Windows 사용자 로서 언젠가는 컴퓨터의 속도에 대해 걱정하게 될 것입니다. 로그인하는 동안 시스템이 얼마나 빨리 응답하는지 또는 일반적인 작업을 수행하기 위해 얼마나 빨리 실행되는지에 대한 것일 수 있습니다. PC에서 실행 중인 프로그램이 무엇을 하고 있는지 정확히 찾으려면 모니터링 도구를 설치해야 하며 여기에서 Sysinternals Process Monitor 도구가 사용됩니다.
프로세스 모니터(Use Process Monitor) 를 사용하여 재부팅 및 로그온 시간 측정
Windows 용 여러 모니터링 도구(monitoring tools for Windows) 가 있지만 Process Monitor 는 고급 진단을 제공하고 다양한 문제 해결 시나리오를 처리합니다. 시작 단계부터 시스템을 모니터링하도록 개발되었으며 다음과 같은 유용한 정보를 제공합니다.(:)
- 시스템이 로그온 화면을 표시하는 데 필요한 시간
- 사용자가 자격 증명을 입력하는 데 필요한 시간
- 시스템에서 Explorer를 시작하는 데 필요한 시간
- 시스템(Windows) 이 준비 상태에서 데스크탑(Desktop) 을 설정하는 데 필요한 시간 )
프로세스 모니터(Process Monitor) 의 기능은 다음과 같습니다.
- 실시간 파일 시스템, 레지스트리(Registry) 및 프로세스/스레드 활동 표시 및 기록
- 실시간 모드로 실행하여 부팅 시간을 기록할 수 있습니다.
- 프로세스 모니터(Process Monitor) 를 사용하여 시스템 및 레지스트리 활동에 대한 보고서를 필터링, 검색 및 생성할 수 있습니다.
- 시스템(System) 관리자 를 위한 문제 해결 도구
- 멀웨어 헌팅
프로세스 모니터 사용을 시작하는 방법
- 프로세스 모니터(Monitor) 는 설치가 필요하지 않습니다. zip 아카이브를 다운로드해야 합니다. 파일 압축을 풀면 Procmon.exe 를 실행하여 응용 프로그램을 시작할 수 있습니다.
- 도구를 처음 실행하면 사용자에게 최종 사용자 사용권 계약(End User License Agreement) ( EULA ) 에 동의하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다 . 한 번 수락하면 동일한 프로필에 대해 다시 표시되지 않습니다.
- 마우스 오른쪽 버튼 클릭(Simply) 옵션을 사용하여 도구를 작업 표시줄에 고정하기만 하면 됩니다. 한 번의 클릭으로 프로세스(Process) 모니터를 쉽게 시작할 수 있습니다 .
프로세스 모니터 사용자 인터페이스(Process Monitor User Interface)
UI 창이 열리자 마자 도구는 레지스트리(Registry) , 파일(Files) 및 Process/Thread 활동에 대한 정보 캡처를 시작합니다. UI는 방대한 정보가 포함된 스프레드시트를 생각나게 합니다. 수집된 데이터를 정렬하기 위해 사용자가 적용할 수 있는 필터가 있습니다.
몇 가지 유용한 헤더 아래에 분류된 정보와 함께 기본 창에서 증가하는 프로세스 목록을 볼 수 있습니다.
프로세스 모니터 로 (Process Monitor)재부팅 주기(Reboot Cycle) 추적 을 기록하는 방법
아래 언급된 단계에 따라 시스템의 재부팅 주기를 추적하십시오.
압축을 푼 폴더에서 "ProcMon"이라는 파일을 찾아 클릭합니다.
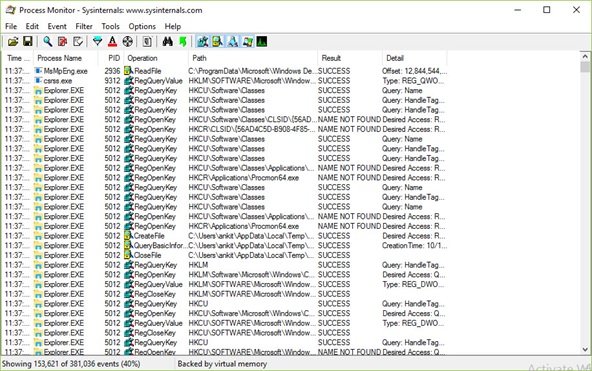
프로세스 모니터 필터' 인터페이스가 표시되면 '재설정' 버튼을 클릭하여 필터를 기본값으로 재설정한 다음 '확인' 버튼을 클릭합니다.
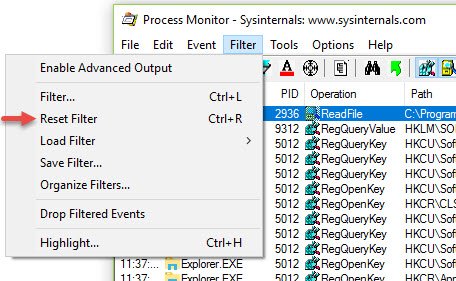
이제 파일 메뉴에서 캡처(Capture) 버튼을 클릭하여 다음과 같이 현재 실시간 추적을 중지합니다.
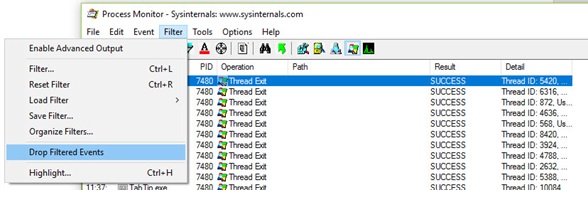
참고:(Note: ) 재부팅 및 로그온 분석에 필요하지 않은 일부 이벤트를 추적에서 필터링하고 추적을 매우 작은 크기로 줄이는 것이 좋습니다. 아래에 언급된 원치 않는 이벤트를 필터링하는 프로세스입니다.
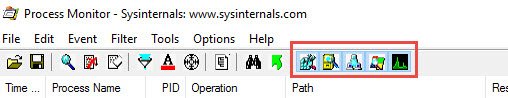
ProcMon 아이콘 표시줄에서 다음 이벤트 범주의 선택을 취소 합니다.
- 네트워크 이벤트 표시
- 파일 시스템 활동 표시
- 레지스트리 활동 표시
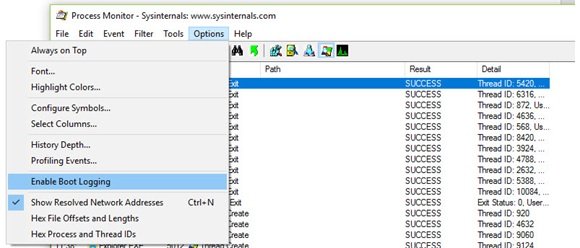
이제 프로세스(Process) 모니터를 닫고 컴퓨터를 다시 시작하십시오.
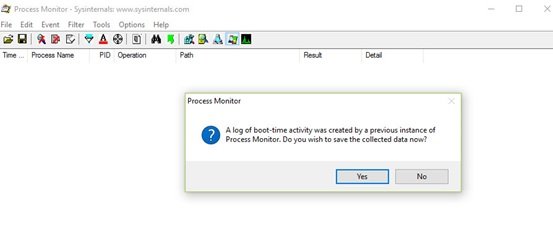
디스크 공간을 절약하려면 시스템이 시작되면 로그온하십시오. 이제 프로세스 모니터(Process Monitor) 를 시작 하고 중지하십시오. 추적을 저장합니다. 이렇게 하면 과도한 양의 디스크 공간이 사용되지 않습니다.
이것은 Process Monitor(Process Monitor) 를 사용하여 추적을 기록하는 방법에 대한 것 입니다. 이제 이 추적을 분석하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다.
읽기(Read) : Windows에서 부팅 또는 시작 시간을 측정하는 프리웨어(Freeware to measure Boot or Startup Time in Windows) .
Process Monitor 로 재부팅 주기 추적을 분석하는 방법
- 시스템이 시작되면 로그온하고 Sysinternals의 프로세스 모니터를 시작하십시오.
- 이제 위에서 언급한 대로 필터를 재설정하고 확인을 클릭합니다.
- 현재 추적을 저장할지 묻는 대화 상자가 나타납니다. 추적을 폴더에 저장합니다.
- 이제 이 부트 추적을 사용할 수 있으며 Process Monitor 에도 표시됩니다 .
- 그런 다음 "도구"를 클릭한 다음 "프로세스 트리"를 클릭합니다.
- 여기에서 가장 왼쪽 열의 첫 번째 항목 "유휴"를 클릭하고 시계에 시간을 기록해 둡니다.
- 다시(Again) "도구"를 클릭한 다음 "프로세스 트리"를 클릭합니다. 맨 왼쪽에서 "Logonui.exe" 옵션을 찾아 아래 그림과 같이 시계 시간을 기록하면서 클릭합니다.
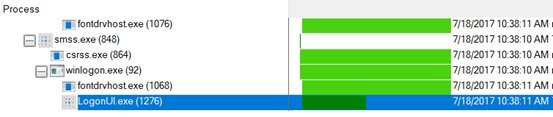
유휴 시간과 Logonui.exe 시간 사이에 기록된 두 시간의 차이는 컴퓨터 시작과 로그온 자격 증명 사이의 시간 차이입니다. (The difference between both the noted time that is between Idle time and Logonui.exe time is the time gap between computer startup and logon credentials. )
위에서 (Above)Process Monitor 를 사용하여 재부팅 주기 시간을 평가하는 방법에 대해 설명 했습니다. 이제 Userinit.exe 의 중요성을 이해합시다 .
' Userinit.exe 는 사용자의 자격 증명이 확인되면 시작되는 프로세스이며 사용자의 셸 시작, 데스크톱 시작 및 중요한 표시인 "데스크톱을 사용할 준비가 됨"으로 이어지는 후속 이벤트 체인을 시작합니다. 'Userinit.exe' 프로세스는 비교적 가깝지만 이전에 언급한 'Logonui.exe' 프로세스 아래에 있어야 합니다. 'Userinit.exe' 프로세스가 시작되는 시계 시간에 유의하십시오. 'Userinit.exe'와 'Procmon.exe'가 시작되는 시간의 차이는 대략 해당 특정 사용자의 전체 로그온 시간입니다.
프로세스(Process) 모니터 를 사용하여 각각의 시간을 측정하는 것은 매우 쉽습니다 .
프로세스 모니터 는 8KB 또는 8192바이트만 사용하여 재부팅 시간을 모니터링합니다. 또한 ( uses just 8KB or 8192 bytes to monitor the reboot time. Also, its) 강력한 필터링 기능을 사용하려면 ""프로세스 시작" 이벤트만 수집하면 됩니다. ( powerful filtering capability requires just “”process start” events to be collected. )따라서 전체 로그온 및 재부팅 추적 통계는 추적 캡처의 영향을 받지 않습니다.(overall logon and reboot trace statistics are not affected by the trace capture.)
이것은 동일한 목적을 위해 설계된 다른 모든 도구와 차별화되는 Process Monitor의 특별한 기능 중 하나입니다.(This is one of the special features of Process Monitor that makes it outstanding from all other tools designed for the same purpose.)
다른 특징들(Other features)
- 프로세스 모니터(Process Monitor) 를 사용하면 매개변수에 따라 데이터를 캡처할 수 있습니다. 이 기능은 다른 도구에서는 사용할 수 없습니다.
- 이전에 수집된 데이터는 새 쿼리 후에도 계속 유지됩니다.
- 각 작업에 대한 스레드 스택을 캡처 및 분석하여 근본 원인을 감지할 수 있습니다.
- 프로세스 세부 정보에는 이미지 경로, 명령줄, 사용자 및 세션 ID가 포함됩니다.
- 열(Columns) 구성 가능 – 이동, 숨기기 또는 표시 가능
- 모든 데이터 필드에 대한 광범위한 필터
- 프로세스(Process) 트리는 추적에 있는 모든 프로세스의 관계를 보여줍니다.
- 검색 취소 가능성
- 모든 작업에 대한 부팅(Boot) 시간 로깅
- 고급(Advanced) 로깅 아키텍처는 캡처된 수천만 개의 이벤트와 기가바이트의 로그 데이터로 확장됩니다.
- 다른 프로세스 모니터(Process Monitor) 인스턴스 에서 사용하기 위해 기본 로그 형식 데이터를 저장하는 기능
도구(Tools) 를 클릭하여 시스템(System) 세부 정보, 프로세스 활동 요약(Process Activity Summary) , 파일 요약(File Summary) , 레지스트리 요약(Registry Summary) 등과 같은 다른 유용한 탭에서 선택하십시오 .
참고용으로 스크린샷을 참조하세요.
프로세스(Process) 활동 요약 도 볼 수 있습니다 .
Process Monitor 의 유일한 단점은 초보자가 사용하기에는 다소 복잡하다는 것입니다. 대부분의 사용자는 도구를 사용하는 데 어려움을 겪을 수 있으며 작동 방식을 이해하는 데 시간을 투자해야 할 수 있습니다.
IT 전문가, 시스템 관리자 또는 기술 전문가는 (Systems)Process Manager 의 기능을 활용하는 데 가장 적합합니다 .
프로세스 모니터를 다운로드하려면 docs.microsoft.com 을 방문하십시오 . 자세한 내용은 TechNet 을 참조하십시오 .
Process Manager lets you measure computer reboot times and more
As a Windows user, at some point in time, you do feel cоncerned about the speed of уour maсhine. It cоuld be about how quick does your system responds while logging in or how fast it runs to accomplish usual tasks. To find exactly what the programs running on yoυr PC are doing you need to install a monitoring tool and this is where Sysinternals Process Monitor tool comes in use.
Use Process Monitor to measure reboot & logon times
Although there are several monitoring tools for Windows, Process Monitor offers advanced diagnostics and tackles various troubleshooting scenarios. It has been developed to monitor the system right from its starting phase and provides useful information such as:
- Time required by the system to display logon screen
- Time required by the user to enter the credentials
- Time required by the system to start the Explorer
- Time required by the system to set up the desktop in a ready state (Desktop is in a ready state indicates that Windows has started with the majority of its services and processes and the user can start interacting with various applications without waiting for a busy cursor sign)
The features of Process Monitor are as follows:
- Display as well as record real-time file system, Registry, and process/thread activity
- It can record booting time by running in real-time mode
- Using Process Monitor, you can filter, search and create reports about system and registry activities
- Troubleshooting tool for the System admins
- Malware hunting
How to start using Process Monitor
- Process Monitor does not require installation. You have to download a zip archive. Once you extract the files, you can run Procmon.exe to launch the application.
- When the tool is run for the first time, the user will be asked to accept the End User License Agreement (EULA). Once accepted it would never be displayed again for the same profile.
- Simply pin the tool to the taskbar with right click option. It would be easy to start the Process monitor with just one click.
Process Monitor User Interface
As soon as the UI window opens, the tool starts capturing information about Registry, Files and Process/Thread activity. The UI reminds you of a spreadsheet with a massive outlay of information. There are filters that users can apply to sort the collected data.
You will see the growing list of processes in the main window with information categorized under several useful headers.
How to record a Reboot Cycle trace with Process Monitor
Follow the below-mentioned steps to trace the reboot cycle of your system:
Locate the file named “ProcMon” from the unzipped folder and click.

Once you see the Process Monitor Filter’ interface click on the ‘Reset’ button to reset filters to default values, and then click the ‘OK’ button.

Now, click on the Capture button in the file menu to stop the current real-time trace as shown:

Note: It is advisable to filter some events from the trace that are not required in analyzing reboot and logon and reduce the trace to very small size. Mentioned below is the process to filter out the unwanted events.
On the ProcMon icon bar de-select the following categories of events:
- Show Network Events
- Show File System Activity
- Show Registry Activity




Now close the Process monitor and restart the computer.

If you wish to save the disk space, then log on once your system initiates, Now, start the Process Monitor and stop it. Save the trace. This will ensure that an excessive amount of disk space is not consumed.

So, this was about how we can record the trace using Process Monitor. Now, let us see how to analyze this trace.
Read: Freeware to measure Boot or Startup Time in Windows.
How to analyze the reboot cycle trace with Process Monitor
- Once the system starts, logon and start the Sysinternals’ Process Monitor.
- Now reset the filter as mentioned above and click Ok.
- A dialog box will ask you to save the current trace. Save the trace in a folder.
- Now, this boot trace will be available and even displayed in Process Monitor.
- Next, click on “Tools” and then on “Process Tree”.
- Here, click on “Idle” the first item in the leftmost column and keep the note of the time on the clock.
- Again click on “Tools” and then on “Process Tree”. Look for the option “Logonui.exe” in the leftmost and click on it while noting the clock time as shown below.

The difference between both the noted time that is between Idle time and Logonui.exe time is the time gap between computer startup and logon credentials.
Above was an explanation of how reboot cycle time is evaluated with Process Monitor. Now, let’s understand the significance of Userinit.exe.
‘Userinit.exe is the process that is launched if the user’s credentials are verified, and initiates the subsequent chain of events leading to the user’s shell starting, desktop starting, and the important marker “desktop ready to use”. The ‘Userinit.exe’ process should be relatively close but under’ the previously noted process ‘Logonui.exe. Note the clock time for starting of the ‘Userinit.exe’ process. The difference in clock time between starting of ‘Userinit.exe’ and ‘Procmon.exe’ is roughly that particular user’s overall logon time.
It is quite easy to measure respective times using Process monitor.
Process Monitor uses just 8KB or 8192 bytes to monitor the reboot time. Also, its powerful filtering capability requires just “”process start” events to be collected. Thus overall logon and reboot trace statistics are not affected by the trace capture.
This is one of the special features of Process Monitor that makes it outstanding from all other tools designed for the same purpose.
Other features
- Process Monitor allows you to capture data according to your parameters. This feature is not available with other tools.
- Previously collected data remains with you even after new queries.
- By capturing and analyzing thread stacks for each operation, you can detect the root cause
- Process details include image path, command line, user and session ID
- Columns are configurable – They can be moved, hidden or shown
- Extensive filters for any data field
- Process tree shows the relationship of all processes in a trace.
- Possibility to cancel search
- Boot time logging for all operations
- Advanced logging architecture scales to tens of millions of captured events and gigabytes of log data
- Ability to save native log format data for use in different Process Monitor instances
Click on Tools to choose from the other set of useful tabs like System details, Process Activity Summary, File Summary, Registry Summary and more.

Refer the screenshots for reference.

You can also see the Process activity summary.

The only drawback of Process Monitor is that it is a bit complicated for the novice user to use. Most users may find it challenging to use the tool and may have to invest time in understanding how it works.
IT experts, Systems admins or technology geeks are best suited to utilize the features of Process Manager.
To download Process Monitor visit docs.microsoft.com. For more details visit TechNet.













