Linux 를 다룰 수 있는지 여부를 확인하기 위해 Ubuntu 를 가지고 놀고 싶습니까? 글쎄(Well) , 그것은 완전히 무료이므로 시도하지 않을 이유가 없습니다. 그러나 현재 컴퓨터를 실행하려면 예비 컴퓨터나 예비 하드 드라이브가 필요합니다.
이러한 옵션이 없거나 기존 시스템을 엉망으로 만들고 싶지 않다면 Ubuntu 를 기본 PC의 가상 머신에 설치할 수 있습니다. 내가 사용하는 무료 도구는 VirtualBox 입니다. 무료라는 점을 제외하면 VMware Workstation 과 매우 유사합니다 .
이 기사에서는 Windows(Windows) , Mac 또는 Linux 와 같은 현재 OS 내에서 가상 머신으로 실행되는 Ubuntu 복사본을 빠르게 얻는 방법을 보여 드리겠습니다 .
VirtualBox에 Ubuntu 설치
먼저 위의 링크를 사용하여 VirtualBox 를 다운로드 하고 설치하십시오. 꽤 작은 프로그램이므로 설정하는 데 오랜 시간이 걸리지 않습니다. 실행했으면 실행 하려는 Ubuntu 버전을 다운로드하십시오 . (download the version of Ubuntu)1.4GB ISO 파일 인 데스크탑(Desktop) 버전을 다운로드했습니다 .
이제 왼쪽 상단의 새로 만들기 버튼을 클릭하여 새 가상 머신을 만듭니다 .(New)
VirtualBox 에서 가상 머신을 설정하는 과정에 익숙해 지면 전문가 모드(Expert Mode) 버튼을 클릭하여 모든 설정을 훨씬 빠르게 완료할 수 있습니다. 처음에는 안내 마법사를 사용해야 합니다. 다음 화면에서 운영체제를 선택해야 합니다.

이 도구를 사용하여 다양한 운영 체제를 설치할 수 있지만 여기서는 Ubuntu Linux 만 사용 합니다. 제 경우에는 Type 으로 (Type)Linux 를 선택한 다음 Ubuntu 를 선택했습니다 . 이전 하드웨어를 사용했기 때문에 프로그램은 32비트용 옵션만 제공했습니다. 이상적으로는 64비트 버전의 운영 체제를 설치해야 합니다. VirtualBox 가 32비트 옵션만 표시하고 64비트 옵션은 표시하지 않는 경우 이 게시물에서 해결 방법을(this post for the remedy) 확인하세요 .

그런 다음 가상 머신에 할당할 메모리 양을 선택합니다. 권장량을 제공하지만 슬라이더를 사용하여 언제든지 수동으로 조정할 수 있습니다.

다음으로 가상 머신에 가상 하드 디스크를 추가할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 하드 드라이브가 없는 VM은 거의 쓸모가 없으므로 이미 가상 하드 디스크를 생성하지 않은 경우 지금 가상 하드 디스크 생성 을 선택합니다.(Create a virtual hard disk now)

만들기(Create) 를 클릭 하면 다음 화면에서 하드 디스크 파일 형식에 대한 세 가지 옵션을 제공합니다. VDI , VHD 또는 VMDK 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다 . VDI 는 VirtualBox에서 사용하는 형식이고 VHD 는 Microsoft의 Hyper-V 에서 사용 되며 VMDK 는 VMware 에서 사용됩니다 . 나중에 이 가상 머신을 다른 플랫폼으로 이동할 계획이라면 적절한 파일 형식을 선택해야 합니다.

다음 화면에서 새 가상 디스크를 동적으로 확장할지 아니면 고정 크기 디스크를 사용할지 선택해야 합니다. 고정 크기 디스크의 유일한 장점은 일반적으로 사용이 더 빠르다는 것입니다. 즉, 가상 머신이 전반적으로 더 빠르게 실행됩니다.

다음으로 가상 하드 디스크의 크기를 조정할 수 있습니다. 이전에 선택한 옵션에 관계없이 이 화면이 표시됩니다. 동적 할당(dynamically allocated) 을 선택한 경우 여기에서 선택하는 디스크 크기는 디스크가 커질 수 있는 최대 크기가 됩니다. 고정 크기(Fixed size) 를 선택한 경우 여기에서 크기는 시작할 가상 하드 디스크의 실제 크기가 됩니다.

그런 다음 Ubuntu 가상 머신을 만들어야 합니다. 아직 Ubuntu(Ubuntu) 를 실제로 설치 하지 않았습니다! 여전히 가상 머신이 ISO 파일을 가리키도록 한 다음 해당 (ISO)ISO 를 사용하여 부팅하여 Ubuntu 를 설치해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 목록에서 Ubuntu 를 클릭한 다음 (Ubuntu)설정(Settings) 을 클릭해야 합니다 .

왼쪽 에서 저장소 를 클릭한 다음 (Storage)컨트롤러: IDE( Controller: IDE) 를 클릭합니다 . Controller: SATA 아래에 Ubuntu.vdi가 표시되어야 합니다 . 작은 녹색 더하기 아이콘이 있는 왼쪽 아이콘을 클릭 합니다. (Click)이렇게 하면 IDE 컨트롤러에 광학 드라이브가 추가됩니다.

팝업 창에서 디스크 선택 을 클릭한 다음 (Choose disk)ISO 이미지 의 위치를 찾습니다 . 그것을 선택하고 IDE(IDE) 아래의 목록에 추가되었는지 확인하십시오 .

이제 기본 인터페이스로 돌아가 시작(Start) 버튼을 클릭합니다. 그러면 가상 머신이 시작되고 ISO 이미지를 자동으로 감지하고 Ubuntu 설치 프로그램 로드를 시작해야 합니다.

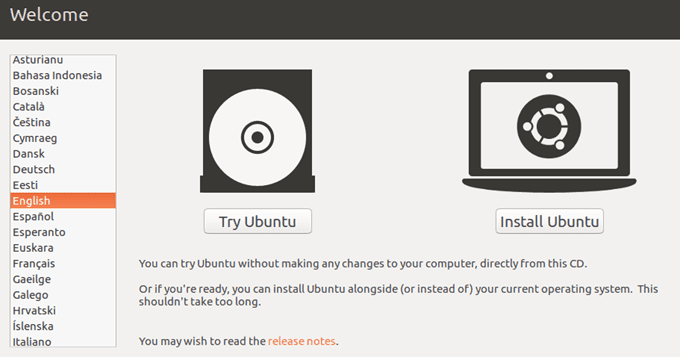
모든 것이 잘 되었다면 Ubuntu 시도(Try Ubuntu) 또는 준비가 되었다면 Ubuntu 설치( Install Ubuntu) 를 선택할 수 있는 대화 상자가 표시되어야 합니다 .
Ubuntu 설치 프로세스는 매우 간단하므로 각 단계를 거치지 않겠습니다. 설정을 사용자 정의할 수 있는 유일한 장소는 설치할 하드 드라이브를 선택할 때입니다. 가상 머신에 있으므로 디스크 지우기를 선택하고 Ubuntu를 설치하기(Erase disk and install Ubuntu) 만 하면 됩니다.

그게 다야! 다음 게시물에서는 Ubuntu(Ubuntu) 가상 머신 에 VirtualBox Guest Additions 를 설치하는 방법에 대해 작성하겠습니다 . 즐기다!
How to Install Ubuntu in VirtualBox
Looking to play arоund with Ubuntu to sеe whether or not you can handle Linυx? Well, it’s completely free, so there’s no reason to not givе it a shot. However, you either need a spare computer or a spare hаrd drive on your сurrent machine to run it.
If you don’t have those options or don’t want to mess up your existing systems, you can install Ubuntu into a virtual machine on your main PC. The free tool that I use is called VirtualBox. It’s very similar to VMware Workstation, except it’s free.
In this article, I’ll show you how to quickly get a copy of Ubuntu running as a virtual machine inside your current OS, which could be Windows, Mac or Linux.
Install Ubuntu in VirtualBox
First, go ahead and download VirtualBox using the link above and install it. It’s a fairly small program, so it shouldn’t take long to get it setup. Once you have it running, go ahead and download the version of Ubuntu you want to run. I downloaded the Desktop version, which was a 1.4GB ISO file.
Now click on the New button at the top left to create a new virtual machine.

Note that once you are familiar with the process of setting up a virtual machine in VirtualBox, you can click on the Expert Mode button to get through all the settings much faster. The first time you should use the guided wizard. On the following screen, we have to choose the operating system.

You can install a lot of different operating systems using this tool, but we are just working with Ubuntu Linux here. In my case, I chose Linux for Type and then chose Ubuntu. The program only gave me options for 32-bit because I used older hardware. Ideally, you should install the 64-bit versions of operating systems. If VirtualBox is showing you only 32-bit options and no 64-bit options, check out this post for the remedy.

Next, choose the amount of memory you would like to assign to your virtual machine. It’ll give you a recommended amount, but you can always manually adjust this by using the slider.

Next, you have the option of adding a virtual hard disk to the virtual machine or not. A VM without a hard drive is pretty useless, so go ahead and choose Create a virtual hard disk now, unless you already have one created.

Click Create and the next screen will give you three options for the hard disk file type. You can choose from VDI, VHD or VMDK. VDI is the format used by VirtualBox, VHD is used by Microsoft’s Hyper-V and VMDK is used by VMware. If you plan to move this virtual machine to another platform in the future, then make sure to choose the appropriate file type.

On the next screen, you have to choose whether you want the new virtual disk to grow dynamically or whether you want to use a fixed size disk. The only advantage to a fixed size disk is that it is usually faster to use. This means your virtual machine will run faster overall.

Next, you can adjust the size of the virtual hard disk. You will get this screen regardless of which option you chose previously. If you chose dynamically allocated, the disk size you choose here will be the max size the disk can grow. If you chose Fixed size, then the size here will be the actual size of the virtual hard disk to start with.

After this, the Ubuntu virtual machine should be created. Note that we have not actually installed Ubuntu yet! We still have to point the virtual machine to the ISO file and then boot up using that ISO to install Ubuntu. To do this, you need to click Ubuntu in the list and then click on Settings.

Click on Storage on the left-hand side and then click on Controller: IDE. You should see Ubuntu.vdi under Controller: SATA. Click on the left icon with the small green plus icon on it. This will add an optical drive to the IDE controller.

In the popup window, click on Choose disk and then browse to the location of the ISO image. Select it and make sure it has been added to the list under IDE.

Now go back to the main interface and click on the Start button. This will start up the virtual machine and it should automatically detect the ISO image and start loading the Ubuntu installer.

If all went well, you should see the dialog where you can choose to Try Ubuntu or to Install Ubuntu if you are ready.

The Ubuntu install process is pretty straight-forward, so I won’t go through each step there. The only place where you can customize settings is when choosing the hard drive to install it on. Since it’s in a virtual machine, just choose Erase disk and install Ubuntu.

That’s about it! In my next post, I’ll write about how you can install VirtualBox Guest Additions to the Ubuntu virtual machine. Enjoy!














