET version 2.0, which you can’t download individually. In order to get 2.0, you have to install .NET Framework 3.5, which include 2.0.
Once you install Sudo for Windows, you need to add the user accounts that you to allow to have elevated privileges to a specific group created by the program called Sudoers. Right-click on My Computer or This PC and click on Manage. Then expand Users and Groups and click on Groups. You should see one called Sudoers.

Double-click on Sudoers and click on the Add button.

On the next dialog, click the Advanced button and then click Find Now. This will list out all users and groups on the system. Double-click the user you want to add.

Repeat this step for however many users you want to add. Then click OK and you should see the members listed in the Members listbox shown above. Click OK and now you should be able to use the sudo GUI and command. If you right-click on a program, you’ll see the Sudo option.

You can also open a command prompt and type sudo to run command with elevated permissions.

Overall, it’s pretty nifty and works very well. However, note that this particular program is really useful for launching programs or processes either via right-click or via the command prompt, but it’s not meant for running command line apps. For example, if you wanted to do sudo mkdir “c:\Program Files\new”, this won’t work using Sudo for Windows. For that functionality, there is another program called the same thing, but by a different developer. Read below.
Sudo for Windows – Luke Sampson
There’s another developer who wrote another Sudo for Windows that lets you execute command line apps too. So let’s go back to the example about creating a new folder in C:\Program Files. You can’t really do this by default.

Above I’m using PowerShell, but you’ll get the same error using the command prompt also. However, once you install Sudo for Windows, just add the word sudo to the front of the command and it works perfectly with no errors!
To install it, you need to open PowerShell and then type in the following commands in order:
iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('https://get.scoop.sh')
set-executionpolicy unrestricted -s cu -f
scoop install sudo
If everything works OK, you should see the following output in PowerShell after each command:

That’s it! Now you can start typing in commands and adding sudo in front. The only annoying thing about this program is that the UAC window still pops up and you have click Yes for it to work. Even with that slight annoyance, the benefits are well worth it.
Elevate
Elevate is a program that works with UAC and doesn’t work exactly like sudo. With Elevate, it will change the executing user to Administrator like the runas command does. However, it’s useful for working in the command line or with batch files.

The main purpose of elevate is not to get around UAC, but to start a process in an elevated state from a non-elevated shell and then continuing on as normal even after the command has completed. Elevate is useful for scripting because you don’t have to worry about trying to script the whole right-clicking and running a command prompt as Administrator process.
Elevation PowerToys for Windows
For those of you who do a lot of work on the command line or work with scripts and batch files, then the Elevation PowerToys for Windows page has quite a few useful tools and scripts.

The script elevation power toys were created to overcome the frustrating aspects of UAC when trying to elevate a program from the command line or running scripts as administrators.
Hopefully, that’s enough tools and programs for you to make you feel like you’re actually using sudo on Windows. There’s no perfect replacement for it, but there are quite a few options that come close. If you use something else to elevate programs, commands or scripts in Windows, let us know in the comments. Enjoy!










