DNS ( Domain Name System ) 서버는 방문한 사이트의 모든 도메인 이름이 저장되는 곳입니다. 웹 브라우저에서 도메인 이름을 검색할 때 라우터에서 DNS 서버로 전달합니다. 특정 사이트의 도메인 이름이 저장되어 있으면 해당 IP 주소를 반환합니다. 이렇게 하면 해당 사이트의 로딩 프로세스가 특히 빨라집니다.
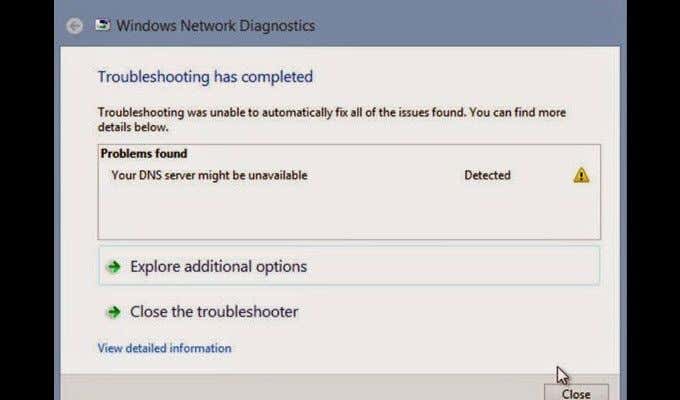
이 프로세스가 훌륭하지만 DNS 서버가 때때로 연결 설정에 실패하는 것은 드문 일이 아닙니다. 이 경우 웹 브라우저의 문제를 해결하려고 하면 종종 ' DNS 서버가 응답하지 않음' 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.

많은 요인으로 인해 이 특정 오류가 화면에 표시될 수 있습니다. 그 중 가장 눈에 띄는 것은 서버 자체가 현재 중단되었을 가능성입니다. 운 좋게도 이 문제에는 몇 가지 쉬운 솔루션이 수반되는 경우가 많습니다.
"DNS 서버를 사용할 수 없음" 오류를 수정하는 방법(How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error)
DNS 서버를 사용할 수 없다는 오류를 수신 하셨습니까? 빠른 수정을 위해 이러한 문제는 때때로 브라우저 변경, 몇 가지 방화벽 설정 변경 또는 라우터 재부팅과 같은 간단한 방법으로 해결할 수 있습니다. 문제의 원인과 후속 수정을 파악하는 것은 사용자에게 달려 있습니다.
열려는 웹 페이지에 대해 다른 브라우저를 사용하여 시작하십시오. 즉, 현재 Mozilla Firefox(Mozilla Firefox) 브라우저 를 사용하는 동안 오류가 발생하는 경우 Microsoft Edge 또는 Google Chrome 으로 전환하세요 . 문제가 지속되면 다른 장치를 테스트할 수 있습니다.
동일한 네트워크에서 모바일 장치를 사용하여 웹 페이지를 열어 문제가 하드웨어 오류의 결과가 아닌지 확인합니다. 또한 데이터 계획을 사용하여 동일한 웹 페이지에 연결하여 원인이 실제로 DNS 서버에 있는지 확인하는 것도 도움이 됩니다.
이 단계를 모두 마치면 라우터를 재부팅하십시오. "DNS 서버를 사용할 수 없음" 오류가 계속 발생하면 몇 가지 더 효과적인 방법을 거쳐야 합니다.
DNS 플러시(Windows)(Flushing Your DNS (Windows))

DNS 서버를 사용할 수 없는 문제를 해결하는 가장 효과적인 방법은 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 를 사용하여 DNS 서버를 플러시하는 것 입니다.
- Windows 키와 R 키(Windows key and R key) 를 동시에 눌러 실행 대화 상자를 엽니 다(Run) .
- 필드에 cmd 를 입력 하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다 .
- 명령 프롬프트 창에서 ipconfig /flushdns 를 입력 하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .

- ipconfig /releaseEnter 키 를 눌러 후속 작업을 수행합니다 .

- 마지막으로 ipconfig /renew 를 입력 하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .

- 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 창 을 닫고 시스템을 재부팅합니다.
DNS 플러시(MacOS)(Flushing Your DNS (MacOS))

Mac 에서 (Mac)DNS 를 플러시할 수도 있습니다 . 이 작업을 수행하는 방법은 컴퓨터에서 실행 중인 Mac 버전에 따라 약간 다릅니다 . 종종 프로세스 중에 사용되는 구문의 변경만 포함됩니다.
- Finder 창을 열고 응용 프로그램(Applications) 으로 이동한 다음 유틸리티(Utilities) 로 이동하고 터미널(Terminal) 에서 끝납니다 .
- 현재 사용 중인 MacOS 버전과 관련된 다음 구문을 입력합니다 .
- MacOS High Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; echo macOS DNS Cache Reset | say
- MacOS Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder, DNS 캐시가 플러시되었다고 가정(sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed)
- MacOS 모하비 – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;sleep 2;
- MacOS X El Capitan/Yosemite – sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;캐시 플러시(sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say cache flushed)
- Return 키를 누르고 암호를 입력한 다음 Return 키를 한 번 더 누르십시오.
- 터미널(Terminal) 을 종료하기 전에 성공적인 DNS 플러시 를 나타내는 오디오 경고를 기다립니다 .
MacOS X 캐시 지우기 는 완전히 플러시하려면 몇 가지 추가 단계가 필요합니다. 이전에 수행한 단계 위에 MDNS 및 UDNS 캐시를 모두 플러시해야 합니다 .
터미널(Terminal) 을 종료하기 전에 다음 명령을 수행하십시오.
- MDNS 캐시의 경우 sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache 를 입력합니다.(sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache)
- UDNS 캐시의 경우 sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches 를 입력합니다.( sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches)
여러 안티바이러스 제거(Remove Multiple Antiviruses)

"너무 많은 보호를 받을 수는 없습니다." 이것은 현실 세계에서는 다소 사실일 수 있지만 기술 세계에서는 동일한 컴퓨터에 여러 안티바이러스 프로그램을 설치하면 실제로 제공되는 보호 기능을 방해할 수 있습니다.
DNS 문제 의 원인일 수 있으므로 현재 실행 중인 바이러스 백신 프로그램이 두 개 이상 있는지 확인하십시오 . 모든 추가 프로그램을 비활성화한 후 시스템을 재부팅하면 문제가 저절로 해결됩니다.
원치 않는 맬웨어 공격으로부터 자신을 보호할 수 있도록 단일 소프트웨어 프로그램만 계속 실행하도록 하십시오. 이렇게 하면 보안이 강화될 뿐만 아니라 더 많은 DNS 서버 오류가 발생하는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다.
DNS 서버 변경(Changing DNS Servers)

여기에 작성된 모든 수정 사항을 이미 시도했지만 여전히 동일한 " DNS 서버를 사용할 수 없음" 오류가 표시되면 DNS 서버를 변경하는 것이 가장 좋습니다. 선택할 수 있는 공개 DNS(DNS) 가 많이 있으며 Google의 무료 DNS 가 가장 인기 있는 선택 중 하나입니다.
이를 위한 프로세스는 매우 간단하며 변경하려는 위치에 따라 몇 번의 클릭으로 수행할 수 있습니다. 각 예제 에서는 Windows 운영 체제를 사용합니다 .
라우터를 통한 DNS 변경(DNS Changes via Router)

- 웹 브라우저를 실행 하고 URL 표시줄에 (URL)기본 게이트웨이(Default Gateway) 주소를 입력하여 라우터에 액세스합니다 .
- 명령(Command) 프롬프트 창 을 열고 ipconfig를 입력하고 Enter 키를 눌러 (Enter)기본 게이트웨이(Default Gateway) 를 찾을 수 있습니다 . 가져온 정보에서 Default Gateway 옆에 있는 번호를 복사합니다 .

- 적절한 자격 증명을 사용하여 라우터에 로그인합니다.
- 비슷한 이름의 탭에서 종종 찾을 수 있는 인터넷 계정 정보를 찾습니다.
- DNS 서버 로 이동 하여 사용하는 인터넷 프로토콜(internet protocol) (IPv4 또는 IPv6) 을 가장 잘 미러링하는 옵션을 선택합니다 .
- (Enter)현재 서버 대신 사용하려는 DNS 서버 의 주소를 입력 합니다.
- Google의 DNS 서버는 기본 설정 DNSv4의 경우 8.8.8.8 이고 (8.8.8.8)대체 DNS 서버(alternate DNS server) 의 경우 8.8.4.4 입니다 . IPv6 의 경우 각각 2001:4860:4860::8888 및 2001:4860:4860::8844 를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다 .
- 편집한 정보를 저장하고 라우터 인터페이스를 종료합니다.
Windows OS를 통한 DNS 변경(DNS Changes via Windows OS)

- (Access)실행(Run) 기능( Windows key + R )을 시작하고 ncpa.cpl을(ncpa.cpl) 입력 하여 네트워크 연결 속성에 액세스 합니다 . Enter 키를 누릅니다 .

- Windows 10 사용자 는 바탕 화면 왼쪽 하단에 있는 Windows 아이콘을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭 하고 메뉴에서 네트워크 연결(Network Connections) 을 선택할 수 있습니다.
- (Select)현재 사용 중인 네트워크 어댑터를 선택 합니다. 일반적으로 이더넷 케이블을 통한 WiFi 연결 용 WLAN 및 직접 연결용 (WLAN)LAN .
- Windows 10의 왼쪽 패널에 옵션이 있습니다. 하나(Select one) 를 선택 하고 기본 창에서 어댑터 옵션 변경 을 선택합니다.(Change)
- 선택 항목을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 속성(Properties) 을 선택 합니다.
- 네트워킹(Networking) 탭 의 메뉴에서 IP 버전(v4 또는 v6)을 강조 표시하고 속성(Properties ) 버튼을 클릭합니다.

- 다음 DNS 서버 주소 사용:(Use the following DNS server addresses:) 에 대한 방사형을 클릭하여 편집 기능을 활성화합니다.

- 사용하려는 DNS(DNS) 서버 주소를 입력 합니다.
- 자동으로 얻지 않는 이전 DNS(DNS) 서버 를 사용하고 있었다면 나중에 다시 사용하려는 경우에 대비하여 주소에 주석을 달아야 합니다.
- 확인(OK) 을 클릭하여 변경 사항을 완료합니다 .
새 DNS 서버 테스트(Test New DNS Server)

DNS 서버가 변경 되면 브라우저를 열고 www.google.com 과 같은 잘 알려진 사이트를 시작합니다 . 사이트에 즉시 액세스할 수 있으면 새 DNS 가 제대로 작동하는 것입니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 Google의 IP 주소 중 하나인 172.217.16.195 를 브라우저에 직접 입력하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다 .
(Wait)익숙한 Google 로고와 검색창이 나타날 때까지 기다리세요 . 이것도 실패하면 문제는 DNS 서버 자체가 아니라 인터넷에 있을 수 있습니다. 이 경우 추가 도움이 필요하면 인터넷 서비스 제공업체에 문의하십시오.
How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error
The Domain Name System (DNS) server is where all of the domain names for the sites yoυ’ve visited are storеd. When searching a domain name in a web browser, іt is forwarded by your router to a DNS server. If the particular site’s domain namе has been savеd, іt then returns the corresponding IP address. Thіs makes the loading process for those sites particularly faster.
As great as this process is, it’s not uncommon for the DNS server to fail to establish a connection from time to time. Attempting to troubleshoot your web browser in this instance can often result in a ‘DNS server not responding’ error.

Many factors could cause this particular error to show up on your screen. The most prominent of which is the possibility that the server itself is currently experiencing an outage. Luckily, this problem is often accompanied by a few easy solutions.
How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error
Have you’ve received an error that the DNS server is unavailable? For a quick fix, these problems can sometimes be corrected by something as simple as changing browsers, messing with a few of your firewall settings, or rebooting your router. It’ll be up to you to figure out the cause and subsequent correction for the problem.

Start by using a different browser for the web pages you’re trying to open. This means that if you’re currently receiving the error while using the Mozilla Firefox browser, switch it up to Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome. Should the problem persist, we can move on to testing out other devices.
Attempt to open a webpage using a mobile device, on the same network, to ensure that the problem isn’t the result of hardware failures. It would also be beneficial to attempt to connect to the same webpages using your data plan to identify if the cause is, in fact, with the DNS server.
Once you’ve exhausted these steps, reboot your router. If the “DNS server unavailable” error is still present, we’ll have to undergo a few more effective methods.
Flushing Your DNS (Windows)

The most effective method for fixing the issue with the DNS server being unavailable is to flush it using Command Prompt.
- Pull up the Run dialog by simultaneously pressing the Windows key and R key.
- Type cmd into the field and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.

- Follow up by typing ipconfig /release and press Enter.

- Finally, type ipconfig /renew and press Enter.

- Close out of the Command Prompt window and reboot your system.
Flushing Your DNS (MacOS)

You can also flush the DNS on a Mac. The way in which you do this will vary slightly depending on the version of Mac your computer is running. It often only involves a change in the syntax used during the process.
- Open a Finder window and then head into Applications, followed by Utilities, and ending in the Terminal.
- Enter in the following syntax pertaining to the version of MacOS you’re currently using:
- MacOS High Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; echo macOS DNS Cache Reset | say
- MacOS Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed
- MacOS Mojave – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;sleep 2;
- MacOS X El Capitan/Yosemite – sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say cache flushed
- Press the Return key, enter your password, and then hit the Return key once more.
- Await the audio alert that indicates a successful DNS flush before exiting the Terminal.
The MacOS X cache clearing will need a few added steps in order to fully flush it out. You’ll have to flush both MDNS and UDNS caches on top of the steps previously taken.
Before exiting from the Terminal, perform the following commands:
- For the MDNS cache, type sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache
- For the UDNS cache, type sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
Remove Multiple Antiviruses

“You can never have too much protection.” This may be somewhat true in the real world, but in the world of technology, having multiple antivirus programs installed on the same computer can actually hinder the protection provided.
Check to see if you have two or more antivirus programs currently running as this may be the reason for the DNS issue. Once you disable all additional programs, reboot your system and the problem should resolve itself.
Ensure that moving forward you only keep a single software program running to help defend yourself from unwanted malware attacks. This not only increases security but can help you avoid running into more DNS server errors.
Changing DNS Servers

If you’ve already attempted all fixes written here and are still receiving the same “DNS server unavailable” error, it may be in your best interest to change your DNS servers. There are plenty of public DNS from which to choose, Google’s free DNS being one of the more popular choices.
The process for this is very simple and can be done in a few clicks, depending on where you choose to change it. We’ll be using the Windows operating system in each of our examples.
DNS Changes via Router

- Access your router by launching your web browser and entering the Default Gateway address into the URL bar.
- You can find the Default Gateway by opening a Command prompt window, typing ipconfig, and pressing Enter. Copy the numbers located beside Default Gateway in the pulled up information.

- Login to the router using the proper credentials.
- Locate your internet account information which can often be found in a similarly named tab.
- Navigate to the DNS server and select the option that best mirrors your used internet protocol (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Enter the address of the DNS server you want to use in place of the current one.
- Google’s DNS server will be 8.8.8.8 in the preferred DNSv4 and 8.8.4.4 in the alternate DNS server. In the case of IPv6, you’ll want to use 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844 respectively.
- Save the edited information and exit the router interface.
DNS Changes via Windows OS

- Access your network connection properties by launching the Run function (Windows key + R) and typing in ncpa.cpl. Press Enter.

- Windows 10 users can right-click the Windows icon at the lower left of the desktop screen and select Network Connections from the menu.
- Select the network adapter currently in use. WLAN for WiFi connections and LAN for direct connection, usually via ethernet cable.
- Windows 10 will have your options on the left side panel. Select one and choose Change adapter options from the main window.
- Right-click your choice and select Properties.

- In the Networking tab, highlight your IP version (v4 or v6) from the menu and click the Properties button.

- Click the radial for Use the following DNS server addresses: to enable editing capabilities.

- Enter in the DNS server addresses you plan to use.
- If you had been using a previous DNS server not obtained automatically, remember to annotate the addresses just in case you want to return using them at a later date.
- Finalize the changes by clicking OK.
Test New DNS Server

Once the DNS servers have been changed, open a browser and attempt to launch a well-known site like www.google.com. If the site is immediately accessible, then the new DNS is functioning properly. If not, enter one of Google’s IP addresses, 172.217.16.195, directly into your browser and hit Enter.
Wait for the familiar Google logo and search bar to appear. If this also fails, then the problem may lie with the internet and not the DNS server itself. Contact your internet service provider for additional help if this is the case.

















