문제 해결을 위해 또는 메뉴에 표시되지 않는 설치한 프로그램을 찾기 위해 최근에 Ubuntu 에 설치된 패키지 목록을 확인해야 하는 경우가 있습니다. 최근에 설치된 것을 찾는 두 가지 방법이 있습니다. Synaptic Package Manager 를 사용하고 (Synaptic Package Manager)터미널(Terminal) 창 을 사용하는 명령 프롬프트에서 날짜별로 최근에 설치된 패키지를 볼 수 있습니다 .
시냅틱 패키지 관리자 사용
Synaptic Package Manager 를 사용하여 최근에 설치된 소프트웨어 패키지를 보려면 Administration | Synaptic Package Manager시스템(System) 메뉴 에서 시냅틱 패키지 관리자 .
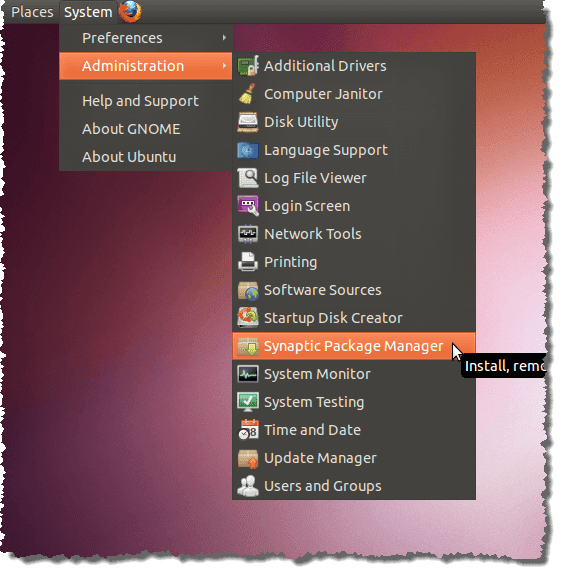
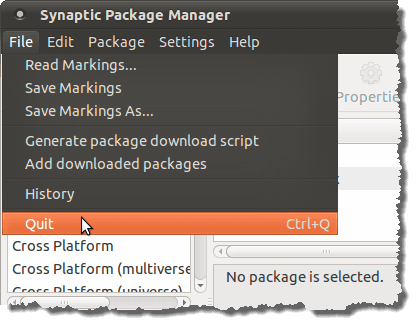
Synaptic Package Manager 대화 상자 의 파일(File) 메뉴 에서 기록(History) 을 선택합니다.

기록(History) 대화 상자가 표시됩니다 . Synaptic Package Manager 를 사용하여 설치 및 제거된 모든 패키지 는 월 및 날짜별로 나열됩니다. 왼쪽 창에서 해당 월의 왼쪽에 있는 화살표를 클릭 하면 해당 월 내에서 소프트웨어 패키지가 설치되거나 제거된 날짜가 표시됩니다. (Click)날짜를 클릭(Click) 하면 오른쪽 창에서 해당 날짜에 설치되거나 제거된 패키지를 볼 수 있습니다.
참고: (NOTE:)Synaptic Package Manager 를 사용하여 설치된 소프트웨어 패키지만 기록(History) 대화 상자 에 표시됩니다 . Ubuntu Software Center 와 같은 다른 방법을 사용하여 다른 소프트웨어를 설치한 경우 여기에 나열되지 않습니다.

기록(History) 대화 상자 를 닫으려면 닫기(Close) 버튼을 클릭합니다.

Synaptic Package Manager 를 닫으려면 파일(File) 메뉴 에서 종료(Quit) 를 선택 하십시오.
터미널 창 사용
터미널(Terminal) 창 에서 작업하는 것을 선호하는 경우 명령줄을 사용하여 설치된 소프트웨어 패키지 목록을 얻을 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하려면 Accessories | Terminal응용 프로그램(Applications) 메뉴 에서 터미널 .

(Enter)프롬프트에서 다음 명령을 입력 하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .
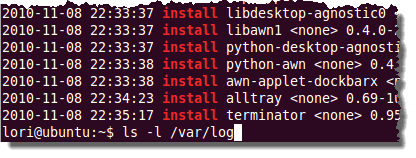
cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “
참고:(NOTE:) 각 백슬래시 뒤에 공백이 있습니다.
이 명령은 앞뒤 공백을 포함하여 " install " 이라는 용어와 일치하는 dpkg.log 파일의 항목을 표시합니다. (dpkg.log)" install " 항목은 완전히 설치된 패키지를 나타냅니다.

dpkg.log 파일의 모든 " 설치 " 항목은 (install)터미널(Terminal) 창에 표시되며 가장 최근 항목이 마지막에 나열됩니다.

dpkg.log 파일 의 날짜가 필요한 만큼 돌아가지 않으면 다른 dpkg 로그 파일이 있을 수 있습니다. dpkg.log 파일은 매주 순환되고 보관됩니다 . /var/log 디렉토리 의 내용을 나열하여 사용 가능한 dpkg 로그 파일을 찾을 수 있습니다 .
이렇게 하려면 프롬프트에서 다음 명령을 입력하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .
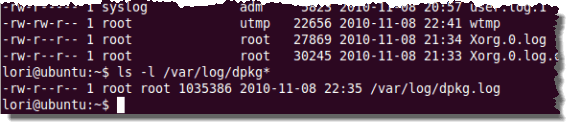
$ ls –l /var/log
참고:(NOTE:) " ls " 뒤에 하나의 대시와 소문자 " L " 다음에 다른 공백이 있습니다.
dpkg(Notice) 에 대한 로그뿐만 아니라 /var/log 디렉토리 의 모든 로그 목록을 가져 옵니다(dpkg) . dpkg 에 대한 로그 파일만 표시하려면 프롬프트에서 다음 명령을 입력하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .
$ ls –l /var/log/dpkg*
참고:(NOTE:) 다시 " ls " 뒤에 하나의 대시와 소문자 " L " 다음에 다른 공백이 있습니다.
최근에 설치한 새 시스템이기 때문에 dpkg.log 파일 이 하나만 표시됩니다. 볼 수 있도록 dpkg.log(dpkg.log) 파일 을 열려면 프롬프트에서 다음 명령을 입력하고 Enter 키를 누릅니다 .
$ gedit /var/log/dpkg.log

dpkg.log 파일이 gedit 에서(gedit) 열립니다 . " 설치(install) " 상태 의 패키지뿐만 아니라 모든 패키지가 나열됩니다 . 이렇게 하면 완전히 설치된 패키지를 찾기가 더 어려워집니다.
팁:(TIP:) cat cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “ 명령은 아마도 설치된 패키지 목록을 보는 가장 좋은 방법일 것입니다. 왜냐하면 로그 파일의 " install " 항목만 표시되기 때문입니다. dpkg.log 파일 에서 사용할 수 있는 것보다 오래된 설치된 패키지를 보려면 cat 명령의 (cat)dpkg.log 파일 이름 을 ls –l /var/log/dpkg* 를 사용하여 찾은 다른 dpkg 로그 파일 이름으로 바꾸십시오. 명령.

gedit 를 닫으려면 파일(File) 메뉴 에서 종료(Quit) 를 선택 하십시오.

터미널(Terminal) 창 을 사용하여 생성된 목록 이 더 완전하다는 것을 알 수 있습니다. Synaptic Package Manager 를 사용하여 설치된 프로그램뿐만 아니라 모든 방법을 사용하여 설치된 프로그램이 나열 됩니다(Programs) .
로리 카우프만
Display a List of Recently Installed Software Packages in Ubuntu
Thеre may be times when you need to view a list of the packages that wеre recently installed in Ubuntu for troubleshooting purposes or maybe just to find a program you installed that doеs not display in the menu. There are two waуs tо fіnd out what was installed recently. You can view recently installed packages by date usіng the Synaptic Package Manager and from the command prompt using a Terminal window.
Use the Synaptic Package Manager
To view software packages installed recently using the Synaptic Package Manager, select Administration | Synaptic Package Manager from the System menu.

On the Synaptic Package Manager dialog box, select History from the File menu.

The History dialog box displays. All packages installed and removed using the Synaptic Package Manager are listed by month and date. Click the arrow to the left of a month in the left pane to display dates within that month on which software packages were installed or removed. Click a date to view what packages were installed or removed on that date in the right pane.
NOTE: Only software packages installed using the Synaptic Package Manager are displayed on the History dialog box. If you installed other software using other methods, such as the Ubuntu Software Center, they are not listed here.

To close the History dialog box, click the Close button.

To close the Synaptic Package Manager, select Quit from the File menu.

Use a Terminal window
If you prefer working in a Terminal window, you can get a list of installed software packages using the command line. To do this, select Accessories | Terminal from the Applications menu.

Enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “
NOTE: There is a space after each of the backslashes.
This command displays entries from the dpkg.log file that match the term “ install “, including the spaces before and after. The “install” entries indicate packages that have been fully installed.

All the “install” entries in the dpkg.log file are displayed in the Terminal window, the most recent entries listed last.

If the dates in the dpkg.log file don’t go back as far as you need, there may be other dpkg log files. The dpkg.log file is rotated and archived weekly. You can find available dpkg log files by listing the contents of the /var/log directory.
To do this, enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
$ ls –l /var/log
NOTE: After “ls ” is one dash and a lowercase “L” followed by another space.

Notice that you get a listing of all the logs in the /var/log directory, not just the logs for dpkg. To display only the log files for dpkg, enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
$ ls –l /var/log/dpkg*
NOTE: Again, after the “ls ” is one dash and a lowercase “L” followed by another space.

Only one dpkg.log file displays in our system, because it is a new system we installed recently. To open the dpkg.log file for viewing, enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
$ gedit /var/log/dpkg.log

The dpkg.log file opens in gedit. All packages are listed, not only the ones with the “install” status. This makes it harder to find the fully installed packages.
TIP: Using the cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “ command is probably the best way of viewing a list of installed packages, because only “install” entries in the log file are displayed. If you need to view installed packages that are older than those available in the dpkg.log file, simply replace the dpkg.log filename in the cat command with other dpkg log filenames you find using the ls –l /var/log/dpkg* command.

To close gedit, select Quit from the File menu.

You may notice that the list generated using the Terminal window is more complete. Programs installed using any method are listed, not just programs installed using the Synaptic Package Manager.
by Lori Kaufman













