Windows 의 (Windows)시스템 구성(msconfig.exe)(System Configuration (msconfig.exe) ) 도구가 얼마나 뛰어난지 아십니까 ? 작지만 숨겨진 도구이지만 Windows 작동 방식에 대한 몇 가지 사항을 변경할 수 있습니다. 무엇보다도 시스템 구성(System Configuration ) 도구를 사용하면 Windows 시작 방법을 구성하고, 부팅 절차(boot procedure) 를 변경하고, 시작 서비스 및 프로그램을 선택하고, 일련의 유용한 관리 프로그램을 시작할 수도 있습니다. 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 으로 할 수 있는 일에 대해 더 알고 싶다면 다음 문서를 읽어보세요.
참고:(NOTE:) 이 문서는 Windows 10 , Windows 7 및 Windows 8.1 을 다룹니다 . 읽기 전에 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 을 시작하는 방법을 이미 알고 있다고 가정합니다 . 그렇지 않은 경우 먼저 Windows 에서 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 을 시작하는 8가지 방법 (모든 버전)을 읽으십시오. 또한 사용 중인 Windows(Windows) 버전을 모르는 경우 이 자습서가 도움이 될 것입니다. 어떤 버전의 Windows 를 설치했습니까?
1. Windows 시작 시(Windows startup) 로드되는 드라이버 및 서비스 선택
msconfig.exe 라고도 하는 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 도구 는 설정과 바로 가기가 있는 창입니다. 그것들은 모두 여러 탭으로 나뉘며 각 탭에서 다양한 항목에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 창의 첫 번째 탭은 일반(General) 이라고 하며 Windows 시작 방법을 구성할 수 있는 곳입니다.

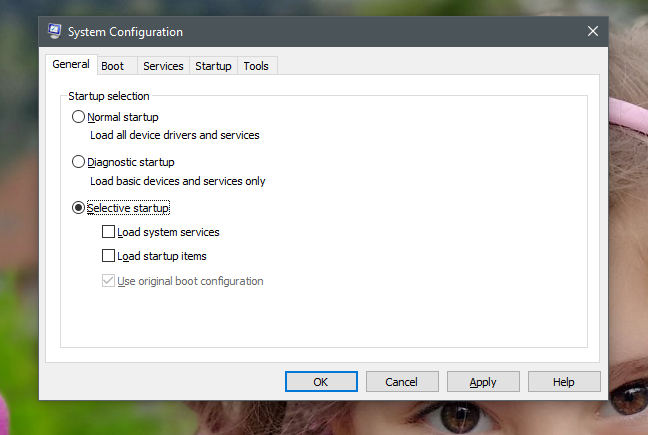
일반(General) 탭 의 "시작 선택"("Startup selection") 목록에서 Windows 가 다음을 수행 하도록 선택할 수 있습니다 .
-
"정상 시작": Windows가 설치된 ("Normal startup": )모든(ALL ) 시작 항목, 드라이버 및 서비스 와 함께 있는 그대로 시작됨을 의미합니다 . 이 모드는 부팅 시(boot time) 로드되는 드라이버, 서비스 또는 앱을 이미 일부 변경한 경우를 제외하고 대부분의 Windows 장치에서 기본적으로 선택되어야 합니다 .
-
"진단 시작"("Diagnostic startup") : 이 모드는 안전 모드(Mode) 로 부팅하는 것과 유사합니다 . 안전 모드 는 (Safe Mode)Windows 서비스와 드라이버 만 실행합니다 . 그 외에도 진단 시작 프로그램 은 네트워킹 서비스 또는 안티바이러스, (Diagnostic startup)방화벽 또는 보안 제품군(firewall or security suite) 과 같은 타사 응용 프로그램의 중요한 서비스를 실행할 수도 있습니다 . 이 모드는 시스템 불안정(system instability) 문제 의 원인이 되는 Windows 파일 및 서비스 를 배제하려는 경우에 유용합니다 . "진단 시작"("Diagnostic startup" ) 을 선택한 다음 적용(Apply) 을 클릭하거나 탭 하면 "선택적 시작"("Selective startup")선택된 것으로 표시되는 것입니다. 그러나 이는 지극히 정상적인 현상이므로 걱정할 필요가 없습니다. "진단 시작"("Diagnostic startup") 이 미리 정의된 설정 집합 이 있는 "선택적 시작"("Selective startup" ) 이기 때문에 발생합니다 .
-
"선택적 시작": ("Selective startup":)Windows 가 필수 서비스 및 드라이버로만 시작되도록 합니다. 또한 서비스 및 시작(Services and Startup) 탭 에서 실행할 다른 서비스 및 시작 항목을 선택할 수도 있습니다 .
시작 모드 사이를 전환하고 몇 가지 문제 해결을 수행한 다음 "정상 시작"("Normal startup") 을 다시 사용하는 경우 시작 시 모든 서비스와 시작 항목이 활성화 된다는 점에 유의하는 것도 중요합니다 .
Windows 에서 일부 앱, 드라이버 또는 서비스가 자동으로 시작되지 않도록 하려는 경우 서비스 및 시작 항목 목록을 살펴보고 다시 편집해야 합니다. 이 가이드의 뒷부분에서 그 방법을 볼 수 있습니다. 그러나 일단 변경하면 "선택적 시작"("Selective startup") 이 활성 시작 선택(startup selection) 으로 선택 됩니다.
2. PC에 설치된 운영 체제를 확인하고 기본 운영 체제를 선택하십시오.
시스템 구성(System Configuration) 도구 는 PC에 설치된 운영 체제 중 먼저 로드할 운영 체제를 선택하는 그래픽 방식도 제공합니다. 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 도구에서 부팅 탭으로 전환하면 컴퓨터 에(Boot) 설치된 모든 운영 체제를 볼 수 있으며 멀티 부팅 설정이 있는 경우 기본 운영 체제를 선택할 수 있습니다. (default one)새 기본 운영 체제(default operating system) 를 선택하려면 해당 운영 체제 를 클릭하거나 탭한(click or tap) 다음 "기본으로 설정"을 클릭합니다.("Set as default.")

3. PC 가 부팅할 운영 체제(operating system) 를 선택할 때까지 기다리는 시간을 선택합니다.
다중 부팅 설정이 있는 경우 또 다른 중요한 설정은 시간 초과(Timeout ) 설정입니다. 설정한 시간(초)은 부팅 시 사용 가능한 운영 체제 중 하나를 선택하기 위해 PC가 대기하는 시간을 나타냅니다. 설정 시간(set time) 동안 선택하지 않으면 기본 운영 체제가 시작됩니다.

기본적으로 시간 초과(Timeout) 는 30초로 설정됩니다. 다중 부팅 설정이 있는 경우 더 작은 값으로 설정할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 Timeout(Timeout) 을 10초로 설정하는 것을 선호합니다 . 이렇게 하면 다른 운영 체제 를 선택하지 않으면 (operating system)기본(default one) 운영 체제 의 총 부팅 타이밍(boot timing) 이 그다지 영향을 받지 않습니다.
4. 프로세서 코어 수 또는 사용할 수 있는 RAM 양과 같이 Windows 부팅 방법에 대한 일부 고급 설정을 변경합니다.(Windows)
컴퓨터에 설치된 Windows 운영(Windows operating) 체제 의 경우 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 도구를 사용하여 부팅 방식에 대한 복잡한 세부 정보를 구성할 수도 있습니다.
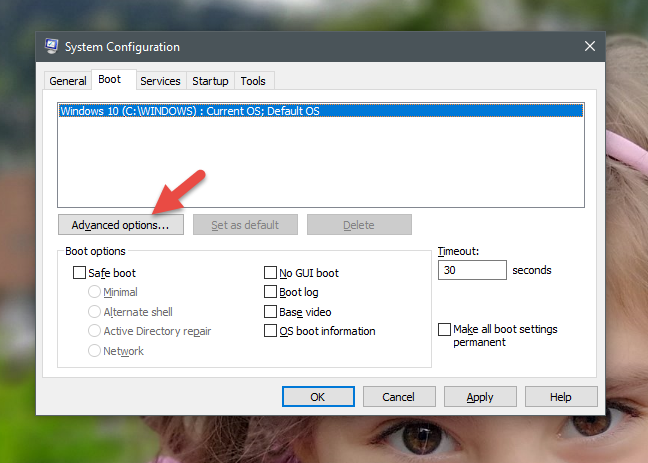
기존 운영 체제 각각에 대해 "고급 옵션"("Advanced options") 버튼 을 클릭하거나 탭하면 부팅 시 운영 체제(operating system) 에 할당된 프로세서(코어) 수 또는 사용 가능한 최대 RAM 양과 같은 항목을 설정할 수 있습니다. 그것.
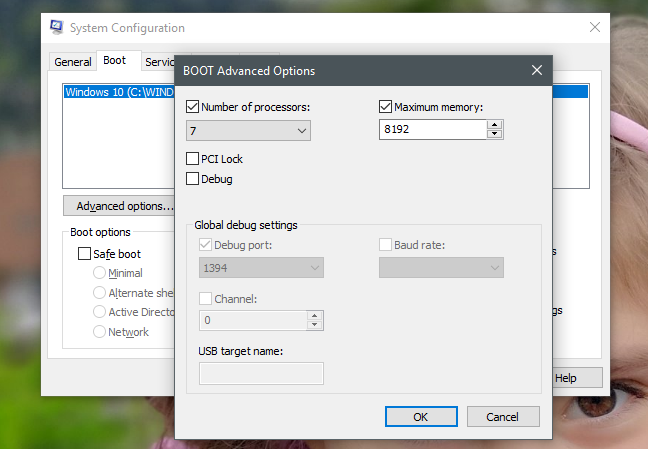
프로세서 코어 및 RAM 의 최대 수를 설정 하면 Windows 는 프로세서에 있는 실제 코어 수와 물리적 (Windows)RAM 의 양을 계속 올바르게 식별합니다 . 그러나 제한된 수의 프로세서 코어와 사용자가 설정한 최대 메모리만 사용할 수 있습니다.
5. Windows를 안전 모드로 부팅
PC에 설치된 각 Windows 운영 체제 에 대해 (operating system)시스템 구성 도구를 사용하여 (System Configuration)안전 모드(Safe Mode) 로 부팅할지 여부를 선택할 수도 있습니다 . 그렇게 하려면 부팅(Boot) 탭에서 "안전 부팅"("Safe boot") 옵션을 선택하고 사용 가능한 옵션 중 하나를 선택 해야 합니다.
-
최소 -(Minimal - ) 사용자 인터페이스가 있고 네트워킹 서비스가 활성화되지 않은 일반 안전 부팅입니다.
-
대체 셸 - (Alternate shell)안전 모드 에서 (Safe Mode)명령 프롬프트(Command Prompt) 를 엽니다 . 네트워킹 서비스와 그래픽 사용자 인터페이스(user interface) 가 비활성화됩니다.
-
Active Directory 복구 - (Active Directory repair)Active Directory 서비스 및 기능 을 추가로 실행하는 일반 안전 부팅입니다 .
-
네트워크(Network) - 네트워킹 서비스가 활성화된 일반 안전 부팅입니다.

Windows 의 (Windows)안전 모드(Safe Mode ) 에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 다음 가이드를 참조하세요.
- Windows 10 에서 안전 모드(Mode) 로 부팅하는 7가지 방법
- Windows 10 에서 (Windows 10)네트워킹(Networking) 을 사용하여 안전 모드(Mode) 로 부팅하는 6가지 방법
- Windows 7 에서 안전 모드(Mode) 로 부팅하는 3가지 방법
- Windows 8.1 에서 안전 모드로 부팅(Boot Into Safe Mode) 하는 5 가지(Ways) 방법
6. Windows 부팅(Windows boot) 로딩 화면 비활성화, 시작 프로세스(startup process) 기록 , 표준 비디오 드라이버 및 기타 사용
또한 부팅(Boot) 탭에서 시스템 구성 도구는 표준 및 (System Configuration)안전 모드(Safe Mode ) 부팅 절차 에 모두 적용할 수 있는 고급 옵션 세트를 제공합니다 .
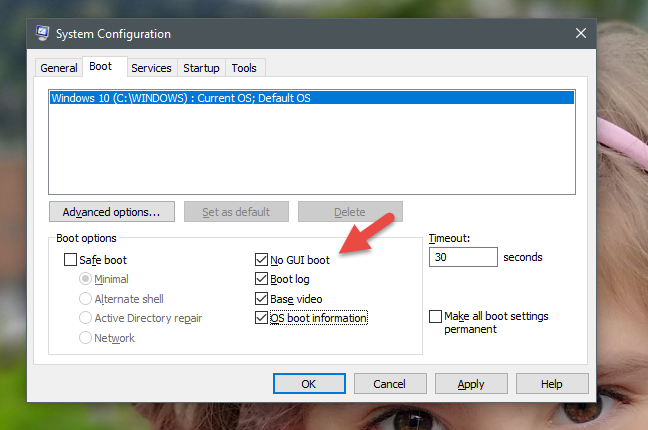
-
"GUI 부팅 없음"("No GUI boot") - 부팅하는 동안 일반적인 로딩 화면(loading screen) 이 표시되지 않고 정보가 없는 검은색 화면만 표시됩니다.
-
"부팅 로그"("Boot log") - 부팅하는 동안 Windows 는 (Windows)시작 프로세스(startup process) 에 대한 정보가 포함된 전체 로그를 작성합니다 . 일반적으로 "C: WindowsNtbtlog.txt(WindowsNtbtlog.txt) " 위치에서 찾을 수 있습니다 .
-
"기본 비디오"("Base video") - 이 옵션은 형편없는 비디오 드라이버를 방금 설치한 경우에 유용합니다. 비디오 카드(video card) 에 특정한 드라이버 대신 Windows 와 함께 제공되는 표준 비디오 드라이버만 로드한다는 차이점이 있는 표준 Windows 시작(Windows startup) 을 만듭니다 .
-
"OS 부팅 정보" - 이 옵션은 ("OS boot information")"GUI 부팅 없음"("No GUI Boot.") 과 함께 사용해야 합니다 . 일반적인 Windows 로딩 화면은 시작 프로세스(startup process) 동안 로드된 드라이버에 대한 완전한 정보를 표시하는 검은색 화면으로 대체됩니다 . 부팅하는 동안 Windows 가 충돌하는 경우 이 시각화 모드(visualization mode) 는 충돌을 일으키는 드라이버를 식별하는 데 유용할 수 있습니다.
7. Windows에서 시작할 서비스 선택
시스템 구성(System Configuration) 도구 의 서비스(Services) 탭에는 Windows 가 시작될 때 시작되는 모든 서비스 목록이 표시 됩니다. 각 서비스에 대해 해당 이름, 제조업체, 현재 상태 및 비활성화된 경우 비활성화된 날짜가 표시됩니다.
시작할 때 실행할 서비스를 선택하고 실행하지 않을 서비스를 선택 취소할 수 있습니다. 응용 프로그램에서 설치한 타사 서비스만 보려면 "모든 Microsoft 서비스 숨기기" 확인란을 선택합니다.("Hide all Microsoft services.")

이 탭에서 선택한 항목은 일반(General) 탭 에서 현재 시작 선택 항목 에만 적용됩니다. (startup selection)"정상 시작"("Normal startup,") 을 사용 중이고 일부 서비스를 비활성화한 경우 시작 선택 이 (startup selection)"선택적 시작"("Selective startup.") 으로 자동 변경됩니다 .
시작 시 실행을 중지할 서비스를 결정하는 데 도움이 필요하면 이 가이드를 읽어보십시오. 어떤 Windows 서비스를 언제 비활성화하는 것이 안전합니까?
8. 시작 프로그램 관리( Windows 7 만 해당 )
Windows 10 또는 Windows 8.1 을 사용 하는 경우 시작 탭에 (Startup)"작업 관리자 열기"("Open Task Manager.") 에 대한 링크만 제공 됩니다. 컴퓨터의 시작 앱 관리가 (startup apps)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 사용하여 수행 되기 때문 입니다.

그러나 Windows 7 을 사용하는 경우 시작 탭에는 (Startup)Windows 가 시작될 때 시작되는 모든 프로그램 및 파일 목록이 표시 됩니다. 각 항목에 대해 이름, 제조업체, 시작하는 데 사용된 명령(일반적으로 사용되는 경우 프로그램 및 추가 매개변수의 경로인 경우), 항목 이 저장된 레지스트리 시작 위치(registry startup location) 및 비활성화된 날짜가 표시됩니다. 비활성화되었습니다.

레지스트리 위치(registry location) 에 대해 기억해야 할 한 가지는 HKLM 으로 시작하는 항목이 표시되는 경우 시작 항목이 "전역"임을 의미 하며 활성 운영 체제 에 정의된 모든 (operating system)사용자 계정(user account) 에 적용됩니다 . 한 사용자 계정(user account) 에서 비활성화하면 모든 사용자 계정(user account) 에 대해 비활성화됩니다 .
HKCU 로 시작하는 위치 는 현재 사용자 계정(user account) 에 대해서만 활성화된 시작 항목을 위한 것 입니다. 다른 사용자 계정(user account) 에 대해 시작되지 않을 수 있습니다 . 또한 완전히 시작되지 않도록 하려면 각 사용자 계정(user account) 에 대해 개별적으로 비활성화해야 합니다.
서비스(Services) 탭과 마찬가지로 선택 항목은 일반(General) 탭 에서 현재 시작 선택 항목(startup selection) 에 적용됩니다 .
9. 관리 프로그램 및 패널 실행
시스템 구성 의 (System Configuration)도구(Tools) 탭 과 그 기능 에 대해 아는 사람은 거의 없습니다 . 클릭하면 시스템 정보(System Information) , 레지스트리 편집기(Registry Editor) , 이벤트 뷰어(Event Viewer) , 성능 모니터 등과 같은 (Performance Monitor)Windows 관리 도구 목록이 나타 납니다.
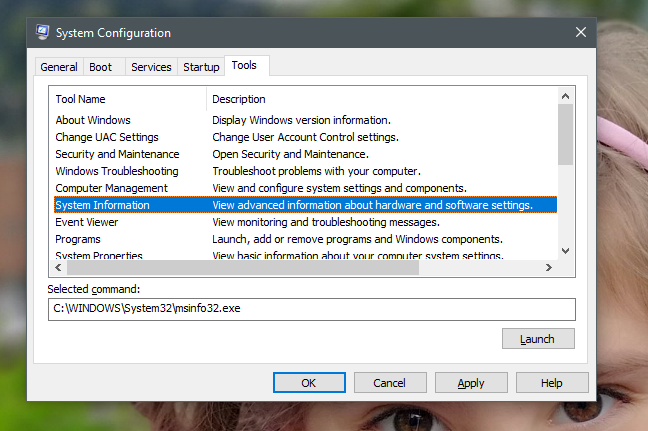
각 도구에 대해 시스템 구성(System Configuration) 에 해당 이름과 설명(name and description) 이 표시 됩니다. 클릭하거나 탭하면 선택한 명령(Selected command) 필드에서 시작하는 데 사용된 명령을 볼 수 있습니다. 사용 가능한 도구를 실행하려면 원하는 도구를 선택하고 시작(Launch) 을 클릭하거나 탭 합니다.

보시다시피 시스템 구성 의 (System Configuration)도구(Tools) 탭은 시스템 안정성 또는 성능 문제(system stability or performance problems) 를 해결하는 동안 일반적으로 사용되는 관리 도구를 나열하므로 편리합니다 .
시스템 구성(System Configuration) 에서 변경한 내용을 저장합니다.
원하는 모든 변경을 완료한 후 적용(Apply) 또는 확인(OK) 을 눌러 적용하는 것을 잊지 마십시오 . 또한 도구를 처음 사용하는 경우 도구를 닫을 때 새 설정을 적용하려면 PC를 다시 시작해야 한다는 메시지가 표시될 수 있습니다.
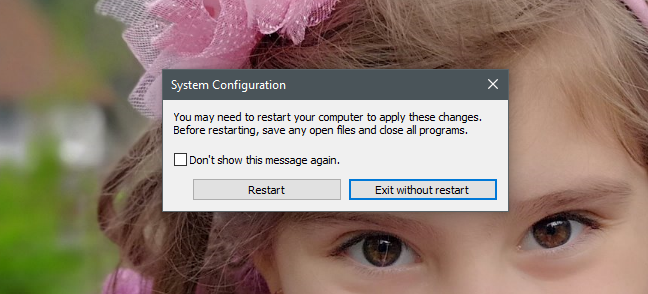
이 메시지를 다시 표시하지 않으려면 "이 메시지를 다시 표시하지 않음"("Don't show this message again") 확인란을 선택하고 원하는 다시 시작 옵션(restart option) 을 선택하십시오.
(Are)시스템 구성 도구(System Configuration tool) 를 사용하여 Windows 작동 방식을 변경하고 있습니까 ?
보시다시피 시스템 구성(msconfig.exe) 유틸리티는 (System Configuration (msconfig.exe) )Windows 시작 및 작동 방식을 변경하려는 사람들에게 유용한 기능을 제공하는 다목적 도구입니다 . Windows 컴퓨터 의 (Windows computer)시작 프로세스(startup process) 를 관리할 뿐만 아니라 안정성 및 성능 문제(stability and performance problems) 를 해결하는 데도 탁월한 도구가 될 수 있습니다 . Windows 를 구성하는 데 사용하고 있습니까? 당신은 그것에 문제가 있었나요? 아래의 의견 섹션에서 논의해 보겠습니다 .(Let)
9 things you can do with System Configuration, in Windows
Do you know how excellent the System Configuration (msconfig.exe) tool from Windows is? Although it is a small and somewhat hidden tool, it allows you to change quite a few things about the way Windows works. Among other things, the System Configuration tool lets you configure how Windows starts, change the boot procedure, select startup services, and programs, and also start a series of useful administrative programs. If you want to know more about the things you can do with System Configuration, read this article:
NOTE: This article covers Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1. Before reading it, you should know that we assume you already know how to start System Configuration. If you do not, read this first: 8 ways to start System Configuration in Windows (all versions). Also, if you do not know the version of Windows that you are using, this tutorial should help: What version of Windows do I have installed?
1. Choose what drivers and services are loaded at Windows startup
The System Configuration tool, also known as msconfig.exe, is a window with settings and shortcuts. They are all split into several tabs, and each tab gives you access to different things. The first tab in the System Configuration window is called General, and it is the place where you can configure how Windows starts.

In the "Startup selection" list from the General tab, you can choose to make Windows do a:
-
"Normal startup": meaning that Windows starts as is, with ALL the installed startup items, drivers, and services. This mode should be selected by default on most Windows devices, except when you have already made some changes to what drivers, services or apps are loaded at boot time.
-
"Diagnostic startup": this mode is similar to booting into Safe Mode. Safe Mode runs only Windows services and drivers. Besides them, the Diagnostic startup might also run, on top of them, networking services or important services from third-party applications such as your antivirus, firewall or security suite. This mode is useful if you want to rule out Windows files and services as being the source of system instability problems. Note that if you select the "Diagnostic startup" and then click or tap Apply, the "Selective startup" is the one shown as selected. However, there is nothing to worry about, as this is quite normal. It happens because the "Diagnostic startup" is a "Selective startup" with a predefined set of settings.
-
"Selective startup": makes Windows start only with its essential services and drivers. Furthermore, it also allows you to select other services and startup items that you want to run, from the Services and Startup tabs.

It is also important to note that if you switch between startup modes, do some troubleshooting and then go back to using the "Normal startup" again, all the services and startup items are going to be enabled at startup.
If what you want is to stop some apps, drivers or services from starting automatically with Windows, you need to go through the list of services and startup items and edit them again. You can see how to do that, later in this guide. For now though, note that once you make changes, the "Selective startup" is going to be checked as the active startup selection.
2. See what operating systems are installed on your PC and choose which one is the default
The System Configuration tool also offers a graphical way of choosing which of the operating systems installed on your PC loads first. In the System Configuration tool, switch to the Boot tab, and you can view all the operating systems installed on your computer and select the default one if you have a multi-boot setup. To select a new default operating system, click or tap on it and then on "Set as default."

3. Choose how long the PC waits for you to select the operating system to be booted
If you have a multi-boot setup, another important setting is the Timeout setting. The number of seconds you set represents how long your PC waits for you to select one of the available operating systems when booting. If no choice is made during the set time, the default operating system starts.

By default, the Timeout is set to 30 seconds. If you have a multi-boot setup, you might want to set it to a smaller value. We, for instance, prefer to set the Timeout to only 10 seconds. This way, if we do not select another operating system, the total boot timing of the default one is not affected that much.
4. Change some advanced settings about how Windows boots, like how many processor cores or how much RAM it can use
For the Windows operating system installed on your computer, the System Configuration tool also lets you configure complicated details about the way it boots.

For each of the existing operating systems, if you click or tap on the "Advanced options" button, you can set things such as the number of processors (cores) allocated to the operating system at boot, or the maximum amount of RAM available to it.

If you set a maximum number of processor cores and RAM, Windows continues to correctly identify the real number of cores that the processor has and the amount of physical RAM. However, it can only use the limited number of processor cores and the maximum memory that you have set.
5. Make Windows boot into Safe Mode
For each Windows operating system installed on your PC, the System Configuration tool also lets you select if you want to make it boot into Safe Mode. To do that, in the Boot tab, you must check the option called "Safe boot" and select one of its available options:
-
Minimal - the normal safe boot, with a user interface and no networking services enabled.
-
Alternate shell - opens the Command Prompt in Safe Mode. The networking services and the graphical user interface are disabled.
-
Active Directory repair - a normal safe boot which runs, additionally, the Active Directory services and features.
-
Network - the normal safe boot with networking services enabled.

If you want to read more about the Safe Mode in Windows, these guides might interest you:
6. Disable the Windows boot loading screen, log the startup process, use standard video drivers and others
Also in its Boot tab, the System Configuration tool gives you a set of advanced options which can be applied to both standard and Safe Mode boot procedures:

-
"No GUI boot" - during boot, you are not shown the usual loading screen, only a black screen with no information.
-
"Boot log" - during boot Windows writes a complete log with information about the startup process. Usually, it can be found at this location: "C:WindowsNtbtlog.txt."
-
"Base video" - this option is handy if you just installed lousy video drivers. It makes a standard Windows startup, with the difference that it loads only the standard video drivers that come with Windows, instead of the ones specific to your video card.
-
"OS boot information" - this option should be used together with "No GUI Boot." The usual Windows loading screen will get replaced with a black screen, displaying complete information about the drivers that are loaded during the startup process. If your Windows crashes during boot, this visualization mode can be useful to identify the driver that causes the crash.
7. Select what services are started with Windows
The Services tab from the System Configuration tool shows a list of all the services that start when Windows starts. For each service, you see its name, the manufacturer, the current status and the date when it was disabled if it was disabled.
You can check the services you want to run at startup and uncheck the ones you do not. If you desire to see only third-party services, installed by your applications, check the box that says "Hide all Microsoft services."

The selections you make in this tab are applied only to your current startup selection, from the General tab. If you were using a "Normal startup," and then you disabled some services, the startup selection gets changed automatically to "Selective startup."
If you need help in deciding which services to stop from running at startup, read this guide: Which Windows services are safe to disable and when?.
8. Manage the startup programs (only in Windows 7)
If you are using Windows 10 or Windows 8.1, the Startup tab gives you just a link to "Open Task Manager." This is because the management of your computer's startup apps is done using the Task Manager.

However, if you are using Windows 7, the Startup tab shows a list of all the programs and files that start when Windows starts. For each item, you see its name, the manufacturer, the command used to start it, which is usually the path towards the program and additional parameters if used, and the registry startup location where it is stored and the date when it was disabled if it was disabled.

One thing to remember about the registry location is that, if you see one starting with HKLM, it means that the startup item is "global" - applied to all user accounts defined on the active operating system. Disabling them from one user account means that they get disabled for all user accounts.
The locations starting with HKCU are for startup items active only for the current user account. They might not be starting up for other user accounts. Also, they need to be disabled individually, for each user account, if you want to prevent them from starting altogether.
Just like the Services tab, the selections you make are applied to your current startup selection, from the General tab.
9. Launch administrative programs and panels
Few people know about the Tools tab in System Configuration and what it does. If you click on it, you get a list of Windows administrative tools such as System Information, the Registry Editor, Event Viewer, Performance Monitor and so on.

For each tool, System Configuration shows its name and description. If you click or tap on it, you can see the command used to start it, in the Selected command field. To run any of the available tools, select the one you want and click or tap Launch.

As you can see, the Tools tab from System Configuration is handy as it lists administrative tools generally used during troubleshooting system stability or performance problems.
Save the changes you have made in System Configuration
After you are done making all the changes you wanted, do not forget to press Apply or OK, so that they are applied. Also, if you are using the tool for the first time, when you close it, you might be informed that you need to restart your PC for the new settings to take effect.

If you do not want to see this message again, check the box that says "Don't show this message again" and choose the restart option you prefer.
Are you using the System Configuration tool to change the way Windows works?
As you can see, the System Configuration (msconfig.exe) utility is a versatile tool that offers useful features for people who want to change the way Windows starts and works. It can be an excellent tool for managing the startup process of your Windows computer but also for troubleshooting stability and performance problems. Are you using it to configure Windows? Have you had any issues with it? Let's discuss in the comments section below.














