Windows 는 (Windows)Windows 레지스트리(Windows Registry) 라고 하는 계층적 파일 기반 데이터베이스에 작동하도록 하는 거의 모든 것을 저장합니다 . 레지스트리에는 운영 체제(operating system) , 프로그램, 서비스, 구성 요소 및 기타 거의 모든 것에 대한 모든 구성 설정이 포함되어 있습니다. 아이콘의 크기부터 작업 표시줄의 색상까지 모든 것이 거기에 저장됩니다.
레지스트리는 수백만 개의 키와 값으로 구성됩니다. 키는 폴더로, 값은 폴더 안에 저장된 데이터로 생각할 수 있습니다. 레지스트리 편집기(registry editor) 에서 키 는 실제로 폴더처럼 보이고 값은 실제 설정을 유지하는 것입니다. 레지스트리의 각 키는 하나 이상의 값을 가질 수 있습니다. 마치 폴더에 둘 이상의 파일이 저장될 수 있는 것과 같습니다.
또한 값은 String(String) , Binary , DWORD , QWORD 등을 포함한 다양한 유형의 데이터를 저장할 수 있습니다 . 그 수준의 세부 사항을 이해할 필요는 없지만 레지스트리의 구조를 이해하기를 바랍니다.

레지스트리 백업과 관련하여 실제로 두 가지 옵션이 있습니다. 내보내기를 통해 레지스트리의 일부를 수동으로 백업하거나 시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 사용하여 전체 레지스트리를 백업하는 것 입니다. 레지스트리를 변경할 때 항상 복원 지점(restore point) 을 만든 다음 레지스트리의 편집된 섹션도 백업하는 것이 좋습니다.
전체 레지스트리를 내보내는 방법이 있지만 여러 가지 이유로 좋은 옵션이 아닙니다. 첫째, 어딘가에 저장해야 하는 큰 파일을 얻게 될 것입니다. 둘째, 설정을 하나만 변경하는 경우 나중에 전체 레지스트리를 다시 가져오려고 하면 내보내기 후 레지스트리의 다른 부분에 기록된 다른 많은 새로운 값을 덮어쓸 수 있습니다. 이것은 실제로 더 많은 문제와 손상을 유발할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, 많은 키가 Windows(Windows) 에서 사용되어 단순히 작성되지 않기 때문에 전체 레지스트리를 다시 가져오지 못할 수도 있습니다.
전체 레지스트리를 백업 및 복원하는 가장 좋은 방법은 시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 사용하는 것 입니다. 따라서 변경 시에는 먼저 복원 지점(restore point) 을 생성한 후 수동으로 편집된 부분만 백업하십시오. 문제가 있는 경우 Windows 에서 (Windows).reg 파일(.reg file) 을 두 번 클릭하여 내보낸 섹션을 언제든지 다시 로드할 수 있습니다 .
레지스트리 변경(registry change) 으로 인해 문제가 더 심각해져서 더 이상 Windows 에 들어갈 수 없는 경우 에는 고급 복구 (Advanced Recovery)옵션(Options) 을 시작하고 이전에 생성한 복원 지점(restore point) 을 선택하기만 하면 됩니다. 두 가지 방법 모두 아래에서 자세히 설명하겠습니다(detail below) .
레지스트리 편집기 열기
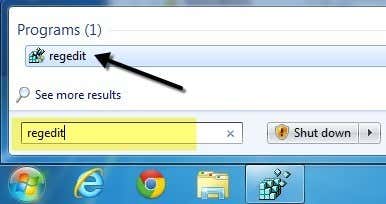
먼저 레지스트리 편집기(registry editor) 를 여는 방법에 대해 알아보겠습니다 . 거의 모든 최신 버전의 Windows 에서 시작 버튼 을 클릭 하고 regedit 를 입력 하여 (Start button and typing)레지스트리 편집기(registry editor) 를 열 수 있습니다 .
레지스트리를 백업하는 방법을 배우려고 하는 동안 이 문서를 발견했다는 점을 고려하면 이 작업을 수행하는 방법을 이미 알고 있을 것입니다. 분명히 레지스트리를 변경하기 전에 항상 백업해야 합니다. 이제 Windows 레지스트리(Windows registry) 를 백업할 수 있는 다양한 방법에 대한 이 기사의 요점을 살펴보겠습니다 .
Backup Parts/Sections레지스트리의 백업 부분/섹션
많은 내 게시물 에서 레지스트리에서 키 또는 값 을 편집해야 하는 조정 또는 팁을 언급했습니다. (key or value)여기저기서 단일 변경을 수행하려는 경우 전체 레지스트리를 반드시 백업할 필요는 없습니다.
다음 키에 저장된 값을 편집한다고 가정해 보겠습니다.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE – SOFTWARE – Microsoft – Windows – CurrentVersion – Explorer
탐색기(Explorer) 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭 하고 내보내기(Export) 를 선택 하여 모든 하위 키 및 해당 값과 함께 전체 키를 백업할 수 있습니다.

기본 Explorer(Explorer key) 키 아래에 꽤 많은 다른 하위 키가 있음을 알 수 있습니다 . 기본적으로 하위 키 및 값과 함께 선택한 분기만 내보내집니다. 전체 레지스트리를 내보내려면 .reg 파일을 저장할 때 내보내기 범위(Export Range) 에서 모두(All) 를 선택해야 합니다.

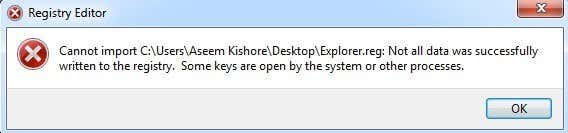
다시 말하지만 , 파일을 다시 가져오려고 할 때 (Again) 가져올 수 없음( Cannot import) 오류가 발생 하므로 이러한 방식으로 전체 레지스트리를 백업하지 않는 것이 좋습니다 .
따라서 선택한 분기만 내보내는 것을 고수하면 나중에 레지스트리 파일(registry file) 을 다시 가져올 수 있는 더 나은 기회를 갖게 됩니다. 이제 시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 사용하여 레지스트리의 전체 백업을 수행하는 방법 에 대해 이야기해 보겠습니다 .
(Backup Entire Registry)시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 통해 전체 레지스트리 백업
시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 사용하면 Windows 가 잠긴 문제와 사용 중인 문제를 모두 처리 하므로 이전 상태로 복원하는 데 문제가 발생하지 않습니다 . Windows 를 사용하는 동안 항상 복원 지점(restore point) 을 생성하며 매우 간단합니다.
시작(Start) 을 클릭 하고 복원 지점 만들기(Create restore point) 를 입력 하고 첫 번째 결과를 클릭합니다. 시스템 속성(System Properties) 대화 상자 의 시스템 보호(System Protection) 탭으로 바로 구매하게 됩니다 .

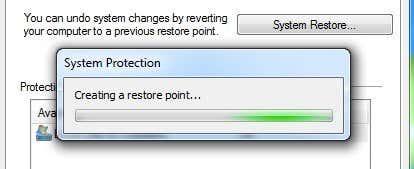
하단 에 있는 만들기(Create) 버튼을 클릭하면 설명을 묻는 또 다른 대화 상자가 나타납니다. 만들기(Create) 버튼을 클릭 하면 복원 지점(restore point) 이 생성됩니다.
복원 지점(restore point) 을 만드는 데 몇 분 밖에 걸리지 않습니다 . 완료되면 이전에 생성한 복원 지점(restore point) 을 두 가지 방법으로 복원할 수 있습니다. Windows의 동일한 시스템 복원(System Restore) 대화 상자 또는 고급 복구 옵션(Advanced Recovery Options) 화면을 사용합니다. 아래에서 두 가지 방법을 모두 보여 드리겠습니다.
Windows를 통해 레지스트리 복원
여전히 Windows를 시작하고 시스템에 로그인 할 수 있는 경우 (Windows and log)시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 열어 레지스트리 복원을 시도할 수 있습니다 . 시작을 (Start and type)클릭(Click) 하고 시스템 복원을 입력(system restore and click) 하고 첫 번째 결과를 클릭하십시오.
시스템 복원 대화 상자(System Restore dialog) 가 나타나면 계속해서 다음(Next) 을 클릭하십시오 . 다음 화면에서 현재 시스템에 있는 다른 모든 복원 지점 목록을 볼 수 있습니다.

자동으로 생성된 복원 지점과 함께 수동으로 생성된 복원 지점도 볼 수 있습니다. 더 많은 복원 지점 표시( Show more restore points) 상자를 선택하여 시스템에 저장된 모든 복원 지점을 볼 수 있습니다 . 영향을 받는 프로그램 검색(Scan for affected programs) 버튼 을 클릭 하면 복원 지점(restore point) 이 생성된 후 설치되어 제거된 프로그램 목록이 표시됩니다. 또한 복원 지점(restore point) 이 생성 된 후 제거되어 복원될 프로그램도 알려줍니다 .
다음(Next) 을 클릭 하고 마침(Finish) 을 클릭하면 됩니다. 시스템이 이전 복원 지점(restore point) 으로 되돌아 갈 것이고 당신은 갈 수 있을 것입니다. 시스템 복원(System Restore) 은 시스템 상태를 변경할 때 개인 데이터를 변경하지 않습니다. 레지스트리, 프로그램 및 시스템 파일만 봅니다.
복구 (Recovery)옵션(Options) 을 통해 레지스트리(Registry) 복원
Windows 에 로그인할 수 없는 경우 에도 시스템 복원(system restore) 을 사용할 수 있지만 Windows 7의 고급 부팅 옵션 과 (Advanced Boot Options)Windows 8 및 Windows 10 의 (Windows 10)고급 복구 옵션(Advanced Recovery Options) 을 통해서만 가능 합니다 . 세 가지 운영 체제마다 방법이 약간 다르기 때문에 아래에서 모두 설명하겠습니다.
윈도우 7 복구
Windows 7 의 경우 컴퓨터를 다시 시작한 다음 초기 부팅 중에 F8 키 를 눌러야 합니다. (F8 key)그러면 고급 부팅 옵션(Advanced Boot Options) 화면이 표시되고 첫 번째 옵션은 컴퓨터 복구(Repair Your Computer) 입니다.

그것을 선택하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다(Enter) . 그러면 시스템 복구 옵션 대화 상자가 로드되며 여기에서 (e System Recovery Options)시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 선택해야 합니다 .

다시 되돌리려는 복원을 선택하기만 하면 됩니다. 일반적으로 Windows(Windows) 를 로드하는 데 문제가 있는 경우 고급 부팅 옵션 화면(Advanced Boot Options screen) 이 자동으로 나타납니다.
F8을 사용하여 부팅 옵션을 로드할 수 없는 경우 시스템 복구 디스크(System Repair Disc) 를 사용해야 할 수 있습니다 . 시작을 클릭 하고 시스템 복구 디스크 (system repair disc)를 입력(Start and typing) 하여 모든 Windows 7 PC 에서 복구 디스크(repair disc) 를 만들 수 있습니다 .

CD 또는 DVD를 넣고 디스크 만들기(Create disc) 버튼을 클릭합니다. 이 디스크가 있으면 이 디스크에서 직접 부팅하여 위에 표시된 시스템 복구(system recovery) 옵션을 얻을 수 있습니다. 확인해야 할 유일한 사항은 부팅 순서에 CD/DVD ROM 드라이브가 먼저 나열되어 있다는 것 입니다.

윈도우 8 복구
Windows 8 에서는 전체 복구 절차와 GUI(recovery procedure and GUI) 가 완전히 다릅니다. 이전 의 지루한 DOS 인터페이스(DOS interface) 대신, 이제 일을 훨씬 쉽게 만들어주는 멋진 현대적인 GUI 를 갖게 되었습니다.(GUI)
이 새 인터페이스에 액세스하려고 할 때 F8이 더 이상 작동하지 않습니다. 운 좋게도 (Luckily)Windows 8 에서 고급 부팅 옵션 화면으로 이동하는 데 사용할 수 있는 다양한 방법에 대한 게시물을 이미 작성했습니다 . 기본 화면으로 이동하면 문제 해결(Troubleshoot) 을 클릭합니다 .
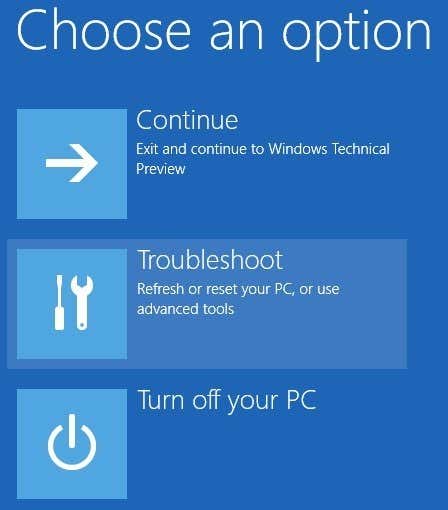
문제 해결(Troubleshoot) 섹션 에서 맨 아래 에 있는 고급 옵션(Advanced options) 을 클릭 합니다.

마지막으로 마지막 화면 에서 시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 클릭하면 친숙한 시스템 복원 대화 상자가 표시 되어 되돌릴 복원 지점 을 선택할 수 있습니다.(restore point)

Windows 8 에서는 Windows 7 에서와 같이 (Windows 7)시스템 복구(system repair) 디스크 를 만들 거나 USB 복구 드라이브(recovery drive) 를 만들 수 있습니다 . 복구 디스크(repair disc) 를 생성하려면 시작을(Start and type) 클릭 하고 recdisc.exe 를 입력하고 복구 드라이브 에 복구 (recovery drive)드라이브 유형(recovery drive type) 을 생성합니다 .

다시 말하지만, 현재 PC에서 복구 옵션을 로드할 수 없는 경우에만 다른 컴퓨터를 사용하여 생성하면 됩니다.
윈도우 10 복구
Windows 10 의 절차 는 고급 부팅 옵션 화면으로 이동하면 정확히 동일하지만 Windows 에서는 약간 다릅니다 . Windows 10 에서 (Windows 10)시작 메뉴(Start Menu) 가 완전한 형태로 돌아왔 으므로 이를 클릭한 다음 설정(Settings) 을 클릭할 수 있습니다 .

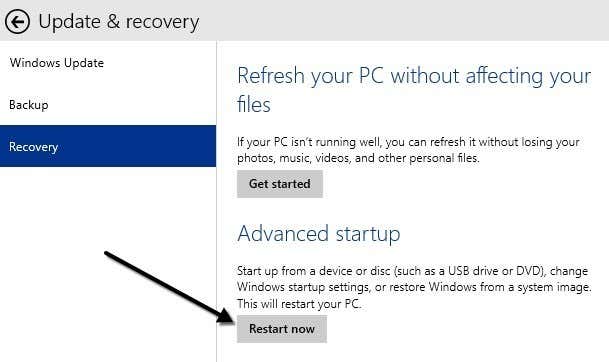
그런 다음 설정(Settings) 대화 상자 에서 업데이트 및 복구 를 클릭합니다. ( Update and recovery)보시다시피 Windows 10 의 (Windows 10)설정 대화 상자(Settings dialog) 는 Windows 8(Windows 8) 의 설정 대화 상자와 완전히 다릅니다 .

마지막으로 고급 시작(Advanced startup) 아래에서 지금 다시 시작( Restart now) 버튼 을 클릭할 수 있습니다 . 이렇게 하면 문제 해결(Troubleshoot) 을 클릭할 동일한 옵션 선택(Choose an option) 화면이 표시됩니다 .
위의 자세한 지침을 통해 Windows 7(Windows 7) , Windows 8 및 Windows 10 에서 레지스트리를 안전하고 쉽게 백업 및 복원할 수 있기를 바랍니다 . 질문이 있으시면 언제든지 댓글을 남겨주세요. 즐기다!
Ultimate Guide to Backing Up and Restoring the Windows Registry
Windows stores just about everything that makes it work in a hierarchal file-based database called the Windows Registry. The regіstry соntains all the configuration settingѕ for the operating system, programs, services, components and pretty much everything else. Everything from the size of the icons to the colоr of the taskbаr is stored thеre.
The registry is made up of millions of keys and values. You can think of keys as folders and values as the data stored inside the folders. In the registry editor, keys actually look like folders and values are what hold the actual settings. Each key in the registry can have more than one value, kind of like a folder can have more than one file stored inside.
Also, values can store data of different types including String, Binary, DWORD, QWORD, and more. You don’t really need to understand that level of detail, but hopefully you understand the structure of the registry.

In terms of backing up the registry, you really have two options: backup parts of the registry manually via export or backup the entire registry using System Restore. When you make a change to the registry, it’s always a good idea to create a restore point and then backup the edited section of the registry also.
There is a way to export the entire registry, but that’s not a good option for several reasons. Firstly, you’re going to get a large file that you have to store somewhere. Secondly, if you’re only changing one setting, trying to import back the entire registry later on may overwrite many other newer values that were written to other parts of the registry after the export. This can actually lead more problems and possible corruption. Lastly, you may not even be able to import back the entire registry because a lot of keys will be in use by Windows and therefore simply won’t be written.
The best option to backup and restore the entire registry is to use System Restore. So when making a change, create a restore point first and then backup the only edited section manually. If there is a problem, you can always reload the exported section by simply double-clicking on the .reg file in Windows.
If you can’t get into Windows anymore because the registry change messed something up more severely, then you can simply start up the Advanced Recovery Options and choose the previous restore point you had created. I’ll explain both methods in detail below.
Opening Registry Editor
First, let’s talk about opening the registry editor. In just about every recent version of Windows, you can open the registry editor by clicking on the Start button and typing in regedit.

You probably already know how to do this considering you found this article while trying to learn how to backup the registry. Obviously, before you make any changes to the registry, you should always back it up. Now let’s get to the main point of this article on the different ways you can backup the Windows registry.
Backup Parts/Sections of the Registry
In many of my posts, I’ve mentioned tweaks or tips that require editing a key or value in the registry. If you’re going to be making a single change here and there, you don’t really need to backup the entire registry necessarily.
Let’s say you are editing a value stored at the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE – SOFTWARE – Microsoft – Windows – CurrentVersion – Explorer
You can right-click on Explorer and choose Export to make a backup of the entire key along with all sub-keys and any of their values.

You’ll notice that there are quite a few other sub-keys under the main Explorer key. By default, only the selected branch along with sub-keys and values will get exported. If you want to export the entire registry, you have to choose All under Export Range when saving the .reg file.

Again, I don’t recommend backing up the entire registry in this manner as you’ll end up getting a Cannot import error when trying to import the file back.

So stick with exporting only selected branches and you’ll have a better chance of being able to re-import the registry file later on. Now let’s talk about using System Restore to perform a full backup of the registry.
Backup Entire Registry via System Restore
Using System Restore, you won’t run into issues restoring to a previous state because Windows handles all the locked and in-use issues for you. You will always create a restore point while using Windows and it’s very simple to do.
Click on Start and type in Create restore point and click on the first result. You’ll be bought straight to the System Protection tab in the System Properties dialog.

Click on the Create button at the bottom and another dialog will pop up asking for a description. Click the Create button and the restore point will be created.

It should only take a few minutes to create the restore point. Once completed, you can restore a previously created restore point in two ways: via the same System Restore dialog in Windows or via the Advanced Recovery Options screen. I’ll show you both methods below.
Restore Registry via Windows
If you are still able to start Windows and log into the system, then you can try to restore the registry by opening System Restore. Click on Start and type in system restore and click on the first result.
When the System Restore dialog pops up, go ahead and click Next. On the following screen, you will see a list of all the different restore points currently on the system.

You will see the manually created restore points along with the automatically created ones too. You can check the Show more restore points box to see all the restore points stored on the system. If you click on the Scan for affected programs button, it will give you a list of any programs that were installed after the restore point was created since those will be removed. It will also tell you which programs were removed after the restore point was created that will be restored.
Click Next and Finish and that’s about it. The system will be reverted back to the previous restore point and you should be good to go. Note that System Restore does not alter any of your personal data when changing the state of the system. It only looks at the registry, programs and system files.
Restore Registry via Recovery Options
If you are not able to log into Windows, then you can still use system restore, but only via Advanced Boot Options in Windows 7 and Advanced Recovery Options in Windows 8 and Windows 10. The method is slightly different for all three operating systems, so I will explain them all below.
Windows 7 Recovery
For Windows 7, you have to restart your computer and then press the F8 key during the initial boot up. This will bring up the Advanced Boot Options screen and the first option there will be Repair Your Computer.

Select it and press Enter. This will load the System Recovery Options dialog and here you will need to choose System Restore.

Again, you just choose the restore you want to revert back to and that’s it. Normally, if you are having problems loading Windows, the Advanced Boot Options screen will appear automatically.
Note that if you are unable to load the boot options using F8, you may have to use a System Repair Disc. You can create a repair disc on any Windows 7 PC by clicking on Start and typing in system repair disc.

Pop in a CD or DVD and click the Create disc button. Once you have this disc, you can boot directly from it to get the system recovery options shown above. The only thing you need to ensure is that the boot order has the CD/DVD ROM drive listed first.

Windows 8 Recovery
In Windows 8, the entire recovery procedure and GUI is completely different. Instead of the boring DOS interface of before, you now have a fancy looking modern GUI, which makes things a lot easier.
F8 no longer works when trying to get to this new interface. Luckily, I’ve already written a post about the different methods you can use to get to the advanced boot options screen in Windows 8. Once you have gotten to the main screen, click on Troubleshoot.

Under the Troubleshoot section, go ahead and click on Advanced options at the bottom.

Finally, click on System Restore on the last screen and you’ll get the familiar system restore dialog to pick the restore point you want to revert back to.

In Windows 8, you can create a system repair disc like in Windows 7 or you can create a USB recovery drive. To create a repair disc, click on Start and type in recdisc.exe and to create the recovery drive type in recovery drive.

Again, you only need to create these using a different computer if you are not able to load the recovery options on your current PC.
Windows 10 Recovery
The procedure in Windows 10 is exactly the same once you get to the advanced boot options screen, but slightly different while in Windows. Since the Start Menu is back in full form in Windows 10, you can click on that and then click on Settings.

Next, click on Update and recovery in the Settings dialog. As you can see, the Settings dialog in Windows 10 is completely different than the one in Windows 8.

Finally, you’ll be able to click on the Restart now button under Advanced startup. This will get you to the same Choose an option screen where you will click Troubleshoot.

Hopefully, the detailed instructions above will allow you to safely and easily backup and restore your registry in Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10. If you have any questions, feel free to post a comment. Enjoy!



















