Microsoft 는 창립 이래 Windows 운영 체제 업데이트와 관련하여 매우 일관되었습니다. 그들은 정기적으로 다양한 유형의 업데이트(기능 팩 업데이트, 서비스 팩 업데이트, 정의 업데이트, 보안 업데이트, 도구 업데이트 등)를 전 세계 사용자에게 푸시합니다. 이러한 업데이트에는 현재 OS 빌드에서 불행히도 사용자가 겪고 있는 여러 버그 및 문제에 대한 수정 사항과 함께 전반적인 성능 및 사용자 경험을 향상시키는 새로운 기능이 포함되어 있습니다.
그러나 새 OS 업데이트로 문제가 해결될 수 있지만 다른 몇 가지 업데이트가 나타날 수도 있습니다. 작년 의 Windows 10 1903 업데이트는 해결한 것보다 더 많은 문제를 일으키는 것으로 악명이 높았습니다. 일부 사용자는 1903 업데이트로 인해 CPU 사용량이 30%, 어떤 경우에는 100% 증가했다고 보고했습니다. 이것은 그들의 개인용 컴퓨터를 실망스럽게 느리게 만들고 머리를 뽑게 만들었습니다. 업데이트 후 발생할 수 있는 몇 가지 다른 일반적인 문제는 극단적인 시스템 정지, 긴 시작 시간, 응답하지 않는 마우스 클릭 및 키 누름, 죽음의 블루 스크린 등입니다.
이 기사에서는 컴퓨터 성능을 개선하고 최신 Windows 10 업데이트를 설치하기 전과 같이 더 빠르게 만드는 8가지 솔루션을 제공합니다.

업데이트 문제 후 Windows 10이 느리게 실행되는 문제 수정(Fix Windows 10 running slow after update problem)
현재 업데이트가 제대로 설치되지 않았거나 시스템과 호환되지 않는 경우 Windows 10 컴퓨터가 느리게 실행될 수 있습니다. 때때로 새 업데이트로 인해 장치 드라이버 세트가 손상되거나 시스템 파일이 손상되어 성능이 저하될 수 있습니다. 마지막으로 업데이트 자체에 버그가 가득할 수 있으며 이 경우 이전 빌드로 롤백하거나 Microsoft 에서 새 빌드를 출시할 때까지 기다려야 합니다.
느리게 실행되는 Windows 10 에 대한 다른 일반적인 솔루션 에는 영향이 큰 시작 프로그램 비활성화, 응용 프로그램이 백그라운드에서 실행되지 않도록 제한( restricting applications from running in the background ) , 모든 장치 드라이버 업데이트, 블로트웨어 및 맬웨어 제거, 손상된 시스템 파일 복구 등이 있습니다.
방법 1: 새 업데이트 찾기
앞서 언급했듯이 Microsoft 는 이전 업데이트의 문제를 수정하는 새로운 업데이트를 정기적으로 출시합니다. 성능 문제가 업데이트에 내재된 문제인 경우 Microsoft 는 이미 알고 있고 이에 대한 패치를 출시했을 가능성이 큽니다. 따라서 보다 영구적이고 긴 솔루션으로 이동하기 전에 새로운 Windows 업데이트가 있는지 확인하십시오.
1. Windows 키를 눌러 시작 메뉴를 불러오고 톱니바퀴 아이콘을 클릭하여 Windows 설정(Windows Settings) 을 엽니다 (또는 단축키 조합 Windows key + I 사용 ).

2. 업데이트 및 보안(Update & Security) 을 클릭합니다 .

3. Windows 업데이트(Windows Update) 페이지에서 업데이트 확인을(Check for Updates) 클릭합니다 .

4. 새 업데이트를 사용할 수 있는 경우 가능한 한 빨리 다운로드하여 설치하여 컴퓨터 성능을 수정하십시오.
방법 2: 시작(Startup) 및 백그라운드 응용 프로그램(Background Applications) 비활성화
우리 모두는 거의 사용하지 않는 많은 타사 응용 프로그램을 설치했지만 드문 기회가 발생할 때를 위해 보관합니다. 이들 중 일부는 컴퓨터가 부팅될 때마다 자동으로 시작하는 권한을 가질 수 있으며 결과적으로 전체 시작 시간이 늘어납니다. 이러한 타사 응용 프로그램과 함께 Microsoft 는 항상 백그라운드에서 실행할 수 있는 기본 응용 프로그램의 긴 목록을 번들로 제공합니다. 이러한 백그라운드 앱(Restricting these background apps) 을 제한하고 영향력이 큰 시작 프로그램을 비활성화하면 유용한 시스템 리소스를 확보하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
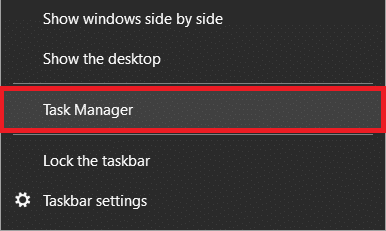
1. 화면 하단의 작업 표시줄을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하고 나타나는 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 작업 관리자 를 선택합니다(또는 키보드에서 (Task Manager)Ctrl + Shift + Esc 를 누름).
2. 작업 관리자 창의 시작 (Startup ) 탭으로 전환합니다.
3. 시작 영향(Startup impact) 열을 확인하여 어떤 프로그램이 가장 많은 리소스를 사용하여 시작 시간에 큰 영향을 미치는지 확인합니다. 자주 사용하지 않는 응용 프로그램을 찾으면 시작 시 자동으로 실행되지 않도록 비활성화하는 것이 좋습니다.
4. 그렇게 하려면 애플리케이션을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭 하고 (right-click )비활성화 (Disable ) 를 선택합니다 (또는 오른쪽 하단 에 있는 비활성화 버튼 클릭).(Disable)

기본 애플리케이션이 백그라운드에서 활성 상태로 유지되지 않도록 하려면:
1. Windows 설정 을 열고 (Settings )개인 정보(Privacy) 를 클릭합니다 .

2. 왼쪽 패널에서 백그라운드 앱(Background apps) 을 클릭합니다 .

3. '앱이 백그라운드에서 실행되도록 허용'(Toggle off ‘Let apps run in the background’) 을 해제하여 모든 백그라운드 애플리케이션을 비활성화하거나 계속해서 백그라운드에서 계속 실행할 수 있는 앱과 그렇지 않은 앱을 개별적으로 선택합니다.
4. PC를 다시 시작 하고 업데이트 문제 후 느리게 실행되는 Windows 10 ( fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem. ) 을 수정할 수 있는지 확인합니다 .
방법 3: 클린 부팅 수행
특정 응용 프로그램으로 인해 컴퓨터가 느리게 실행되는 경우 클린 부팅을 수행하여(performing a clean boot) 정확한 원인을 찾을 수 있습니다 . 클린 부팅을 시작하면 OS는 필수 드라이버와 기본 응용 프로그램만 로드합니다. 이렇게 하면 성능 저하를 유발할 수 있는 타사 응용 프로그램으로 인해 발생하는 소프트웨어 충돌을 방지하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
1. 클린 부팅을 수행 하려면 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 애플리케이션 을 열어야 합니다 . 이를 열려면 실행 명령 상자( Windows key + R ) 또는 검색 창 에 msconfig 를 입력하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다.(msconfig )

2. 일반 탭에서 옆에 있는 라디오 버튼을 클릭하여 선택적 시작 을 활성화합니다.(Selective startup)
3. 선택적 시작을 활성화하면 그 아래에 있는 옵션도 잠금 해제됩니다. 시스템 서비스 로드 옆의 확인란을 선택합니다. ( Check the box next to Load system services.)시작 항목 로드(Load) 옵션이 비활성화(선택 해제) 되어 있는지 확인합니다 .

4. 이제 서비스 탭으로 이동하여 (Services )모든 Microsoft 서비스 숨기기(Hide all Microsoft services) 옆의 확인란을 선택 합니다 . 그런 다음 모두 비활성화(Disable all) 를 클릭합니다 . 이렇게 하면 백그라운드에서 실행 중인 모든 타사 프로세스 및 서비스가 종료됩니다.

5. 마지막으로 적용 (Apply ) 을 클릭하고 확인 (OK ) 을 클릭 하여 변경 사항을 저장한 다음 다시 시작합니다(Restart) .
또한 읽기: (Also Read:) Windows 10 크리에이터 업데이트를 다운로드할 수 없는 문제 수정(Fix Unable To Download Windows 10 Creators Update)
방법 4: 원치 않는 및 맬웨어(Malware) 응용 프로그램 제거(Remove Unwanted)
타사 및 기본 응용 프로그램을 제외하고 악성 소프트웨어는 의도적으로 시스템 리소스를 잡아먹고 컴퓨터를 손상시키도록 설계되었습니다. 그들은 사용자에게 경고하지 않고 컴퓨터에 침입하는 것으로 유명합니다. 인터넷에서 응용 프로그램을 설치할 때 매우 주의해야 하며 신뢰할 수 없는/확인되지 않은 소스를 피해야 합니다(대부분의 맬웨어 프로그램은 다른 응용 프로그램과 함께 제공됨). 또한 이러한 메모리를 많이 사용하는 프로그램을 방지하기 위해 정기적인 검사를 수행하십시오.
1. Cortana 검색 창( Windows 키 + S)에 (Windows)Windows 보안(Windows security) 을 입력하고 Enter 키를 눌러 내장 보안 응용 프로그램을 열고 맬웨어를 검사합니다.

2. 왼쪽 패널에서 바이러스 및 위협 방지 를 클릭합니다.(Virus & threat protection)

3. 이제 빠른 검사 를 실행하거나 (Quick Scan)검사(Scan) 옵션 에서 전체 검사(Full Scan) 를 선택하여 맬웨어에 대한 보다 철저한 검사를 실행할 수 있습니다(또는 Malwarebytes와 같은 타사 안티바이러스 또는 맬웨어 방지 프로그램이 있는 경우 해당 프로그램 을 통해 검사 실행(Malwarebytes, run a scan through them) ).
방법 5: 모든 드라이버 업데이트
Windows 업데이트는 하드웨어 드라이버를 엉망으로 만들고 호환되지 않게 하는 것으로 유명합니다. 일반적으로 그래픽 카드 드라이버가 호환되지 않거나 구식이 되어 성능 문제가 발생합니다. 드라이버 관련 문제를 해결하려면 장치 관리자를 통해 오래된 드라이버를 최신 드라이버로 교체하십시오 .(replace the outdated drivers with the latest ones)

Driver Booster 는 (Driver Booster)Windows 용으로 가장 널리 사용되는 드라이버 업데이트 응용 프로그램입니다 . 공식 웹 사이트로 이동하여 설치 파일을 다운로드하십시오. 다운로드가 완료되면 .exe 파일을 클릭하여 설치 마법사를 시작하고 화면의 모든 지시에 따라 응용 프로그램을 설치합니다. 드라이버 응용 프로그램을 열고 지금 스캔 을 클릭합니다.( Scan)
(Wait)스캔 프로세스가 완료될 때까지 기다린 다음 각 드라이버 옆에 있는 드라이버 업데이트 버튼 또는 모두 (Update Drivers)업데이트(Update All) 버튼을 개별적으로 클릭 합니다(클릭 한 번으로 모든 드라이버를 업데이트하려면 유료 버전이 필요함).
방법 6: 손상된 시스템 파일 복구(Repair Corrupt System Files)
업데이트를 잘못 설치하면 중요한 시스템 파일이 손상되고 컴퓨터 속도가 느려질 수 있습니다. 시스템 파일이 손상되거나 완전히 누락되는 것은 기능 업데이트의 일반적인 문제이며 앱을 열 때 다양한 오류, 죽음의 블루 스크린, 완전한 시스템 오류 등을 유발합니다.
손상된 시스템 파일을 복구하려면 이전 Windows(Windows) 버전 으로 롤백 하거나 SFC 스캔을 실행할 수 있습니다. 후자는 아래에 설명되어 있습니다(전자는 이 목록의 최종 솔루션입니다).
1. Windows 검색 창 에서 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 를 검색하고 검색 결과를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭한 다음 관리자 권한으로 실행(Run As Administrator) 을 선택 합니다.

명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 가 시스템을 변경할 수 있도록 권한을 요청 하는 사용자 계정 컨트롤(User Account Control) 팝업이 표시됩니다. 예 를 (Yes )클릭(Click) 하여 권한을 부여합니다.
2. 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 창이 열리면 다음 명령을 주의해서 입력하고 Enter 키를 눌러 실행합니다.
sfc /scannow

3. 스캔 프로세스는 시간이 걸리므로 편안하게 앉아서 명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 가 작동하도록 하십시오. 스캔에서 손상된 시스템 파일이 발견되지 않으면 다음 텍스트가 표시됩니다.
Windows 리소스 보호에서 무결성 위반을 찾지 못했습니다.(Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.)
4. SFC 스캔을 실행한 후에도 컴퓨터가 계속 느리게 실행되면 아래 명령( Windows 10 이미지 복구)을 실행합니다.(Windows 10)
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

5. 명령 처리가 완료되면 PC를 재부팅 하고 업데이트 문제 후 느리게 실행되는 Windows 10 ( fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem. ) 을 수정할 수 있는지 확인합니다 .
또한 읽기: (Also Read:) Windows 10 업데이트가 매우 느린 이유는 무엇입니까?(Why are Windows 10 Updates Extremely Slow?)
방법 7: 페이지 파일 크기 수정(Modify Pagefile) 및 시각 효과 비활성화(Disable Visual)
대부분의 사용자는 이 사실을 모를 수 있지만 RAM 및 하드 드라이브와 함께 컴퓨터 성능을 결정하는 또 다른 유형의 메모리가 있습니다. 이 추가 메모리를 페이징 파일(File) 이라고 하며 모든 하드 디스크에 있는 가상 메모리입니다. 이것은 RAM(RAM) 의 확장 역할을 하며 시스템 RAM 이 부족할 때 컴퓨터는 자동으로 일부 데이터를 페이징 파일로 전송합니다 . 페이징 파일은 최근에 액세스하지 않은 임시 데이터도 저장합니다.
일종의 가상 메모리이기 때문에 값을 수동으로 조정하고 사용 가능한 공간이 더 있다고 믿도록 컴퓨터를 속일 수 있습니다. 페이징(Paging) 파일 크기 를 늘리는 것과 함께 더 선명한 경험을 위해 시각 효과를 비활성화하는 것도 고려할 수 있습니다(미학은 줄어들지만). 이러한 조정은 모두 성능 (Performance) 옵션(Options) 창 을 통해 수행할 수 있습니다 .
1. 실행(Run) 명령 상자( Windows 키 + R)에 Control 또는 (Windows)Control Panel 을 입력하고 Enter 키를 눌러 응용 프로그램을 엽니다.

2. 시스템(System) 을 클릭합니다 . 항목을 더 쉽게 찾을 수 있도록 오른쪽 상단에 있는 보기 기준 옵션을 클릭하여 아이콘 크기를 크거나 작게 변경합니다.

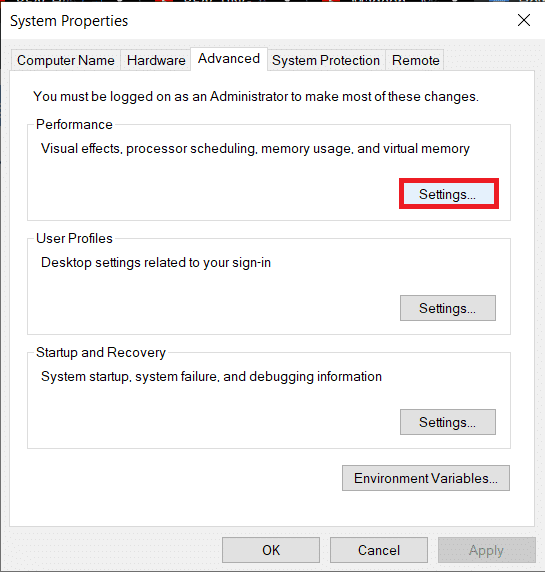
3. 다음 시스템 속성(Properties) 창 에서 왼쪽의 고급 시스템 설정 을 클릭합니다.(Advanced system settings)

4. 성능 아래 의 설정… 버튼을 클릭합니다.(Settings…)
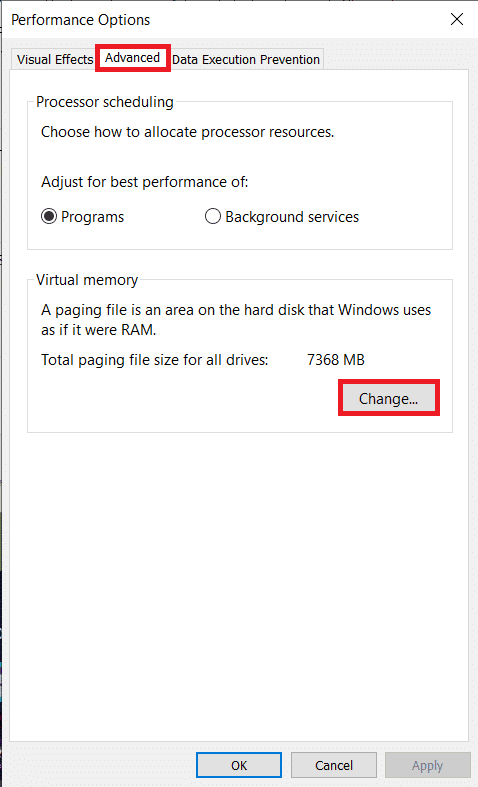
5. 성능 (Performance)옵션(Options) 창의 고급 (Advanced ) 탭으로 전환하고 변경... 을 클릭합니다.(Change…)
6. '모든 드라이브의 페이징 파일 크기 자동 관리'(‘Automatically manage paging file size for all drives’) 옆에 있는 상자를 선택 취소 (Untick ) 합니다 .
7. Windows 를 설치한 드라이브(일반적으로 C 드라이브)를 선택하고 (Windows)사용자 지정 크기(Custom size) 옆에 있는 라디오 버튼을 클릭합니다 .
8. 경험상 초기 크기 는 (Initial size)시스템 메모리(RAM)의 1.5배와(one and a half times of the system memory (RAM)) 같아야 하고 최대 크기 는 (Maximum size)초기 크기의 3배(three times the initial size) 여야 합니다 .

예:(For example:) 컴퓨터에 8GB의 시스템 메모리가 있는 경우 초기(Initial) 크기는 1.5 * 8192MB(8GB = 8 * 1024MB) = 12288MB여야 하므로 최대(Maximum) 크기는 12288 * 3 = 36864가 됩니다. 메가바이트.
9. 초기(Initial) 및 최대(Maximum) 크기 옆에 있는 상자에 값을 입력했으면 설정(Set) 을 클릭합니다 .
10. 성능 (Performance) 옵션(Options) 창이 열려 있는 동안 모든 시각 효과/애니메이션도 비활성화하겠습니다.
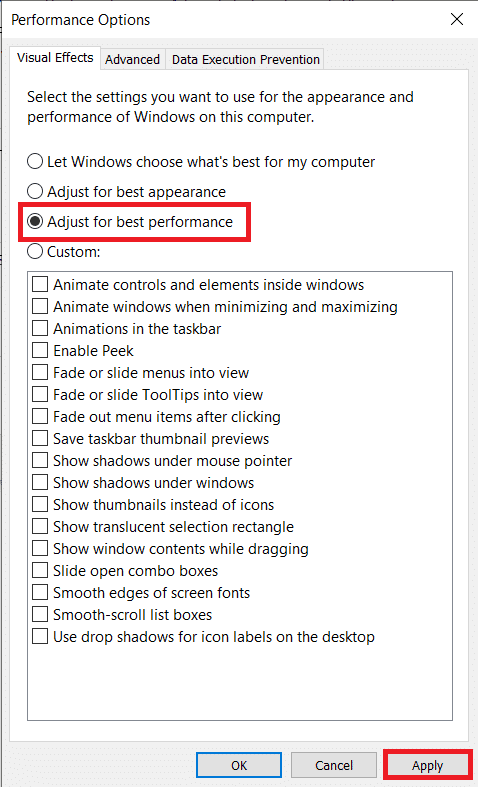
11. 시각 효과 탭에서 최상의 성능을 위해 조정을 활성화 (enable Adjust for best performance ) 하여 모든 효과를 비활성화합니다. 마지막으로 확인 (OK ) 을 클릭하여 저장하고 종료합니다.
방법 8: 새 업데이트 제거
궁극적으로 위의 솔루션 중 어느 것도 컴퓨터 성능을 개선하는 데 도움이 되지 않았다면 현재 업데이트를 제거하고 현재 겪고 있는 문제가 없는 이전 빌드로 롤백하는 것이 가장 좋습니다. Microsoft 가 앞으로 더 좋고 덜 번거로운 업데이트를 출시할 때까지 언제든지 기다릴 수 있습니다 .
1. Windows 키 + I 을 눌러 Windows 설정 을 열고 (Settings )업데이트 및 보안(Update & Security) 을 클릭합니다 .
2. 오른쪽 패널에서 아래로 스크롤 하여 (Scroll)업데이트 기록 보기(View update history) 를 클릭합니다 .

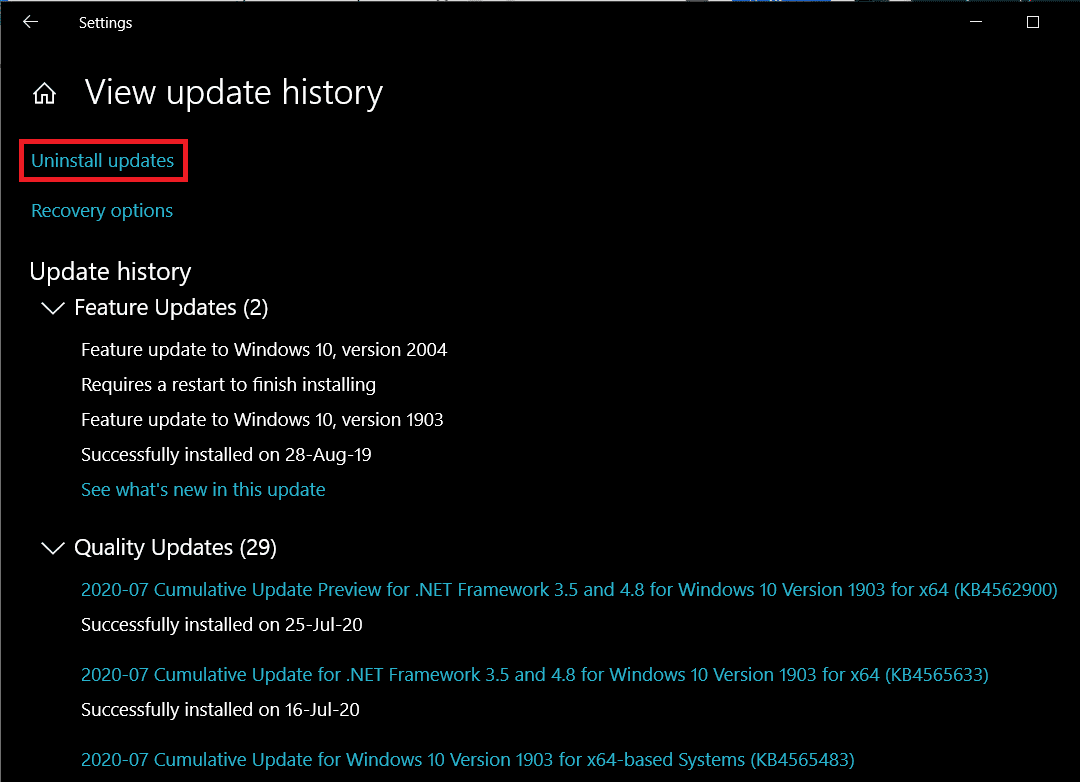
3. 그런 다음 업데이트 제거(Uninstall updates) 하이퍼링크를 클릭합니다.
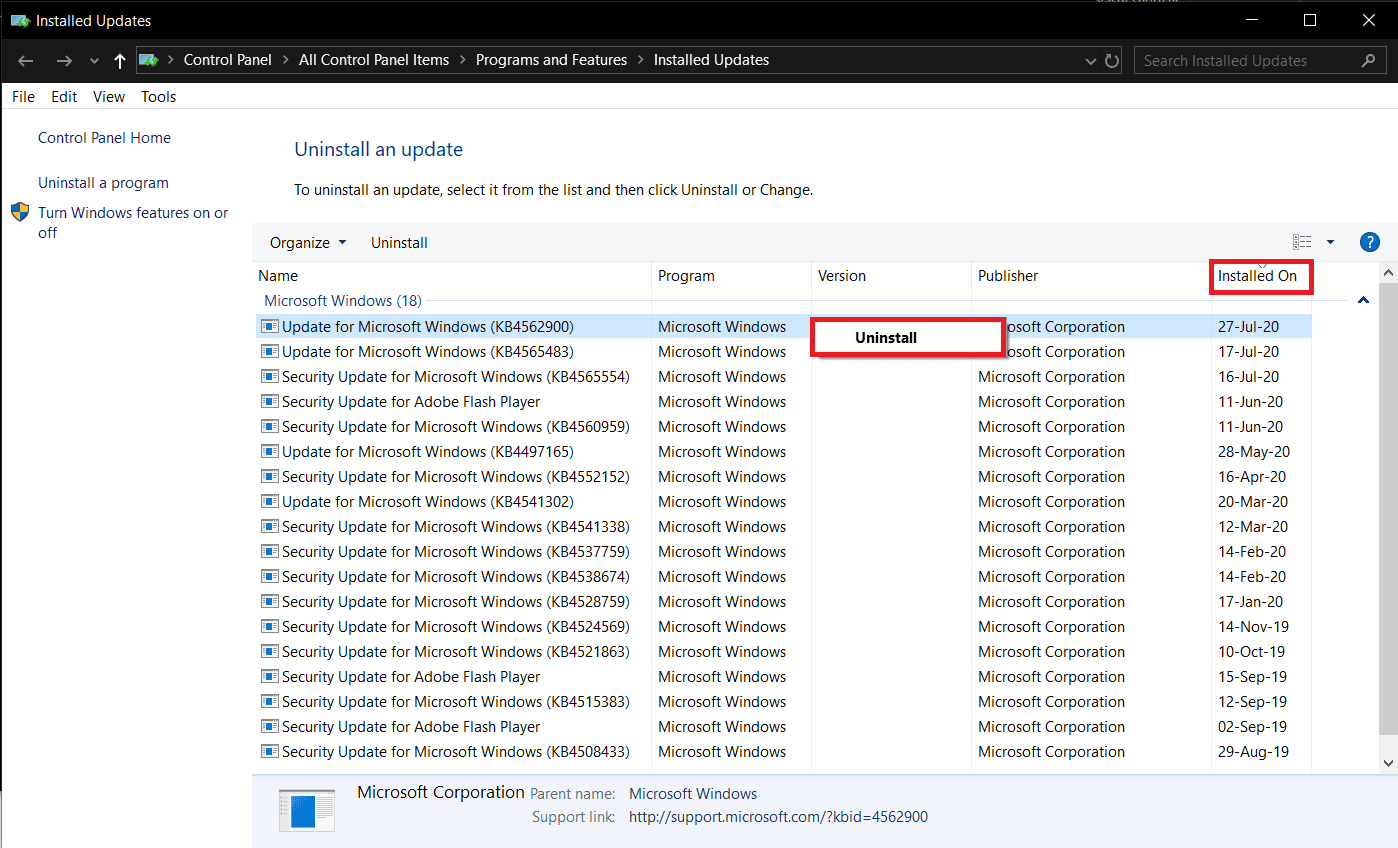
4. 다음 창에서 Installed On 헤더를 클릭하여 설치 날짜를 기준으로 모든 기능 및 보안 OS 업데이트를 정렬합니다.
5. 가장 최근에 설치된 업데이트를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭 하고 (Right-click )제거(Uninstall) 를 선택합니다 . 다음 화면 지침을 따릅니다.
추천:(Recommended:)
위의 방법 중 어떤 것이 Windows 10 컴퓨터의 성능을 부활시켰는지 아래 의견에 알려주십시오. 또한 컴퓨터가 계속 느리게 실행되는 경우 HDD 에서 SSD 로 업그레이드 ( SSD와 HDD 비교: 어느 것이 더 나은지(SSD Vs HDD: Which one is better) 확인 )하거나 RAM 양을 늘려 보십시오 .
How to Fix Windows 10 running slow after update
Microsoft, sinсe its inception, has been pretty consistent when it comes to updating its Windоws operating system. They regulаrly push various types of updates (feature pасk υpdate, service pack update, definition update, security update, tool updates, etc.) to their υsers across the globe. These updаtes include fixes for a number of bugs and issuеs that users аre unfortunately encountering on the current OS build along with new features to boost the overall performance and user experience.
However, while a new OS update may solve an issue, it can also prompt another few to appear. The Windows 10 1903 update of yesteryear was infamous for causing more problems than it solved. Some users reported that the 1903 update caused their CPU usage to shoot up by 30 percent and in some situations, by 100 percent. This made their personal computers frustratingly slow and had them pulling their hair out. A few other common issues that may occur after updating are extreme system freezes, prolonged startup times, unresponsive mouse clicks and key presses, blue screen of death, etc.
In this article, we will be providing you with 8 different solutions to improve your computer’s performance and make it as snappier as it was before you installed the latest Windows 10 update.

Fix Windows 10 running slow after update problem
Your Windows 10 computer may be running slow if the current update hasn’t been installed properly or is incompatible with your system. Sometimes a new update can damage a set of device drivers or render system files corrupt prompting low performance. Lastly, the update itself may be full of bugs in which case you will have to roll back to the previous build or wait for Microsoft to release a new one.
Other common solutions for Windows 10 running slow include disabling high-impact startup programs, restricting applications from running in the background , updating all device drivers, uninstalling bloatware and malware, repairing corrupt system files, etc.
Method 1: Look for any new update
As mentioned earlier, Microsoft regularly releases new updates fixing issues in the previous ones. If the performance issue is an inherent problem with an update, then chances are Microsoft is already aware and has most likely released a patch for it. So before we move onto the more permanent and lengthy solutions, check for any new Windows updates.
1. Press the Windows key to bring up the start menu and click on the cogwheel icon to open Windows Settings (or use the hotkey combination Windows key + I).

2. Click on Update & Security.

3. On the Windows Update page, click on Check for Updates.

4. If a new update is indeed available, download and install it as soon as possible to fix your computer’s performance.
Method 2: Disable Startup & Background Applications
All of us have a bunch of third-party applications installed that we barely use, but keep them nevertheless for when a rare opportunity arises. Some of these may have the permission to start automatically every time your computer boots up and as a result, increase the overall startup time. Along with these third-party applications, Microsoft bundles in a long list of native applications that are allowed to always run in the background. Restricting these background apps and disabling high-impact startup programs can help free up some useful system resources.
1. Right-click on the taskbar at the bottom of your screen and select Task Manager from the ensuing context menu (or press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard).

2. Switch to the Startup tab of the Task Manager window.
3. Check the Startup impact column to see which program utilizes the most resources and therefore, has a high impact on your startup time. If you find an application that you do not use frequently, consider disabling it from launching automatically at startup.
4. To do so, right-click on an application and select Disable (or click on the Disable button at the bottom-right).

To disable native applications from staying active in the background:
1. Open Windows Settings and click on Privacy.

2. From the left panel, click on Background apps.

3. Toggle off ‘Let apps run in the background’ to disable all background applications or go ahead and individually select which apps can continue running in the background & which ones can’t.
4. Restart your PC and see if you’re able to fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem.
Method 3: Perform a Clean Boot
If a specific application is causing your computer to run slow, you can pinpoint it by performing a clean boot. When you initiate a clean boot, the OS loads only the essential drivers and default applications. This helps avoid any software conflicts caused due to third-party applications that might be prompting low performance.
1. We will need to open the System Configuration application to perform a clean boot. To open it, type msconfig in either the Run command box (Windows key + R) or the search bar and press enter.

2. Under the General tab, enable Selective startup by clicking on the radio button next to it.
3. Once you enable Selective startup, the options underneath it will also unlock. Check the box next to Load system services. Ensure the Load startup items option is disabled (unticked).

4. Now, move over to the Services tab and tick the box next to Hide all Microsoft services. Next, click Disable all. By doing this, you terminated all third-party processes and services that were running in the background.

5. Finally, click on Apply followed by OK to save the changes and then Restart.
Also Read: Fix Unable To Download Windows 10 Creators Update
Method 4: Remove Unwanted and Malware applications
Third-party and native applications aside, malicious software is purposely designed to hog up system resources and damage your computer. They are notorious for finding their way onto computers without ever alerting the user. One should be extremely cautious when installing applications from the internet and avoid untrusted/unverified sources (most malware programs are bundled with other applications). Also, perform regular scans to keep these memory-hungry programs at bay.
1. Type Windows security in the Cortana search bar (Windows key + S) and press enter to open the built-in security application and scan for malware.

2. Click on Virus & threat protection in the left panel.

3. Now, you can either run a Quick Scan or run a more thorough scan for malware by choosing Full Scan from Scan options (or if you have a third-party antivirus or antimalware program like Malwarebytes, run a scan through them).
Method 5: Update All Drivers
Windows updates are infamous for messing up hardware drivers and causing them to become incompatible. Usually, it is the graphic card drivers that become incompatible/outdated and prompt performance issues. To resolve any driver-related problem, replace the outdated drivers with the latest ones via the Device Manager.

Driver Booster is the most popular driver updating applications for Windows. Head over to their official websites and download the installation file. Once downloaded, click on the .exe file to launch the installation wizard and follow all the on-screen prompts to install the application. Open the driver application and click on Scan Now.
Wait for the scanning process to complete and then individually click on the Update Drivers button next to each driver or the Update All button (you will require the paid version to update all drivers with a single click).
Method 6: Repair Corrupt System Files
A poorly installed update can also end up breaking important system files and slow down your computer. System files being rendered corrupt or going missing altogether is a common issue with feature updates and leads to a variety of errors when opening apps, blue screen of death, a complete system failure, etc.
To repair corrupt system files, you can either roll back to the previous Windows version or run an SFC scan. The latter of which is explained below (the former is the final solution in this list).
1. Search for Command Prompt in the Windows search bar, right-click on the search result, and select Run As Administrator.

You will receive a User Account Control pop-up requesting your permission to allow Command Prompt to make changes to your system. Click on Yes to grant permission.
2. Once the Command Prompt window opens up, carefully type the following command and press enter to execute.
sfc /scannow

3. The scanning process will take some time so sit back and let the Command Prompt do its thing. If the scan didn’t find any corrupt system files, then you will see the following text:
Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations.
4. Execute the below command (to repair Windows 10 image) if your computer continues to run slow even after running an SFC scan.
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

5. Once the command finishes processing, reboot your PC and see if you’re able to fix Windows 10 running slow after an update problem.
Also Read: Why are Windows 10 Updates Extremely Slow?
Method 7: Modify Pagefile size & Disable Visual Effects
Most users might be unaware of this, but along with your RAM and hard drive, there is another type of memory that dictates your computer’s performance. This additional memory is known as Paging File and is a virtual memory present on every hard disk. It serves as an extension to your RAM and your computer automatically transfers some data to the paging file when your system RAM is running low. The paging file also stores temporary data that hasn’t been accessed lately.
Since it is a type of virtual memory, you can manually adjust its values and fool your computer into believing that there is more space available. Along with increasing the Paging file size, you can also consider disabling the visual effects for a crispier experience (although the aesthetics will go down). Both these adjustments can be made through the Performance Options window.
1. Type Control or Control Panel in the Run command box (Windows key + R) and press enter to open the application.

2. Click on System. To make looking for the item easier, change the icon size to large or small by clicking on the View by option at the top-right.

3. In the following System Properties window, click on Advanced system settings on the left.

4. Click on the Settings… button under Performance.

5. Switch to the Advanced tab of the Performance Options window and click on Change…

6. Untick the box next to ‘Automatically manage paging file size for all drives’.
7. Select the drive on which you have installed Windows (normally the C drive) and click on the radio button next to Custom size.
8. As a rule of thumb, the Initial size should be equal to one and a half times of the system memory (RAM) and the Maximum size should be three times the initial size.

For example: If you have 8gb of system memory on your computer, then the Initial size should be 1.5 * 8192 MB (8 GB = 8 * 1024 MB) = 12288 MB, and consequently, the Maximum size would be 12288 * 3 = 36864 MB.
9. Once you have entered the values in the boxes next to Initial and Maximum size, click on Set.
10. While we have the Performance Options window open, let’s also disable all the visual effects/animations.
11. Under the Visual Effects tab, enable Adjust for best performance to disable all effects. Finally, click on OK to save and exit.

Method 8: Uninstall the new update
Ultimately, if none of the above solutions helped you improve your computer’s performance, it might be best for you to uninstall the current update and roll back to a previous build that didn’t have any of the issues you are currently experiencing. You can always wait for Microsoft to release a better and less troublesome update in the future.
1. Open Windows Settings by pressing Windows key + I and click on Update & Security.
2. Scroll down on the right panel and click on View update history.

3. Next, click on the Uninstall updates hyperlink.

4. In the following window, click on the Installed On header to sort all feature and security OS updates based on their installation dates.
5. Right-click on the most recently installed update and select Uninstall. Follow the on-screen instructions that follow.

Recommended:
Let us know which of the above methods revived the performance of your Windows 10 computer in the comments below. Also, if your computer continues to run slow, consider upgrading from an HDD to an SSD (Check out SSD Vs HDD: Which one is better) or try increasing the amount of RAM.



























