친구들이 항상 Linux(Linux) 에 대해 이야기하는 것을 듣 거나 Windows 또는 Linux 중 어떤 OS가 더 나은지(which OS is better for you, Windows or Linux) 궁금 할 수 있습니다 . 시도해 보고 싶지만 Linux 를 좋아할지 확신할 수 없습니다 . 먼저 시도해 볼 수 있는 방법이 있습니까? 다행히도 있습니다.
VirtualBox 를 사용하여 (VirtualBox)Windows 10 내에서 Linux 기반 OS를 설치할 수 있습니다 . Windows 와 함께 Linux OS 를 이중 부팅할 수 있지만 VirtualBox 는 며칠 후에 Linux OS 를 포기하기로 선택한 경우 훨씬 더 깨끗한 상태를 제공합니다 .

VirtualBox를 사용하여 Windows 에 (Windows Using VirtualBox)Linux 를 설치하는 방법
이 방법을 사용하여 모든 Linux OS를 설치할(install any Linux OS) 수 있지만 이 자습서에서는 Ubuntu 가 가장 널리 사용되므로 Ubuntu를 사용합니다.
1. Ubuntu용 ISO 다운로드(1. Download the ISO for Ubuntu)
Ubuntu용 ISO를(ISO for Ubuntu) 다운로드하여 시작합니다 . 여유 공간이 있는 빈 디스크나 플래시 드라이브가 없다고 걱정하지 마십시오. VirtualBox와 함께 Ubuntu를 설치(installing Ubuntu with VirtualBox) 하기 때문에 ISO만 있으면 됩니다.
LTS (장기 지원) 버전 을 사용하는 것이 이상적입니다 . 현재 LTS 버전은 Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS 입니다.

2. 버추얼박스 다운로드
PC에 VirtualBox 를 (VirtualBox)다운로드(download) 하여 설치 해야 합니다 . Windows 패키지 를 다운로드할 수 있지만 Linux 및 macOS용 패키지도 있습니다. 설치 과정은 약간 다를 수 있습니다.

설치를 실행하고 프롬프트를 따릅니다. 설치가 완료되면 Ubuntu ISO 다운로드가 완료되었는지 확인합니다. 있는 경우 Ubuntu 용 (Ubuntu)VirtualBox 를 구성하고 진행할 수 있습니다 .
3. Ubuntu용 VirtualBox 구성
VirtualBox 를 시작하면 다음 시작 화면이 표시됩니다 . 새로 만들기 를 (New)클릭(Click) 하여 구성 프로세스를 시작합니다.

대화 상자가 나타나야 합니다. 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 가상 머신에 이름(Name) 을 지정하십시오(예: Ubuntu v20.04.2 LTS ) .
- (Click)유형(Type ) 옆의 드롭다운 메뉴를 클릭 하고 Linux 를 선택 합니다.
- 버전(Version ) 을 Ubuntu (64비트) 또는 Ubuntu (32비트) 로 선택 합니다.

- 가상 머신에 메모리 크기(Memory size) 를 할당 합니다. 이상적으로는 PC RAM(RAM) 의 약 4분의 1을 할당하도록 선택해야 합니다 . 예를 들어 총 RAM 이 16GB인 경우 가상 머신에 4GB를 할당합니다.
- 다음(Next ) 버튼을 선택 합니다.
또한 하드 디스크의 일부를 가상 머신에 할당해야 합니다. 이 부분은 가상 운영 체제(예: 이 경우 Ubuntu(Ubuntu) )에서만 액세스할 수 있습니다 . 두 가지 옵션 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다. 스토리지를 계속 사용함에 따라 증가하는 동적 할당(Dynamically allocated) 스토리지를 사용하거나 더 빠른 성능을 제공하는 고정 크기(Fixed-size) 스토리지 제한을 할당할 수 있습니다.
- 다음 화면에서 가상 머신을 위한 새 하드 디스크를 생성해야 합니다. 지금 가상 하드 디스크(Create a virtual hard disk now) 만들기 옵션을 선택하고 만들기(Create) 를 클릭 합니다.
- 다음으로 가상 하드 디스크에 사용할 파일 유형을 선택해야 합니다. VDI(VirtualBox 디스크 이미지)(VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)) 를 선택하고 다음 을(Next) 선택 합니다.
- 동적 할당(Dynamically allocated) 을 선택하고 다음 을(Next) 선택 합니다.
- 다음 화면 에서 기본 VDI 스토리지 위치와 크기가 표시되고 그대로 두고 만들기(Create) 를 선택 합니다.

이것으로 구성 프로세스의 첫 번째 부분이 완료됩니다. 가상 머신이 설정되었으므로 이제 가상 머신에 Ubuntu ISO 를 추가해 보겠습니다. Ubuntu CD/DVD 가 이미 있는 경우 드라이브에 삽입하고 가상 머신에서도 사용할 수 있습니다.
계속 진행하기 전에 BIOS 설정에서 하드웨어 가상화가 활성화되어 있는지 확인하십시오. 활성화되어 있지 않으면 다음 단계가 작동하지 않습니다.
이제 VirtualBox의 왼쪽 사이드바에 Ubuntu 가 나열됩니다. (Ubuntu)그것을 선택하고 설정(Settings) 을 클릭하십시오 .

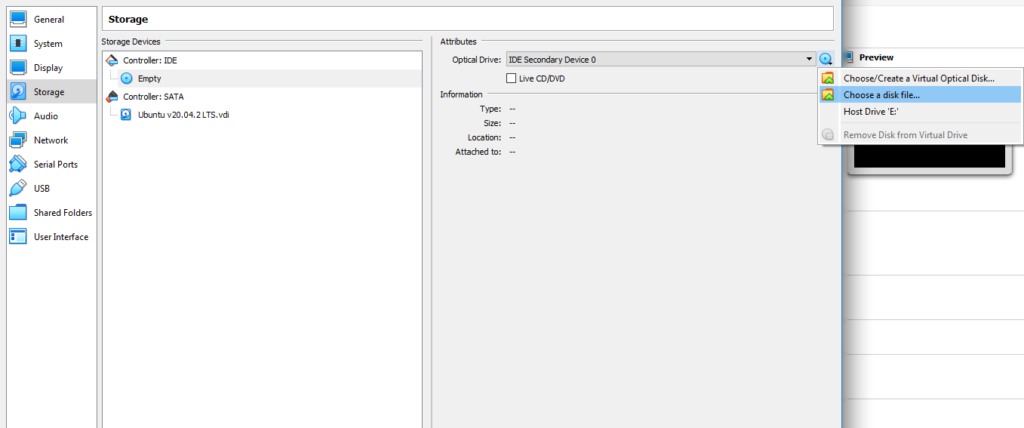
설정(Settings) 대화 상자 의 왼쪽 사이드바에서 저장소(Storage) 를 찾습니다 . 속성(Attributes) 섹션 에서 작은 디스크 아이콘을 클릭 (Click)하고 디스크 파일(Choose a disk file) 선택 을 선택 하고 ISO로 이동한 다음 확인을 선택 합니다(OK) .
이제 가상 머신에 Ubuntu 를 설치할 준비가 되었습니다.(Ubuntu)
4. 우분투 설치 시작
VirtualBox 홈 화면 에서 시작(Start ) 버튼을 클릭하여 시작합니다. 팝업 대화 상자에서 Ubuntu ISO(Ubuntu ISO) 를 시동 디스크로 선택하고 시작 을(Start) 선택 합니다.
기계가 프로세스를 시작하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 이 작업은 몇 분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.

이 시점에서 두 가지 옵션이 있습니다. 설치를 진행하기 전에 Ubuntu(Try Ubuntu) 를 사용해 보거나 이미 확신이 있다면 Ubuntu 를 설치할 수 있습니다.(Install Ubuntu)

Try Ubuntu 를 선택하면 Ubuntu 사용을 바로 시작할 수 있습니다. 또는 Ubuntu 설치(Install Ubuntu) 를 선택할 수 있습니다 .
Ubuntu 를 설치하기 전에 다른 운영 체제처럼 사용할 수 있지만 가상 머신에 데이터를 저장할 수는 없음을 기억하십시오. 모든 재부팅은 이전 세션에서 보존된 데이터 없이 새로 시작됩니다.
설치 옵션을 계속 진행하기로 선택한 경우 Ubuntu 설치(Install Ubuntu) 를 선택하여 설치 를 시작합니다.
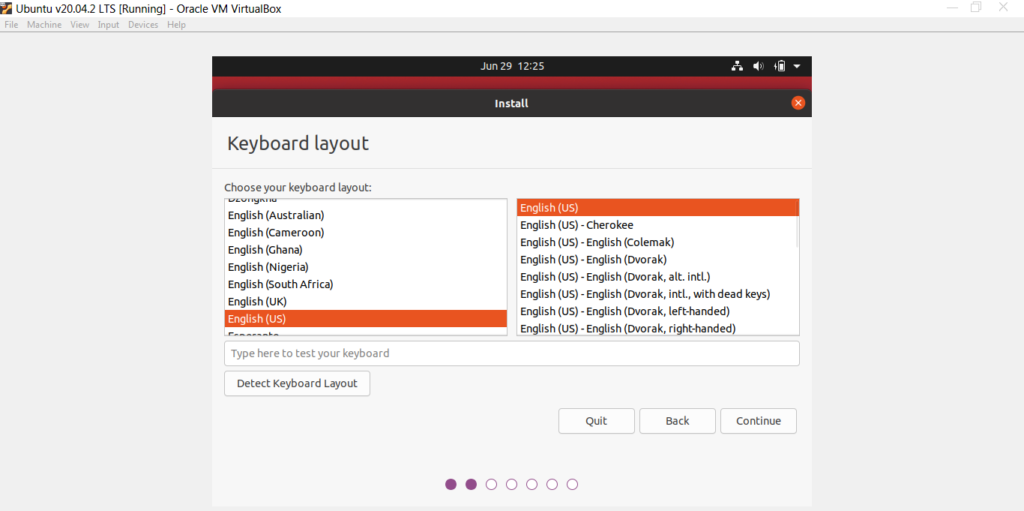
- 선호하는 키보드 레이아웃(Keyboard layout) 을 선택하십시오 .
- 설치 마법사의 프롬프트를 계속 따르십시오. 디스크를 지우고 Ubuntu를 설치할(Erase disk and install Ubuntu) 것인지 묻는 메시지가 나타날 수 있습니다 . 이것은 정상 입니다. 지금 설치(Install Now ) 를 선택 하고 계속 진행하십시오.

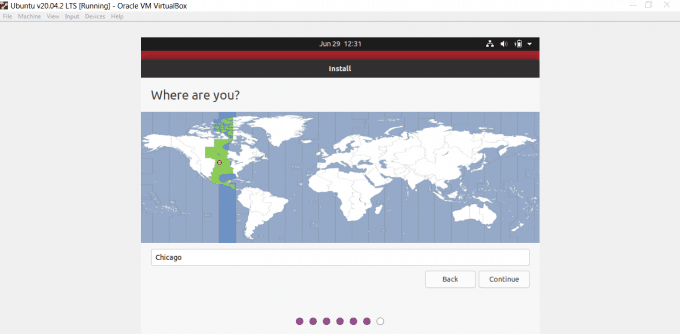
- 다음으로 지역을 선택하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다. 지역을 선택하고 계속(Continue) 을 선택합니다 .
- 그런 다음 이름, 컴퓨터 이름, 사용자 이름 및 암호와 같은 세부 정보를 입력하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다.
- 설치 마법사는 세부 정보를 수집한 후 자체적으로 설치 프로세스를 계속합니다. 몇 분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.
설치가 완료되면 가상 머신이 자동으로 재부팅됩니다. 가상 머신을 다시 실행하면 Ubuntu 로 부팅됩니다 .

Ubuntu 를 기본 OS(Primary OS) 로 사용할 준비가 되셨 습니까?
시스템에 별도로 설치하고 싶을 만큼 이 무료 오픈 소스 OS와 사랑에 빠지게 될 수도 있습니다. Ubuntu 를 기본 OS로 설치 하거나 Windows로 이중 부팅할 수 있습니다(dual-boot it with Windows) .
How to Install Linux on Windows With VirtualBox
Yоu hear your friends talk aboυt Linux all the time, or maybe you’re just wondering which OS is better for you, Windows or Linux. You’re tempted to try it, but you’re not entirely sure if you’ll like Linux. Is there a way you could just try it out first? Fortunately, there is.
You can use VirtualBox to install a Linux-based OS within Windows 10. While you could dual-boot a Linux OS alongside Windows, VirtualBox offers a much cleaner slate if you choose to abandon the Linux OS after a few days.

How to Install Linux on Windows Using VirtualBox
You can install any Linux OS using this method, but we’ll use Ubuntu for this tutorial since it’s the most popular.
1. Download the ISO for Ubuntu
Start by downloading the ISO for Ubuntu. Don’t worry about not having a spare blank disk or flash drive lying around. Since you’re installing Ubuntu with VirtualBox, all you need is the ISO.
It’s ideal to use the LTS (long-term support) version. The current LTS version is Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS.

2. Download VirtualBox
You’ll need to download and install VirtualBox on your PC. You can download the Windows package, but there are packages available for Linux and macOS as well. Note that the installation process may vary slightly among them.

Run the installation and follow the prompts. Once installed, check if the Ubuntu ISO has finished downloading. If it has, you can move forward and configure VirtualBox for Ubuntu.
3. Configure VirtualBox for Ubuntu
You’ll see the following welcome screen when you launch VirtualBox. Click on New to begin the configuration process.

A dialog box should pop up. Next, follow these steps:
- Give your Virtual Machine a Name, for instance, Ubuntu v20.04.2 LTS.
- Click on the drop-down menu besides Type and select Linux.
- Choose the Version as Ubuntu (64 bit) or Ubuntu (32 bit).

- Allocate Memory size to your virtual machine. Ideally, you should choose to allocate about a fourth of your PC’s RAM. For instance, if you have 16GB total RAM, allocate 4GB to the virtual machine.
- Select the Next button.
You’ll also need to allocate a portion of your hard disk to the virtual machine. This portion will only be accessible to your virtual operating system, i.e., Ubuntu in this case. You have two options to choose from; you could either use Dynamically allocated storage which grows as you keep using the storage, or allocate a Fixed-size storage limit that offers faster performance.
- On the next screen, you’ll need to create a new hard disk for your virtual machine. Choose the Create a virtual hard disk now option and click Create.
- Next, you’ll need to choose the type of file you’d like to use for the virtual hard disk. Choose VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) and select Next.
- Choose Dynamically allocated and select Next.
- You’ll see the default VDI storage location and size on the next screen, leave them as they are, and select Create.

This completes the first part of the configuration process. Our virtual machine has been set up, so let’s now move forward and add the Ubuntu ISO to the virtual machine. If you already have an Ubuntu CD/DVD, you could insert that into the drive and use it in the virtual machine too.
Before moving forward, ensure that you have hardware virtualization enabled in your bios settings. If it’s not enabled, the next steps will not work.
You’ll now see Ubuntu listed on VirtualBox’s left sidebar. Select it and click on Settings.

Look for Storage on the left sidebar of the Settings dialog box. Click on the tiny disc icon in the Attributes section, select Choose a disk file, navigate to the ISO, and select OK.

You’re now ready to install Ubuntu on your virtual machine.
4. Begin Ubuntu Installation
Start by clicking the Start button on the VirtualBox home screen. Select the Ubuntu ISO as the start-up disk in the dialog box that pops up and select Start.
You’ll see the machine initiate the process. This may take a few minutes.

You have two options at this point. You could either Try Ubuntu before you move forward with the installation or Install Ubuntu if you feel confident already.

If you choose Try Ubuntu, you can start using Ubuntu right away. Alternatively, you could choose to Install Ubuntu.
Before installing Ubuntu, remember that you can use it like any other operating system, but you can’t store any data on a virtual machine. Every reboot is a fresh start with no data preserved from the previous session.
If you’ve chosen to move forward with the install option, select Install Ubuntu to initiate installation.
- Choose your preferred Keyboard layout.

- Keep following the installation wizard’s prompts. You may be asked if you want to Erase disk and install Ubuntu. This is normal, just select Install Now and move forward.

- Next, you’ll be asked to choose your region. Select your region and select Continue.

- You’ll then be asked to input your details such as your name, computer’s name, username, and password.
- The installation wizard will continue the installation process by itself after collecting the details. This could take a few minutes.
When the installation completes, your virtual machine will automatically reboot. Run the virtual machine again, and it should boot into Ubuntu.

Ready to Use Ubuntu as a Primary OS?
You might just end up falling in love with this free, open-source OS enough to want to install it separately on your system. You can either install Ubuntu as your primary OS or dual-boot it with Windows.














