작업 관리자의 (Task Manager's) 프로세스(Processes) 탭은 프로그램이 시스템 리소스를 사용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 정보를 제공하지만 실행 중인 프로세스(및 기타)에 대해 알아야 할 모든 것을 찾을 수 있는 세부 정보 탭입니다 . (Details)작업 관리자의 (Task Manager's) 세부 정보(Details) 탭은 Windows 10 컴퓨터 또는 장치(computer or device) 에서 실행되는 각 프로세스에 대한 풍부한 데이터를 제공하며 고급 문제 해결 중에 유용할 수 있습니다. 이 튜토리얼에서는 제공하는 방대한 양의 정보와 할 수 있는 작업에 대해 알아봅니다.
참고:(NOTE:) 이 가이드의 스크린샷과 지침은 Windows 10 2019년 5월(May 2019) 업데이트 이상에 적용됩니다. 사용 중인 Windows 10(Windows 10) 버전을 모르는 경우 Windows 10 버전, OS 빌드(OS build) , 에디션 또는 유형 을 확인하는 방법을 읽어 보세요.
가장 먼저 해야 할 일: (First)Windows 10 의 작업 관리자 에서 (Task Manager)세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에 액세스합니다.
시작하려면 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 시작하십시오 . 키보드 단축키 (keyboard shortcut) "Ctrl + Shift + Esc" 를 사용했습니다 . 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 가 압축 보기에서 시작되는 경우 자세한 내용(More details) 을 클릭하거나 탭 합니다.
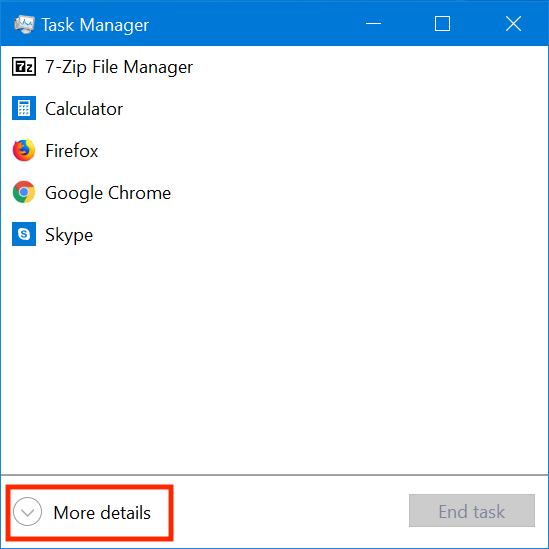
그런 다음 세부 정보(Details) 탭 을 클릭하거나 탭합니다 .

특정 프로세스에 대한 추가 세부 정보에 액세스해야 하는 경우 프로세스 탭 에서 해당 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 (Processes tab)"세부 정보로 이동"("Go to details") 을 클릭하거나 눌러 세부 정보(Details) 탭 을 엽니다 .

서비스(Services) 탭에서 실행 중인 서비스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 "세부 정보로 이동"을 클릭하거나 탭 하여 (")동일한("Go to details) 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다 .

Windows 10 에서 (Windows 10)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에 표시되는 기본 데이터
Windows 10 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보(Details) 탭은 처음 액세스할 때 많은 정보를 표시합니다. 처음에는 압도감을 느낄 수 있습니다.

이 데이터는 7개의 기본 열에 표시됩니다.
-
이름(Name) - 실행 중인 프로세스(running process) 의 이름을 표시합니다 . 보기에서 숨길 수 없는 유일한 열입니다.
-
PID - 고유한 프로세스 식별자 번호를(Process Identifier number) 표시합니다 . 이 숫자는 PID(PID) 를 나열 하는 오류 또는 이벤트(error or event) 와 실행 중인 서비스를 일치시키는 데 사용할 수 있습니다 .
-
상태(Status) - 프로세스가 실행 중인지 일시 중단되었는지 표시합니다. 유니버설 Windows 플랫폼 앱(Universal Windows Platform apps) 은 사용되지 않을 때 리소스를 절약하기 위해 일시 중단됩니다.
-
사용자 이름(User name) - 프로세스가 실행 중인 사용자(시스템 계정 포함)의 이름을 표시합니다.
-
CPU - 모든 코어에서 각 프로세스가 사용하는 CPU 의 백분율을 표시 합니다.
-
메모리(활성 개인 작업 집합) - 일시 중단된 (Memory (active private working set))UWP 프로세스 의 데이터를 제외하고 각 프로세스에 사용 및 예약된 메모리 양을 표시합니다 .
-
UAC 가상화(UAC virtualization) - 사용자 계정 컨트롤 가상화(User Account Control virtualization) 가 각 프로세스에 대해 활성화(Enabled) , 비활성화(Disabled) 또는 허용되지 않음 을 나타냅니다. (Not allowed)나중에 세부 정보(Details) 탭에서 프로세스 가상화를 변경할 수 있는 방법을 설명할 때 UAC 가상화(UAC virtualization) 주제로 돌아갑니다 .
Windows 10 에서 (Windows 10)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에 추가할 수 있는 추가 열
탭에 더 많은 정보를 추가하려는 경우 선택할 수 있는 항목이 많습니다. 추가할 수 있는 항목을 보려면 열 머리글을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 열 (column header and click)선택(Select columns) 을 클릭 하거나 탭 합니다.
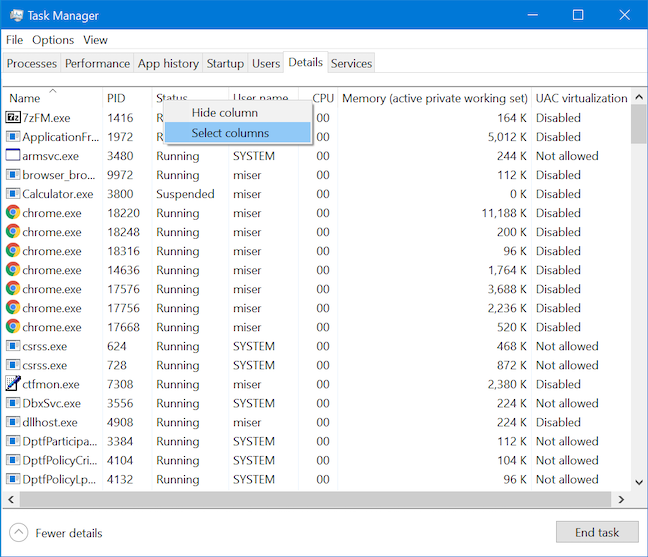
열 선택 창이 열리고 이미 살펴본 열 외에 (Select Columns)세부 정보(Details) 탭에 추가할 수 있는 열이 40개 더 표시 됩니다 . 표시(Just) 할 항목을 선택한 다음 확인 을 클릭하여 (OK)세부사항(Details) 탭 에 추가 하십시오.

열 머리글(column header) 위로 마우스를 가져 가면 열이 표시하는 데이터에 대한 아이디어를 얻을 수 있습니다. 각각이 보여주는 것은 다음과 같습니다.
-
패키지 이름(Package name) - UWP 앱(UWP app) 이 속한 패키지의 이름을 표시합니다. UWP가 아닌 앱(UWP app) 의 경우 열이 비어 있습니다.
-
세션 ID - 프로세스를 실행하는 사용자 세션의 고유 번호를 표시하며 (Session ID)사용자 탭(Users tab) 에 표시된 ID 번호(ID number) 와 일치시킬 수 있습니다 .
-
작업 개체 ID(Job object ID) - 프로세스가 실행 중인 작업 개체 의 ID를 표시합니다.(job object)
-
CPU 시간(CPU time) - 실행을 시작한 이후 각 프로세스에서 사용한 총 프로세서 시간 (초)을 표시합니다. (processor time)이 데이터는 프로세스가 다시 시작되면 재설정됩니다.
-
주기(Cycle) - 프로세스가 사용 중인 CPU 주기(CPU cycle) 시간 의 현재 백분율을 표시합니다 .
-
작업 집합(메모리)(Working set (memory)) - 각 프로세스에서 현재 사용 중인 물리적 메모리의 양을 표시합니다.
-
피크 작업 세트(메모리)(Peak working set (memory)) - 각 프로세스에서 사용하는 물리적 메모리의 최대 양을 표시합니다.
-
작업 집합 델타(메모리)(Working set delta (memory)) - 마지막 새로 고침에서 각 프로세스가 사용한 작업 집합 메모리의 변화량을 표시합니다.
-
메모리(개인 작업 집합) - 일시 중단된 (Memory (private working set))UWP 프로세스 의 데이터를 포함하여 각 프로세스에 사용 및 예약된 메모리 양을 표시 합니다.
-
메모리(공유 작업 집합)(Memory (shared working set)) - 필요한 경우 다른 프로세스에서 사용할 수 있는 각 프로세스에서 사용하는 메모리의 양을 표시합니다.
-
커밋 크기 - (Commit size)Windows 10 에서 각 프로세스에 대해 예약한 가상 메모리의 양 을 표시합니다.
-
페이징 풀 - (Paged pool)Windows 커널 또는(Windows kernel or drivers) 각 프로세스에 대해 드라이버 가 할당한 페이징 가능한 커널 메모리의 양을 표시합니다 . 페이징 가능한 메모리는 하드 디스크와 같은 다른 저장 매체(storage medium) 에 쓸 수 있습니다 .
-
NP 풀(NP pool) - 각 프로세스에 대해 Windows 커널 또는 드라이버(Windows kernel or drivers) 에서 할당한 페이징 불가능한 커널 메모리의 양 을 표시합니다.
-
페이지 부재(Page faults) - 실행을 시작한 이후에 생성된 각 프로세스의 페이지 부재 수를 표시합니다. 페이지 폴트는 프로세스가 현재 프로세스에 할당되지 않은 메모리에 액세스하려고 할 때 발생합니다.
-
PF Delta - 마지막 새로 고침에서 각 프로세스에 의해 생성된 페이지 폴트 수의 변화를 표시합니다.
-
기본 우선 순위(Base priority) - 각 프로세스의 현재 우선 순위를 표시하며 이 순위는 프로세스의 스레드가 예약되는 순서를 결정합니다. 프로세스의 우선 순위를 변경할 수 있는 방법을 살펴볼 때 이 문제로 돌아갑니다.
-
핸들(Handles) - 각 프로세스가 연 핸들의 현재 수를 표시합니다. 핸들은 파일, 레지스트리 키(registry key) 또는 스레드 와 같은 시스템 리소스 입니다.(system resource)
-
스레드(Threads) - 각 프로세스의 활성 스레드 수를 표시합니다.
-
사용자 개체(User objects) - 각 프로세스가 사용하는 창 관리자 개체의 수를 표시합니다. 창 관리자(Window manager) 개체에는 창, 메뉴, 커서, 키보드 레이아웃 및 모니터가 포함됩니다.
-
GDI 개체(GDI objects) - 각 프로세스에서 사용자 인터페이스를 그리는 데 사용하는 그래픽 장치 인터페이스 개체의 수를 표시합니다.(Graphics Device Interface)
-
I/O reads - 파일, 네트워크 및 장치 I/O를 포함하여 실행을 시작한 이후 각 프로세스에서 생성한 읽기 Input/Output
-
I/O writes - 파일, 네트워크 및 장치 I/O를 포함하여 실행을 시작한 이후 각 프로세스에 의해 생성된 쓰기 Input/Output
-
I/O other - 실행을 시작한 이후 각 프로세스에 의해 생성된 읽기 및 쓰기가 아닌 Input/Output
-
I/O read bytesInput/Output 작업 에서 각 프로세스가 읽은 총 바이트 수를 표시합니다 .
-
I/O write bytesInput/Output 작업 에서 각 프로세스가 쓴 총 바이트 수를 표시 합니다.
-
I/O other bytes - 프로세스 가 시작된 이후 읽기 및 쓰기가 아닌 Input/Output
-
이미지 경로 이름(Image path name) - 각 프로세스에 해당하는 실행 파일의 전체 경로를 표시합니다.
-
명령줄(Command line) - 명령 줄 인수를 포함하여 각 프로세스를 시작하는 데 사용되는 전체 명령줄 을 표시합니다.(command line)
-
운영 체제 컨텍스트(Operating system context) - 해당 매니페스트 파일(manifest file) 에 해당 정보가 있는 경우 각 프로세스가 실행할 수 있는 최소 운영 체제 를 표시합니다. (minimum operating system)이 필드는 대부분의 프로세스에서 비어 있지만 이전 Windows 버전(예: Windows Vista , Windows 7 )도 표시할 수 있습니다 .
-
플랫폼(Platform) - 각 프로세스가 실행 중인 플랫폼을 표시합니다(64비트 또는 32비트).
-
상승됨 - 프로세스가 관리자 권한( 상승(Elevated) 된)으로 실행 중인지 여부를 지정합니다.
-
설명(Description) - 프로세스가 무엇인지에 대한 짧은 텍스트 설명 을 표시합니다.(text description)
-
데이터 실행 방지 - (Data execution prevention)보안 기능인 (security feature)데이터 실행 방지(Data Execution Prevention) 를 각 프로세스에 대해 활성화 또는 비활성화 할지 여부를 지정합니다 .
-
엔터프라이즈 컨텍스트(Enterprise context) - 조직의 정책이 올바르게 적용되고 실행되고 있는지 확인하기 위해 WIP ( Windows Information Protection ) 에서 실행되는 동안 각 프로세스의 컨텍스트를 표시합니다.
-
DPI 인식(DPI Awareness) - 응용 프로그램이 높은 DPI (인치당 도트 수) 디스플레이 와 상호 작용하는 방식에 대한 기본 모드 를 표시합니다.(default mode)
-
전원 조절(Power throttling) - 각 프로세스에 대해 전원 조절(power throttling) 이 활성화 또는 비활성화되어 있는지 표시합니다. 일부 프로세스는 Windows 10 장치의 배터리를 절약하기 위해 사용하지 않을 때 자동으로 조절될 수 있습니다.
-
GPU - 모든 그래픽 (Graphics) 처리 장치(Processing Unit) 엔진에서 가장 높은 사용률을 표시합니다.
-
GPU 엔진(GPU engine) - 각 프로세스에서 가장 많이 사용 되는 그래픽 처리 장치 엔진 을 공유합니다.(Graphics Processing Unit engine)
-
전용 GPU 메모리 - 각 프로세스가 모든 (Dedicated GPU memory)그래픽 처리 장치(Graphics Processing Units) 에서 사용하는 전용 그래픽 메모리의 총량을 표시합니다 .
-
Shared GPU memory - 각 프로세스가 모든 그래픽 처리 장치 에서 사용하는 (Graphics Processing Units)시스템 메모리(system memory) 의 총량을 표시합니다 .
(Hide columns)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 보기에서 열 숨기기
상상할 수 있듯이 46개의 선택적 열을 모두 활성화하면 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보(Details) 탭이 심각하게 과밀해질 수 있으므로 관심 있는 열만 유지하는 것이 더 쉬울 수 있습니다. 더 이상 필요하지 않은 열이 열려 있는 경우 열 머리글 을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 (right-clicking or pressing-and-holding)열 숨기기(Hide column) 를 선택하여 보기에서 숨길 수 있습니다 .

동시에 보기에서 더 많은 열을 숨기려면 열 머리글을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 상황에 맞는 메뉴에서 열 선택 을 클릭하거나 탭하는 것이 더 간단할 수 있습니다.(Select columns)

열 선택(Select Columns) 창이 열리고 불필요한 열을 선택 취소하여 보기 에서 숨길 수 있습니다. 완료되면 확인 을 (OK)클릭 하면 (Just click) 세부 정보(Details) 탭에서 제거됩니다.

작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 정렬 옵션
기본적으로 세부 정보(Details) 탭의 프로세스는 알파벳순으로 정렬됩니다. 열 머리글을 클릭하면 해당 열에 표시된 값을 기준으로 표시된 데이터가 정렬됩니다.

표시된 데이터에 만족하지만 표시되는 순서를 변경하려면 열 머리글을 클릭하거나 탭한(click or tap) 다음 끌어 해당 열을 왼쪽이나 오른쪽으로 이동합니다.
Windows 10 의 작업 관리자 (Task Manager)세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 프로세스 종료
세부 정보(Details) 탭 의 가장 일반적인 용도 중 하나는 프로세스를 빠르게 중지하여 시스템 리소스를 확보하는 것입니다. 프로세스를 종료하려면 프로세스를 선택한 다음 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 오른쪽 하단 모서리에서 작업 종료(End task) 버튼을 클릭하거나 누릅니다 .
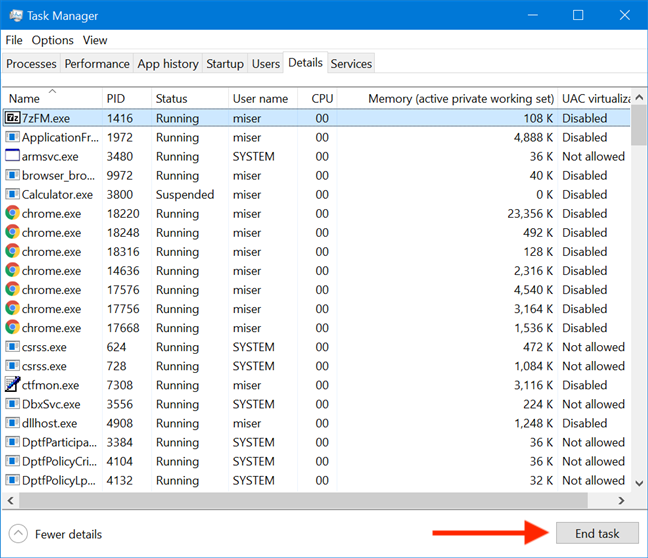
프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 눌러 상황에 맞는 메뉴를 열 수도 있습니다. 작업 종료 를 (End task)클릭(Click) 하거나 탭하여 해당 작업을 닫습니다.
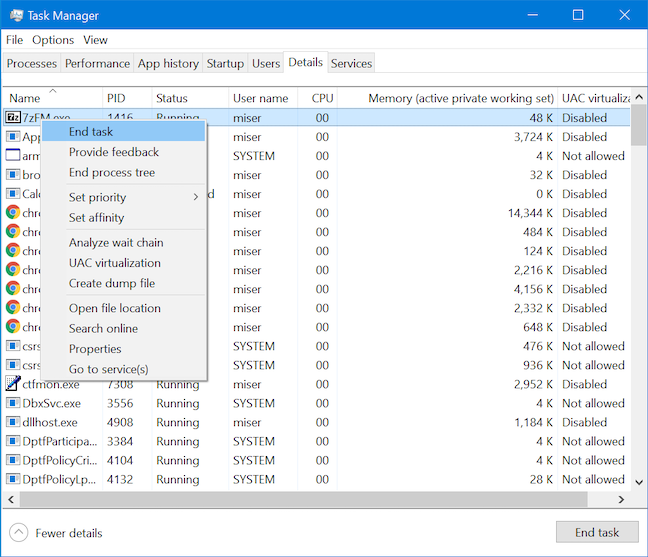
전체 프로세스 트리(process tree) 를 종료 하려면 동일한 상황에 맞는 메뉴에서 "프로세스 트리 종료"("End process tree") 를 클릭하거나 탭할 수 있습니다 .

(Provide feedback)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 Microsoft 에 프로세스에 대한 피드백 제공
이제 세부 정보(Details) 탭을 사용 하여 나열된 프로세스에 대한 피드백을 Microsoft 에 신속하게 제공할 수 있습니다 . 마우스(Just) 오른쪽 버튼을 클릭하거나 길게 눌러 상황에 맞는 메뉴를 연 다음 피드백 제공(Provide feedback) 을 클릭하거나 탭합니다 .
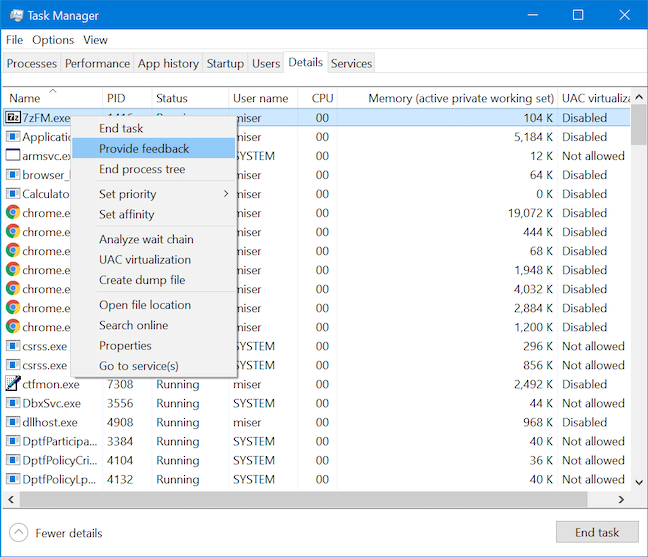
피드백 허브(Feedback Hub) 가 열리고 Microsoft 계정 으로 로그인하면 (Microsoft account)문제나 의견(issue or opinion) 을 Microsoft 에 보낼 수 있습니다 .

작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 프로세스의 우선 순위를 변경하는 방법
세부 정보(Details) 탭에서는 각 프로세스의 우선 순위를 볼 수 있습니다 . Windows는 이 순위를 기반으로 프로세스의 스레드를 예약합니다. 그러나 세부 정보(Details) 탭에서 더 많은 작업을 수행하고 프로세스의 우선 순위를 변경할 수 있습니다. 프로세스를(process and hover) 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 우선 순위 설정(Set priority) 옵션 위로 마우스를 가져 가면 프로세스의 현재 우선 순위를 볼 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 새 우선 순위 수준(priority level) 을 선택할 수도 있는 메뉴가 열립니다 .
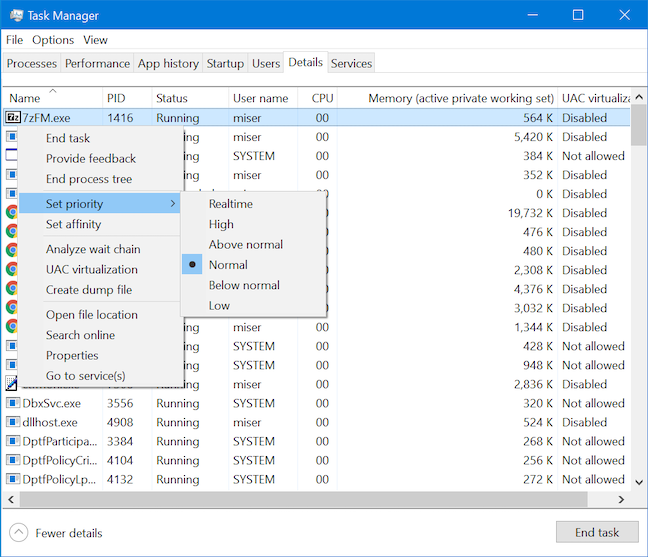
우선 순위 설정(Set priority) 메뉴는 실시간(Realtime) , 높음(High) , 정상(Above normal) 초과 , 보통(Normal) , 정상 미만(Below normal) 및 낮음(Low) 의 6가지 가능한 우선 순위 수준을 표시합니다 . 대부분의 프로세스에는 일반적인 우선 순위 수준(priority level) 이 있으며 프로세스의 우선 순위를 높이면 더 잘 실행되지만 시스템의 나머지 부분을 불안정하게 만들고 충돌을 일으킬 수도 있습니다. 성능 문제를 방지하려면 한 번에 한 단계 이상 우선 순위를 높이지 마십시오. 더 높이려면 더 진행하기 전에 각 단계를 테스트하십시오. 실시간(Realtime) 우선 순위도 까다롭기 때문에 Microsoft에서 권장하는(recommended by Microsoft) 대로 그대로 두는 것이 좋습니다 .
작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 특정 프로세서에 프로세스 연결
세부 정보(Details) 탭 은 Windows 10 컴퓨터 또는 장치 에서 프로세스가 실행되는 방식을 변경하는 또 다른 옵션을 제공하므로 프로세스를 실행할 시스템의 특정 (computer or device)프로세서 또는 코어(processor or core) 를 선택할 수 있습니다 . 일부 프로세스는 기본적으로 시스템의 모든 프로세서에서 실행되고 특정 프로세서로 제한하면 효율성을 높이고 시스템 성능(system performance) 을 최대화하는 데 도움이 될 수 있으므로 이는 유용할 수 있습니다 . 상황에 맞는 메뉴를 열려면 프로세스를 길게 누릅니다. 그런 다음 선호도 설정 을 (Set affinity)클릭하거나 탭(click or tap) 하여 해당 프로세스를 프로세서 또는 코어(processor or core) 에 연결하기 시작 합니다.
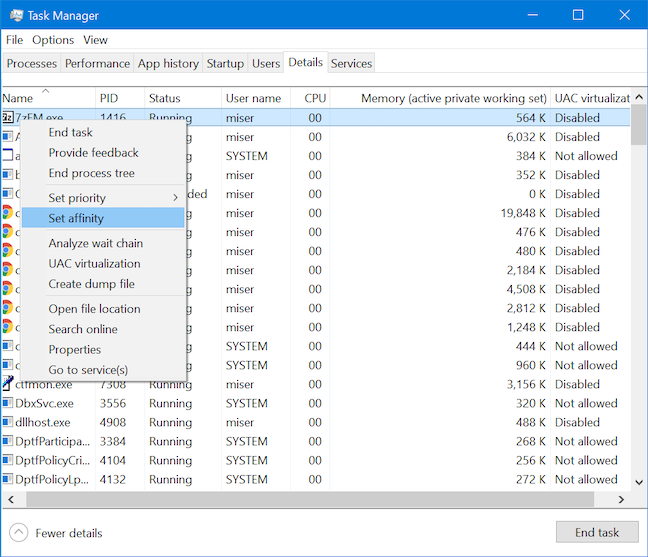
프로세서 선호도(Processor affinity) 창이 열리면 프로세스 를 실행할 코어 를 선택한 다음 확인을 클릭하거나 탭 (core or cores)합니다(OK) .

Windows 가 모든 코어에 부하를 균등하게 분배 하도록 하는 것이 좋은 생각처럼 보일 수 있지만 단일 코어 프로세서용으로 설계된 90년대 또는 2000년대의 오래된 게임과 같은 특정 오래된 응용 프로그램은 단일 코어 프로세서(single-core processor) 에 푸시할 때 더 잘 실행될 수 있습니다. 핵심.
(Troubleshoot problem)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭 을 사용하여 (Details tab)문제 프로세스 문제 해결
세부 정보(Details) 탭 을 사용하여 컴퓨터에서 프로그램이 실행되는 방식을 변경할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 특정 문제를 해결하는 데 도움이 될 수 있는 정보를 얻을 수도 있습니다. 프로그램(program lock) 이 잠기고 응답하지 않는 경우 세부 정보(Details) 탭 에서 해당 프로그램을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 눌러 상황에 맞는 메뉴를 연 다음 "대기 체인 분석" ("Analyze wait chain)을(") 누를 수 있습니다.
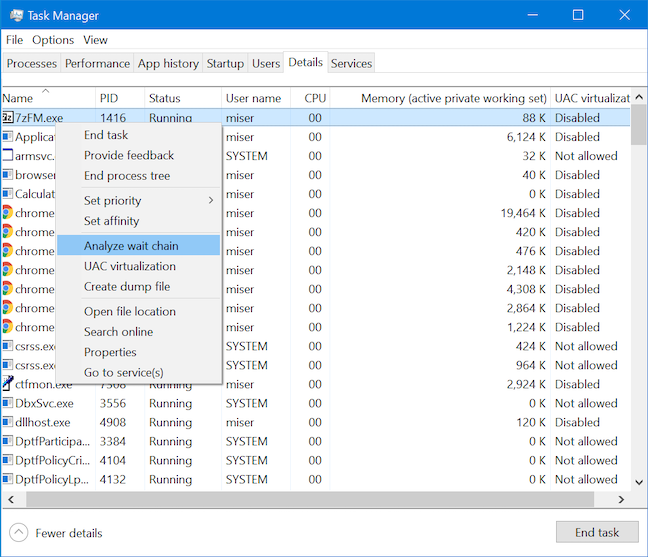
" 대기 체인 분석"(Analyze wait chain") 창이 열리면 프로세스를 검사하고 현재 작업을 완료하려고 시도하는 모든 하위 프로세스를 나열 할 수 있습니다. (process and list)이러한 하위 프로세스를 종료하면 상위 프로세스(parent process) 가 해제되어 손실될 수 있는 데이터를 저장할 수 있습니다. 문제가 되는 하위 프로세스를 조사하여 리소스를 너무 많이 사용하는 이유를 확인할 수도 있습니다.
실행 중인 프로세스(running process) 에 현재 문제가 없으면 정상적으로 실행 중임을 알리는 메시지가 표시됩니다.

성능 문제, 정지 또는 오류와 같이 문제를 일으키는 프로세스가 있는 경우 덤프 파일이 생성될 때 프로세스가 메모리에서 수행하는 모든 작업에 대한 자세한 설명을 제공하는 덤프 파일을 생성 할(dump file) 수 있습니다 .(dump file) . 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 상황에 맞는 메뉴에서 "덤프 파일 만들기" 를 클릭하거나 누릅니다.("Create dump file")

일부 프로세스의 경우 이 작업에 시간이 걸릴 수 있으며 이 경우 덤핑 프로세스(Dumping process) 창 에서 기다리라는 메시지가 표시됩니다.

파일이 생성되면 덤핑 프로세스(Dumping process) 창에서 파일의 위치를 파악하고 공유할 수 있습니다. 창을 스크린샷(Screenshot) 하거나 경로를 기억한 다음 확인 을 클릭하거나 탭 합니다(OK) . 생성된 파일은 WinDBG(WinDBG) 와 같은 디버깅 소프트웨어로 열 수 있지만 대부분의 사용자는 덤프 파일(dump file) 을 기술 지원 에이전트(support agent) 에게 보내 이 기능에서 더 많은 가치를 얻습니다 .

이 파일이 저장된 폴더에 액세스하려면 숨김 파일을 활성화해야 할 수 있습니다.

작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭 에서 (Details tab)UAC 프로세스(UAC process) 가상화 활성화
작업 관리자의 (Task Manager's) 세부 정보(Details) 탭 에서 액세스하는 또 다른 기능 은 UAC 가상화(UAC Virtualization) 입니다. 이 옵션을 사용하면 특정 프로그램에 대해 사용자 계정 컨트롤 가상화 를 활성화할 수 있습니다. (User Account Control virtualization)대부분의 사용자는 이 기능과 자주 상호 작용할 이유가 없지만 중요한 목적을 수행합니다.
일부 이전 응용 프로그램은 중요한 시스템 위치에 직접 쓰도록 구성되며 실행하려면 사용자 계정에 관리자 자격 증명이 있어야 합니다. 이러한 앱에 관리자 권한을 부여하지 않으려면 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에서 가상화를 활성화할 수 있습니다 . 이로 인해 Windows 는 잠재적인 문제가 실제 시스템 파일에 영향을 미치는 것을 방지하기 위해 가상 환경에서 System32 디렉터리 및 시스템 레지스트리 키와(directory and system registry keys) 같은 중요한 위치를 다시 만듭니다 .
이 기능을 활성화하려면 프로세스 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르면(right-clicking or pressing-and-holding) 나타나는 상황에 맞는 메뉴에서 UAC 가상화(UAC virtualization) 를 선택 합니다.
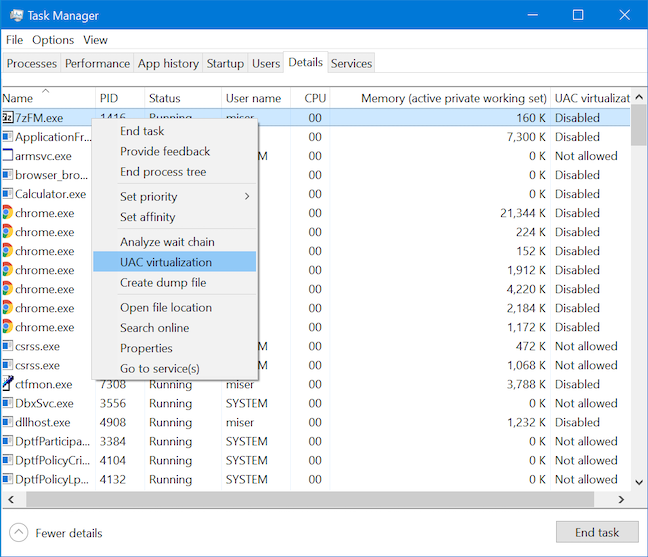
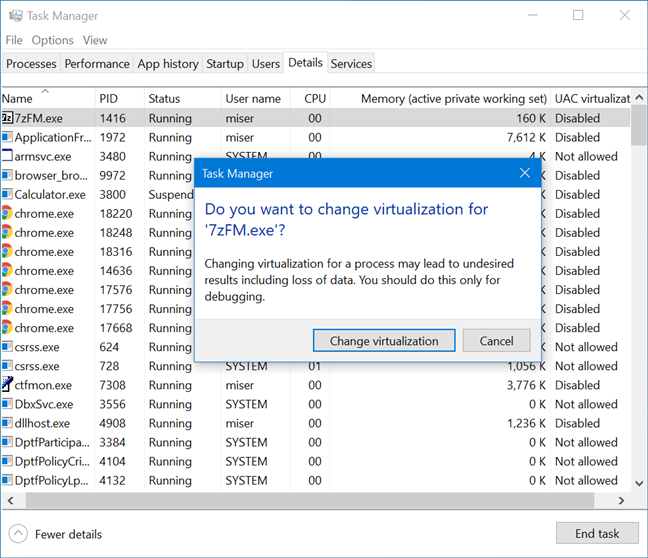
가상화 변경(Change virtualization) 을 클릭하거나 탭 하여 선택한 프로세스에 대한 기능을 활성화하거나 비활성화합니다.
작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 실행 중인 프로세스의 위치 찾기
Windows 10 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)세부 정보(Details) 탭에서 프로세스에 해당하는 실행 파일의 하드 드라이브에서 정확한 위치를 찾을 수 있습니다 . 나열된 프로세스를(process and click) 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "파일 위치 열기"("Open file location.") 를 클릭 하거나 탭 합니다.

파일 탐색기(File Explorer) 는 응용 프로그램의 실행 파일이 저장된 폴더를 엽니다. 폴더가 열리면 해당 파일이 강조 표시됩니다.

(Research)Windows 10 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 을 사용하여 알 수 없는 프로세스 조사
리소스를 소모하는 알 수 없는 프로세스가 발생할 수 있습니다. 세부 정보(Details) 탭은 해당 프로세스를 조사하고 해당 프로세스가 무엇인지 이해할 수 있는 옵션을 제공합니다. 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 온라인 검색(Search online) 을 클릭하거나 탭합니다 .

기본 웹 브라우저는 새 탭을 열고 기본 검색 엔진(default search engine) 에 관계없이 Bing 에서 프로세스 의 이름과 설명(name and description) 으로 웹 검색을 실행하여 이에 대한 추가 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다.

(View)작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 프로세스 속성 보기
프로세스의 속성은 이를 실행하는 실행 파일에 대한 많은 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다. 파일의 크기, 위치, 액세스 날짜 및 보안 설정이 표시되며 호환성 문제도 해결할 수 있습니다. 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)세부 정보(Details) 탭에 나열된 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 속성(Properties) 을 클릭하거나 탭 합니다.

속성(Properties) 창이 열리고 선택한 프로세스에 대한 유용한 정보에 액세스할 수 있습니다.

작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 에서 프로세스와 연결된 서비스를 보려면 서비스(Services) 탭으로 전환 하십시오.
세부 정보(Details) 탭 에 나열된 일부 프로세스 에는 서비스(Services) 탭 에 표시된 해당 서비스가 있습니다. 프로세스를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 "서비스로 이동" ("Go to service(s))을(") 클릭하거나 탭 합니다.
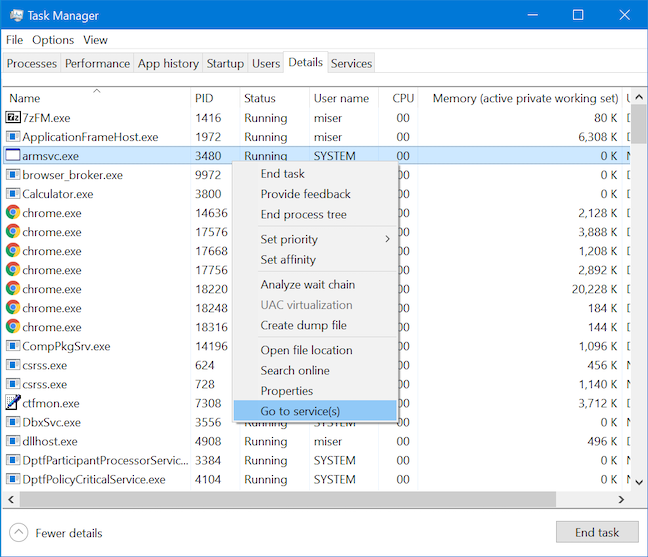
이 작업은 서비스 탭으로 전환되고 (Services) 선택한 프로세스(chosen process) 와 관련된 모든 서비스 를 강조 표시(tab and highlights) 합니다 . 그러한 서비스가 없으면 서비스(Services) 탭으로 전환하고 아무 것도 선택하지 않습니다.

작업 관리자 의 (Manager)세부 정보 탭(Details tab) 이 얼마나 복잡 합니까?
(Thank)제가 작성한 튜토리얼 중 가장 긴 시간을 할애해 주셔서 감사 합니다! 마침내 작성을 마쳤을 때 세부 정보(Details) 탭이 내가 계속 추가하고 숨겼던 모든 다른 열로 어수선한 것을 발견했습니다. 우리는 이 탭에서 사용할 수 있는 풍부한 세부 정보가 고급 사용자와 기술 지원 에이전트에게 매우 중요하다는 것을 알고 있지만 실제로 작업 관리자의 (Task Manager's) 세부 정보(Details) 탭에 46개 열 중 절반 이상이 열려 있는 사람이 있습니까? 외부에 계시다면 저희에게 알려주십시오. 그러면 이 탭을 최대한 효율적으로 사용할 수 있는 새로운 방법을 모두 찾을 수 있을 것입니다.
View details about running processes with the Windows 10 Task Manager
Although Task Manager's Processes tab offers detailed information about how programs use system resources, it is the Details tab that allows you to find out everything you need to know about running processes (and more). Task Manager's Details tab provides generous data about each process running on your Windows 10 computer or device, and it can come in handy during advanced troubleshooting. In this tutorial, we go over the massive amount of information that it offers and what it can do:
NOTE: The screenshots and the instructions in this guide apply to Windows 10 May 2019 update or newer. If you do not know what version of Windows 10 you have, read: How to check the Windows 10 version, OS build, edition, or type.
First things first: Access the Details tab in Windows 10's Task Manager
To begin, launch the Task Manager. We used the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." Click or tap on More details if the Task Manager starts in its compact view.

Then, click or tap the Details tab.

If you need to access more details for a specific process, right-click or press-and-hold on it in the Processes tab and then click or tap "Go to details" to open the Details tab.

You can do the same from the Services tab, by right-clicking or pressing-and-holding on any running service, and then clicking or tapping "Go to details."

The default data displayed in Task Manager's Details tab in Windows 10
The Details tab in Windows 10's Task Manager shows a lot of information when you first access it. You might feel overwhelmed at first.

This data is displayed in seven default columns:
-
Name - Shows the name of the running process. It is the only column that can not be hidden from view.
-
PID - Displays a unique Process Identifier number. These numbers can be used to match a running service with an error or event that lists the PID.
-
Status - Displays whether a process is running or suspended. Universal Windows Platform apps are suspended to conserve resources when they are not used.
-
User name - Reveals the name of the user (including system accounts) a process is running under.
-
CPU - Shows the percentage of CPU used by each process across all cores.
-
Memory (active private working set) - Displays the amount of memory used and reserved for each process, excluding data from suspended UWP processes.
-
UAC virtualization - Indicates if User Account Control virtualization is Enabled, Disabled, or Not allowed for each process. We return to the topic of UAC virtualization later on, when we explain how the Details tab allows you to change the virtualization of a process.
The additional columns you can add to Task Manager's Details tab in Windows 10
If you want to add more information to the tab, there is a lot to choose from. To see what you can add, right-click or press-and-hold a column header and click or tap Select columns.

The Select Columns window opens, revealing forty more columns that you can add to the Details tab, on top of the ones we already went over. Just select the ones you want to be displayed and then click OK to have them added to the Details tab.

Hovering over a column header should give you an idea about the data that column displays. Here is what each of them shows:
-
Package name - Shows the name of a package that a UWP app belongs to. The column is empty when it comes to non-UWP apps.
-
Session ID - Displays the unique number of the user session running a process and can be matched with the ID number shown in the Users tab.
-
Job object ID - Shows the ID of the job object in which the process is running.
-
CPU time - Reveals the total processor time in seconds used by each process since it started running. This data resets if a process is restarted.
-
Cycle - Displays the current percentage of CPU cycle time a process is using.
-
Working set (memory) - Shows the amount of physical memory currently used by each process.
-
Peak working set (memory) - Shows the maximum amount of physical memory used by each process.
-
Working set delta (memory) - Displays the amount of change in working set memory each process has used from the last refresh.
-
Memory (private working set) - Shows the amount of memory used and reserved for each process, including data from suspended UWP processes.
-
Memory (shared working set) - Displays the amount of memory used by each process, that can be used by other processes if needed.
-
Commit size - Shows the amount of virtual memory reserved by Windows 10 for each process.
-
Paged pool - Displays the amount of pageable kernel memory allocated by the Windows kernel or drivers for each process. Pageable memory can be written to another storage medium, like a hard-disk.
-
NP pool - Shows the amount of non-pageable kernel memory allocated by the Windows kernel or drivers for each process.
-
Page faults - Reveals the number of page faults each process generated since it started running. Page faults occur when a process attempts accessing memory that is not currently allocated to the process.
-
PF Delta - Displays the change in the number of page faults generated by each process from the last refresh.
-
Base priority - Shows the current priority of each process, this ranking determining the order in which the threads of a process are scheduled. We return to this when we go over how you can change the priority of a process.
-
Handles - Displays the current number of handles that each process opened. A handle is a system resource such as a file, a registry key or a thread.
-
Threads - Shows the number of active threads for each process.
-
User objects - Displays the number of window manager objects that each process uses. Window manager objects include windows, menus, cursors, keyboard layouts, and monitors.
-
GDI objects - Reveals the number of Graphics Device Interface objects used by each process to draw the user interface.
-
I/O reads - Shows the number of read Input/Output operations generated by each process since it started running, including file, network, and device I/O.
-
I/O writes - Displays the number of write Input/Output operations generated by each process since it started running, including file, network, and device I/O.
-
I/O other - Shows the number of non-read and non-write Input/Output operations, generated by each process since it started running — e.g., control functions.
-
I/O read bytes - Displays the total number of bytes read by each process in Input/Output operations.
-
I/O write bytes - Shows the total number of bytes written by each process in Input/Output operations.
-
I/O other bytes - Reveals the total number of bytes a process used in non-read and non-write Input/Output operations since it started — e.g., control functions.
-
Image path name - Displays the full path to the executable file corresponding to each process.
-
Command line - Shows the full command line used to launch each process, including command-line arguments.
-
Operating system context - Displays the minimum operating system that each process can run on if the corresponding manifest file has that information. This field remains blank for most processes, but can also show older Windows versions — e.g., Windows Vista, Windows 7.
-
Platform - Shows the platform each process is running on: 64 bit or 32 bit.
-
Elevated - Specifies whether the process is running with administrator privileges (elevated) or not.
-
Description - Displays a short text description of what the process is.
-
Data execution prevention - Specifies whether Data Execution Prevention, which is a security feature, is enabled or disabled for each process.
-
Enterprise context - Shows the context of each process while running in Windows Information Protection (WIP) to make sure that your organization's policies are applied and running correctly.
-
DPI Awareness - Displays the default mode for how the application interacts with high DPI (dots per inch) displays.
-
Power throttling - Shows if power throttling is enabled or disabled for each process. Some processes can be automatically throttled when you are not using them, to conserve the battery of your Windows 10 device.
-
GPU - Displays the highest utilization across all Graphics Processing Unit engines.
-
GPU engine - Shares which Graphics Processing Unit engine is utilized the most by each process.
-
Dedicated GPU memory - Displays the total amount of dedicated graphics memory that each process is using across all Graphics Processing Units.
-
Shared GPU memory - Shows the total amount of system memory that each process is using across all Graphics Processing Units.
Hide columns from view in Task Manager's Details tab
As you can imagine, having all forty-six optional columns activated can seriously overcrowd your Task Manager's Details tab, so it might be easier to only keep the ones that interest you. If you have a column open that you no longer need, you can hide it from view by right-clicking or pressing-and-holding the column's header and then choosing Hide column.

If you want to hide more columns from view at the same time, it might be simpler to right-click or press-and-hold on a column's header and then click or tap Select columns from the contextual menu.

The Select Columns window opens, and you can uncheck any unnecessary columns to hide them from view. Just click OK when you are done, to have them removed from the Details tab.

Sorting options in Task Manager's Details tab
By default, the processes in the Details tab are sorted alphabetically. Clicking on any of the column headers sorts the data displayed based on the values shown in that column.

If you are happy with the data displayed but want to change the order in which it appears, click or tap and then drag a column's header to move that column left or right.
End processes from Task Manager's Details tab in Windows 10
One of the most common uses for the Details tab is to stop processes quickly, to free up system resources. To end a process, select it and then click or tap the End task button from the bottom-right corner of the Task Manager.

You can also right-click or press-and-hold on any process to open a contextual menu. Click or tap on End task to close that task.

You can click or tap "End process tree" from the same contextual menu if you want the entire process tree to be terminated.

Provide feedback on a process to Microsoft from Task Manager's Details tab
The Details tab now allows you to quickly provide feedback to Microsoft on any listed process. Just right-click or press-and-hold to open the contextual menu and then click or tap Provide feedback.

The Feedback Hub opens, and, once you to sign in with your Microsoft account, you can send your issue or opinion to Microsoft.

How to change the priority of a process from Task Manager's Details tab
The Details tab lets you see the priority of each process. Windows schedules the threads of a process based on this ranking. However, you can do more with the Details tab and change the priority of a process. Right-click or press-and-hold on a process and hover over the Set priority option to open a menu that not only lets you see a process's current priority but also allows you to choose a new priority level.

The Set priority menu displays six possible priority levels: Realtime, High, Above normal, Normal, Below normal, and Low. Most processes have a normal priority level and, while raising the priority of a process should make it run better, it could destabilize the rest of your system and even cause a crash. To avoid performance issues, never raise priority more than a single step at a time. If you want to raise it even higher, test each step before progressing further. The Realtime priority is also tricky, and we suggest leaving it alone, as recommended by Microsoft.
Link a process to a particular processor from Task Manager's Details tab
The Details tab offers yet another option to change the way a process runs on your Windows 10 computer or device, allowing you to select a particular processor or core on your system that you want a process to run on. This can be useful because some processes run on all processors on your system by default, and limiting them to a particular processor can help increase efficiency and maximize your system performance. Right-click on press-and-hold on a process to open the contextual menu. Then click or tap on Set affinity to start linking that process to a processor or core.

When the Processor affinity window opens, choose the core or cores you want the process to run on and then click or tap OK.

While it may seem like a good idea to let Windows divvy up the load evenly among all cores, certain older applications, like old games from the 90s or 2000s that were designed for a single-core processor, might run better when pushed onto a single core.
Troubleshoot problem processes using Task Manager's Details tab
Not only can you change how programs run on your computer using the Details tab, but you can also get information that might help you resolve certain issues. If you have a program lock up and become unresponsive, you can right-click or press-and-hold on it in the Details tab to open its contextual menu and then press on "Analyze wait chain."

The "Analyze wait chain" window opens, allowing you to examine the process and list all subprocesses that are currently attempting to complete a task. Killing these subprocesses often frees up the parent process allowing you to save data that might otherwise be lost. You can also research the offending subprocesses to see why they may be using resources so heavily.
If a running process has no current issues, it shows displays a message informing you it is running normally.

If there is a process that is giving you trouble, such as performance issues, freeze-ups or errors, you can create a dump file that provides a detailed account of everything that your process is doing in memory at the time the dump file is created. Right-click or press-and-hold on a process, and then click or tap "Create dump file" from its contextual menu.

For some processes, this action can take some time, in which case you receive a message asking you to wait in the Dumping process window.

Once the file is created, the Dumping process window lets you know and shares its location. Screenshot the window or remember the path, and then click or tap OK. The generated file can be opened with debugging software such as WinDBG, but most users get more value from this feature by sending the dump file to a tech support agent.

You might need to enable hidden files to access the folder where this file is stored.

Enable UAC process virtualization in Task Manager's Details tab
Another feature accessed from Task Manager's Details tab is UAC Virtualization. This option allows you to enable User Account Control virtualization for a particular program. While most users should have no reason to interact with this feature often, it does serve an important purpose.
Some older applications are configured to write directly to important system locations and require your user account to have admin credentials to run. If you do not want to grant admin rights to any such app, you can enable virtualization from the Task Manager. This causes Windows to recreate important locations, such as the System32 directory and system registry keys, in a virtual environment in order to prevent potential problems from affecting your actual system files.
To enable this feature, select UAC virtualization from the contextual menu that shows up after right-clicking or pressing-and-holding on a process.

Click or tap Change virtualization to enable or disable the feature for the selected process.

Find the location of a running process from Task Manager's Details tab
You can find the exact location on your hard drive of the executable file corresponding to a process from the Details tab in Windows 10's Task Manager. Right-click or press-and-hold on a listed process and click or tap "Open file location."

The File Explorer opens the folder your application's executable file is stored in. The corresponding file is highlighted when the folder opens.

Research an unknown process using the Details tab in Windows 10's Task Manager
You might come across an unknown process that is eating up your resources. The Details tab offers the option to research that process and understand what it is all about. Right-click or press-and-hold on a process and then click or tap Search online.

Your default web browser opens a new tab, and runs a web search with the name and description of the process on Bing (regardless of your default search engine), helping you get more information on it.

View the properties of a process from Task Manager's Details tab
The properties of a process can offer a lot of information about the executable that runs it. They show the file's size, location, access dates, and security settings, and you can even troubleshoot compatibility issues. Right-click or press-and-hold on a process listed in the Details tab of your Task Manager and click or tap Properties.

The Properties window opens, providing you access to useful information about the selected process.

Switch to the Services tab to see any services associated with a process from Task Manager's Details tab
Some of the processes listed in the Details tab have a corresponding service displayed in the Services tab. Right-click or press-and-hold on a process and then click or tap "Go to service(s)."

This action switches you over to the Services tab and highlights any service(s) associated with the chosen process. If there are no such services, it just switches to the Services tab and selects nothing.

How cluttered is the Details tab from your Task Manager?
Thank you for taking the time to read the longest ever tutorial I wrote! When I finally finished writing it, I found my Details tab was cluttered with all the different columns I kept adding and hiding. We know the wealth of detailed information available on this tab is invaluable for power users and tech support agents, but is there anyone who actually has at least half of the forty-six columns open in their Task Manager's Details tab? If you are out there, let us know, and maybe we can all find out new ways this tab can be used for a maximum of efficiency.



































