하드 드라이브를 분할하는 것은 답답하고 힘든 작업이 될 수 있습니다. 그러나 프로세스가 어떻게 작동하는지 이해하면 훨씬 덜 무섭습니다. 그렇다면 왜 드라이브를 파티션하고 싶습니까?
내가 대학에 다닐 때 다른 많은 학생들과 마찬가지로 사용하기 쉽고 미니멀한 미학을 위해 MacBook Pro 를 가지고 있었습니다. (MacBook Pro)학교에서 필요로 하는 일부 응용 프로그램이 Mac(Mac) 과 호환되지 않는다는 사실에 대해 생각하지 않았습니다 . 그 때 Mac에서 Windows를 실행할(run Wi) 수 있도록 드라이브를 분할하는 것에 대해 생각 했습니다.
또한 OS X 와 Windows 모두에서 사용할 수 있는 외장 하드 드라이브가 있었습니다 . 이 기사에서는 Mac(Mac) 에서 내부 및 외부 하드 드라이브를 분할하는 단계를 안내합니다 .
시작하기 전에 Time Machine 을 사용 하여 전체 Mac 컴퓨터 를 백업(backup) 해야 합니다 . 아무 것도 망치지 않더라도 OS가 시스템을 망치고 망가뜨릴 가능성이 높습니다.
파티션 외장 드라이브
대용량 외장 하드 드라이브가 있는 경우 전체 드라이브를 활용하도록 쉽게 파티션할 수 있습니다. 저는 Mac 에서 1.5TB 외장 드라이브를 사용하고 있었지만 실제로 공간의 1/4 이상을 사용하지 않았습니다.
대신, 다음은 내가 드라이브를 분할하는 방법을 보여주고 결과적으로 훨씬 더 유용하게 되었습니다.
- 33%: Mac(추가 스토리지) – 500GB
- 33%: Mac ( Time Machine 백업(Time Machine Backup) ) – 500GB
- 33%: Windows ( 추가 스토리지(Extra Storage) 및 백업(Backup) 은 동일한 파티션에 갈 수 있음) – 500GB
보시다시피 각 파티션은 고유한 파일 형식을 가질 수 있습니다. 더 큰 드라이브가 있는 경우 Linux(Linux) 등과 같은 다른 운영 체제에 대해 더 많은 파티션을 만들 수 있습니다 .
드라이브를 파티션하려면 MacBook 화면(MacBook Screen) 상단의 Spotlight ( 알림 표시줄(Notification Bar) )로 이동하고 디스크 유틸리티(Disk Utility) 를 입력 하십시오.

왼쪽에서 EXTERNAL 이라는 탭으로 이동합니다 .

당신은 나와 조금 다르게 보일 것입니다. 왼쪽 의 외부(External) 제목 아래 에 3개 대신 1개의 하드 드라이브가 있어야 합니다(이미 파티션을 나눴습니다). 해당 외장 하드 드라이브로 이동(Navigate) 하여 필요에 따라 파티션을 나누십시오.
참고: 외장 하드 드라이브가 Mac 운영 체제용으로 포맷되지 않은 경우 먼저 초기화한 다음 지워야 할 수 있습니다. 이것은 정말 쉽습니다:(NOTE: If your external hard drive is not formatted for the Mac operating system, you may first need to Initialize it and then Erase it. It’s very easy:)
- 왼쪽의 외부 탭에서 사용하려는 드라이브를 선택합니다.
- 그런 다음 상단 의 지우기 옵션을 선택하십시오.(Erase)
- 일단 거기에 이름을 지정하고 Mac OS Extended(Journaled) 로 포맷하십시오.( Mac OS Extended (Journaled))
- Scheme 의 경우 GUID , MBR 또는 Apple 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다 . 드라이브를 저장용으로만 사용하는 경우 어느 것을 선택하든 상관 없습니다. 그러나 드라이브에서 부팅하려는 경우 Windows 및 Linux 의 경우 (Linux)MBR 을 선택 하고 OS X 의 경우 (OS X)GUID 를 선택해야 합니다 . Boot Camp 용 드라이브를 사용할 계획이라면 GUID 도 선택해야 합니다 .

보안 옵션(Security Options) 을 클릭하고 다양한 보안 수준에서 선택할 수도 있습니다. 기본적으로 OS X 은 드라이브를 안전하게 지우지 않는 가장 빠른 방법을 사용합니다. 슬라이더를 가장 보안(Most Secure) 으로 이동하면 데이터를 7번 덮어써 데이터를 지우는 DOD 표준을 충족합니다 . 이렇게 하면 다른 사람이나 소프트웨어가 드라이브에서 이전에 기록된 데이터를 복구하는 것을 방지할 수 있습니다.

OS X 에서 (OS X)Time Machine 백업에 드라이브를 사용할지 묻는 메시지가 표시될 수 있지만 백업 에 전체 드라이브를 사용하지 않으려면 나중에 결정 을 선택해야 합니다. (Decide Later)이제 외장 드라이브를 분할할 준비가 되었습니다!
First Aid , Partition , Erase , Restore , Mount 등 옵션이 있는 맨 위로 이동합니다. 파티션을 선택 하고 특정 요구 사항에 따라 파티션을 만듭니다 . (Partition)제 경우에는 드라이브의 1/3인 500GB 크기를 선택했습니다.

드라이브 파티션 방법을 선택하고(여기 스크린샷에서 사용한 백분율이므로 다시 참조) 적용(Apply, ) 을 선택한 다음 파티션(Partition) 을 클릭 합니다. 그런 다음 파티션을 나누는 데 몇 분이 걸리므로 인내심을 가지십시오!

완료되면 드라이브 옆에 녹색 확인 표시가 나타나야 하고 Operation Success( Operation Successful) 라고 표시되어야 합니다 . 이제 완료(Done) 를 선택하면 첫 번째 파티션이 완료됩니다.

이제 나머지 공간을 분할하려면 외부 에서 (External)제목 없음(Untitled) 을 클릭한 다음 파티션(Partition) 을 다시 클릭 합니다.
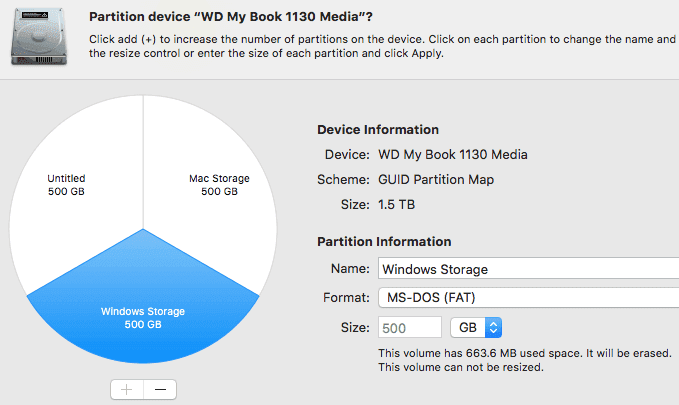
파티션에 이름을 지정하고 크기를 선택한 다음 형식을 선택합니다. Windows 스토리지 용이므로 MS-DOS(FAT)를(MS-DOS (FAT)) 선택했습니다 . Windows 와 Mac 모두와 호환되므로 원하는 경우 exFAT 를 선택할 수도 있습니다 .
파티션 내부 드라이브
내부 하드 드라이브를 파티셔닝하는 것은 따라야 하는 절차 측면에서 거의 동일하지만 구현 방식에서 약간 다릅니다.
내부 드라이브에 이미 OS X 이 설치되어 있으므로 (OS X)파티션(Partition) 을 클릭 하고 크기를 선택하면 드라이브에서 이미 사용된 공간보다 작은 파티션을 만들 수 없다는 것을 알 수 있습니다.

내 내부 드라이브는 이미 359GB의 공간을 사용하고 있었기 때문에 200GB를 입력하면 자동으로 359GB로 변경되고 첫 번째 볼륨을 제거할 수 없고 결과 볼륨이 너무 커서 볼륨을 분할할 수 없다는 메시지가 표시됩니다. 작은.
그래서 추가 파티션을 만들고 싶다면 먼저 OS X 를 포함할 파티션을 만들고 프로그램 등을 설치할 수 있는 추가 공간을 제공하는 것입니다. 아래에서는 이름을 Macintosh HD 로 남겨두고 파티션을 500GB로 만들었습니다. 즉, OS X 이 설치된 파티션에는 추가 데이터를 위한 약 140GB의 여유 공간이 있습니다.
기본적으로 전체 디스크를 차지하는 원래 파티션을 축소하고 있습니다. 그런 다음 여유 공간을 원하는 대로 분할합니다.

보시다시피 원래 파티션을 1TB 대신 500GB로 만들었습니다. 그러면 다른 파티션을 만들기 위해 디스크에서 500GB가 확보됩니다. 외장 하드 드라이브와 마찬가지로 파티션이 생성되면 Untitled 를 클릭합니다. 그러나 이번에는 Internal 제목 아래에서 Partition 을 클릭합니다 .
그것이 기본적으로 OS X에서 드라이브를 분할하는 모든 것입니다. 다행히도(OS X. Hopefully) , 그것이 당신을 위해 일했습니다. 즐기다!
How to Partition an External or Internal Hard Drive in OS X
Pаrtitioning your hаrd drіve can be a frustrating and daunting task. Howеver, once you understand hоw the process works, it’s a lot less scary. So why would you want to partition a drive?
Back when I was in college, like many other students, I had a MacBook Pro for ease of use and its minimalist aesthetic. I didn’t think about the fact that some applications that I needed for school were not compatible with Mac. That is when I thought about partitioning my drive so that I could run Windows on Mac.
In addition, I had an external hard drive that I also wanted to be able to use with both OS X and Windows. In this article, I’ll walk you through the steps for partitioning internal and external hard drives on a Mac.
Before you start, you should make sure to backup your entire Mac computer using Time Machine. Even if you don’t mess anything up, the chances are good that the OS will screw up and break your system.
Partition External Drive
If you have a large external hard drive, you can easily partition it so that the entire drive gets utilized. I was using a 1.5 TB external drive with my Mac, but never really used more than 1/4 of the space.
Instead, here’s how I ended up partitioning my drive, which ended up making it much more useful:
- 33%: Mac (Extra Storage) – 500GB
- 33%: Mac (Time Machine Backup) – 500GB
- 33%: Windows (Extra Storage and Backup can go on same partition) – 500GB
As you can see, each partition can have its own file format. If you have an even larger drive, you can create even more partitions for other operating systems like Linux, etc.
To partition the drive, go to Spotlight at the top of your MacBook Screen (Notification Bar) and type in Disk Utility.

On the left-hand side, navigate to the tab that says EXTERNAL.

Yours will look a little bit different than mine. Under the External heading on the left-hand side, you should have one hard drive instead of 3 (I have already partitioned mine). Navigate to that external hard drive and partition it according to your needs.
NOTE: If your external hard drive is not formatted for the Mac operating system, you may first need to Initialize it and then Erase it. It’s very easy:
- Under the external tab on the left side, select the drive you want to use.
- Then select the Erase option at the top
- Once there, give it a name and format it to Mac OS Extended (Journaled)
- For the Scheme, you can pick from GUID, MBR or Apple. If you’re only using the drive for storage, then it doesn’t really matter which one you pick. However, if you plan to boot from the drive, you should pick MBR for Windows and Linux and GUID for OS X. If you plan to use the drive for Boot Camp, you should also pick GUID.

Note that you can also click on Security Options and choose from different levels of security. By default, OS X will use the fastest method, which not does securely erase the drive. If you move the slider to Most Secure, it will meet the DOD standard for erasing data by overwriting the data 7 times. This will prevent anyone or any software from recovering any previously written data from the drive.

OS X may ask you if you want to use the drive for Time Machine backups, but you should choose Decide Later unless you want to use the entire drive for the backups. Now you’re ready to partition the external drive!
Go to the top where it has the options: First Aid, Partition, Erase, Restore, Mount, etc. Select Partition and create the partitions based on your specific needs. In my case, I chose a size of 500 GB, which is one-third of the drive.

Select how you would like to partition the drive (refer back to my percentages, as that’s what I have used in the screenshots here), select Apply, and then click Partition. After this, it will take a few minutes to partition, so be patient!

When completed should see the green checkmark next to your drive and it should say Operation Successful. Now select Done and you’re done with the first partition.

Now to partition the rest of the space, you will click on Untitled under External and then click on Partition again.

Give the partition a name, pick a size and choose the format. Since this is going to be for Windows storage, I chose MS-DOS (FAT). You can also choose exFAT if you like as that is compatible with both Windows and Mac.
Partition Internal Drive
Partitioning an internal hard drive is pretty much the same in terms of the procedure you have to follow, but it’s a little bit different in how it gets implemented.
Since you already have OS X installed on your internal drive, when you click Partition and choose a size, you’ll notice that you can’t create a partition that is smaller than the amount of space already used on the drive.

My internal drive was already using 359GB of space, so when I typed in 200GB, it automatically changed it to 359GB and put up a message stating that the first volume cannot be removed and the volume could not be split because the resulting volumes would be too small.
So if you want to create an additional partition, the first thing is to create a partition that will include OS X and give you some additional space for installing programs, etc. Below, I left the name as Macintosh HD and made the partition 500GB. That means the partition where OS X is installed has about 140GB of breathing room for extra data.
Basically, we are just shrinking the original partition, which took up the entire disk to something smaller. Then we will partition the free space as we like.

As you can see, I have made the original partition 500GB instead of 1TB, which frees up 500GB on the disk for creating other partitions. As with the external hard drive, once the partition has been created, click on Untitled, but this time under the Internal heading and click on Partition.
That’s basically all there is to partitioning drives in OS X. Hopefully, it worked for you. Enjoy!










