Linux 에서 (Linux)USB 드라이브 및 하드 드라이브와 같은 저장 장치를 사용하려면 Linux 운영 체제 를 사용할 때 구성하는 방법도 이해해야 합니다 . 저장 장치는 종종 파티션이라는 별도의 부분으로 분할됩니다. 이를 통해 하드 드라이브를 여러 가상 부분으로 분할하여 파일 시스템을 생성할 수 있습니다.
Linux 디스크 파티션은 각 파일 시스템이 사용할 수 있는 공간을 알려주는 경계 장치와 같습니다. 공유 드라이브를 생성(creating shared drives) 할 때 편리 하며 드라이브 공간(edit drive space) 을 보다 효과적으로 할당 및 편집할 수 있습니다.

예를 들어, 2GB USB 드라이브가 있는 경우 전체 드라이브를 차지하는 파티션, 각각 1GB의 파티션 2개 또는 다양한 크기의 파티션을 만들 수 있습니다. 각 Linux 디스크 파티션은 자체 하드 드라이브 역할을 합니다. 동일한 컴퓨터에서 둘 이상의 운영 체제를 사용하는 경우 특히 유용합니다.
Parted 명령 사용(Use The Parted Command)
우분투에는 parted 가 사전 설치되어 있습니다. 다른 배포판을 사용하는 경우 다음 명령을 사용하여 설치합니다.
apt-get-install parted
시스템의 하드 드라이브를 보려면 다음을 입력하십시오. sudo parted -l . 아래 스크린샷에서 장치 목록을 참조하십시오.

Disk /dev/sdaUbuntu 파티션 디스크 가 있음을 볼 수 있습니다 . /dev/sda5 라는 파티션 을 사용하여 새 파티션을 생성해 보겠습니다.
다음 단계는 parted 를 시작하는 것 입니다. 그러나 루트 권한을 사용하고 있는지 확인하십시오. 파티션할 드라이브를 선택합니다. 우리는 /dev/vdc 를 사용할 것 입니다.
다음 명령을 입력합니다.
(parted) select /dev/vdc
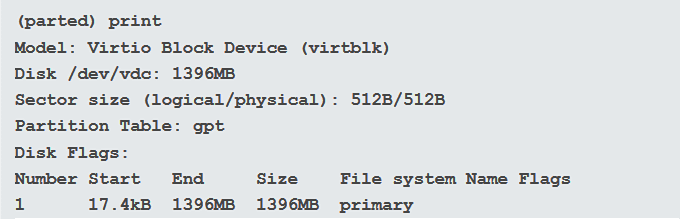
Linux 디스크 파티션 에 무엇이 있는지 보려면 다음을 입력 하십시오(print) . 하드 드라이브, 크기 및 파티션 테이블에 대한 요약이 표시됩니다.
아래 예에서 하드 드라이브는 모델: Virtio Block Device,(Model: Virtio Block Device, ) 크기는 1396MB , 파티션 테이블은 gpt 입니다.

Ubuntu 파티션 디스크 를 구성하려면 먼저 quit 를 입력하여 종료해야 합니다 . 다음 단계는 parted를 사용하여 선택한 저장 장치를 여는 것입니다. (parted.)이 기사에서는 /dev/vdc 장치를 사용합니다.
사용하려는 특정 장치를 지정하지 않으면 시스템이 임의로 장치를 선택합니다. 장치 이름(vdc)이 포함된 아래 명령을 사용합니다.
sudo parted /dev/vdc
파티션 테이블을 설정하려면 GPT 를 입력한 다음 Yes 를 입력하여 수락합니다. 유지하려는 데이터가 없는 파티션에서만 이 작업을 수행해야 합니다.

다음 명령을 사용하여 저장 장치에 대한 정보를 표시하려면 파티션 테이블을 검토하십시오.
(parted) 인쇄((parted) print)
새 파티션을 만드는 방법에 대한 지침을 보려면 (parted) help mkpart 를((parted) help mkpart) 입력하십시오 .

이 기사에서는 아래 명령을 사용하여 새 Linux 디스크 파티션을 생성합니다.
(parted) mkpart 기본 0 1396MB((parted) mkpart primary 0 1396MB)
0 은 드라이브 시작 부분에서 파티션을 시작한다는 의미입니다. 위의 스크린샷에서 드라이브에 1396MB 가 있음을 알 수 있습니다. 위의 명령은 시스템에 파티션을 0 에서 시작하고 (0)1396MB 에서 끝내도록 지시 합니다.
파티션을 사용하려면 포맷해야 합니다. 먼저 (First)quit 를 입력하여 parted 를 종료해야 합니다 . 그런 다음 ext4 파일 시스템을 사용하여 아래 명령을 입력하여 디스크를 포맷합니다.
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdc
sudo parted /dev/vdc 를 입력하여 확인합니다 . parted 를 종료하려면 quit 를 입력 하십시오. parted 를 종료 하면 변경 사항이 자동으로 저장됩니다.
명령 모드에서 단일 문자 명령을 사용하여 수행할 수 있는 작업 목록을 표시합니다. m 을 입력 하고 Enter 키(Enter) 를 누릅니다 .

cfdisk를 사용하여 디스크 파티션 생성(Create Disk Partitions Using cfdisk)
Cfdisk 는 디스크 장치에서 파티션을 생성, 삭제 및 수정하는 데 사용되는 Linux 유틸리티 프로그램입니다. 이를 사용하여 파티션을 생성하려면 다음 명령을 입력하십시오.
# cfdisk /dev/sda
이 예의 드라이브 이름은 sda 입니다.

위의 스크린샷에서 디스크 장치에 대한 요약 정보를 볼 수 있습니다. 창 중앙에 파티션 테이블이 표시됩니다. 하단의 괄호는 선택 가능한 명령을 보여줍니다.
목록에서 파티션을 선택하려면 위쪽 및 아래쪽 화살표 키를 사용합니다. 오른쪽 및 왼쪽 화살표를 사용하여 명령을 선택합니다.
위의 예는 세 개의 기본 파티션(1,2 & 3)을 보여줍니다. 여유 (Notice)공간(free space) 파티션 유형을 확인 하십시오 .
하단 창에서 새로(New) 만들기를 선택하여 새 파티션을 만듭니다 . 이 파티션을 /dev/sdb 라고 합니다. # cfdisk /dev/sdb 명령을 입력합니다 . 다음 화면에서 파티션 유형으로 기본(primary ) 을 선택 합니다.
다음 화면에서 파티션의 크기를 지정합니다. 800KB의 파티션을 생성합니다. 이제 파티션을 시작할 위치를 결정하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다. 여유 공간(beginning of free space) 의 시작 부분을 선택합니다 .
다음 화면에서 쓰기(Write) 를 선택 하여 변경 사항을 저장하고 파티션 데이터를 디스크에 씁니다. 다음 명령을 사용하여 새 파티션을 인쇄하여 확인하십시오.
fdisk -l /dev/sdb

Linux 디스크 파티션 생성을 위한 결론적 팁(Concluding Tips for Creating Linux Disk Partitions)
항상 데이터를 백업해야 합니다. 아주 작은 실수라도 중요한 드라이브의 파티션을 파괴할 수 있습니다.
또한 파티션을 만들 때 올바른 드라이브를 사용하고 있는지 확인하고 다시 확인하십시오. 그렇지 않으면 데이터가 손실될 수 있습니다.
아래 의견에 질문을 알려주십시오.
How to Create a Linux Disk Partition
To uѕe storage devices such as USB drivеs and hard drives in Linux, you need to also understand how to structure them when using Linux оperating sуstem. Storage devices are often split іntо separate portions called partitions. This enаbles you to create a file sуstem bу splitting уour hard drive into multіple virtual parts.
A Linux disk partition is like a boundary device that tells each file system how much space it can use. It’s handy when creating shared drives and enables you to allocate and edit drive space more effectively.

For example, if you have a 2GB USB drive, you can create a partition that takes up the entire drive, two partitions of 1GB each, or variations of sizes. Each Linux disk partition acts as its own hard drive. It is especially useful if you are using more than one operating system on the same computer.
Use The Parted Command
Ubuntu comes preinstalled with parted. If you are using a different distribution, install it using the following command:
apt-get-install parted
To see the hard drives on your system, type: sudo parted -l. See the list of devices in the screenshot below:

You can see above that there are three Ubuntu partition disks on Disk /dev/sda. Let’s use the partition called /dev/sda5 to create a new partition.
The next step is to launch parted. But be sure you are using root privileges. Choose the drive you want to partition. We will be using /dev/vdc.
Type the following command:
(parted) select /dev/vdc
To see what is in the Linux disk partition, type: print. You will see a summary of your hard drive, the size, and the partition table.
In the example below, the hard drive is Model: Virtio Block Device, the size is 1396MB, and the partition table is gpt.


To configure the Ubuntu partition disk, you must exit first by typing quit. The next step is to open the selected storage device using parted. In this article, we will use the /dev/vdc device.
If you don’t specify the specific device you want to use, your system will randomly select a device. Use the command below that includes the device name (vdc):
sudo parted /dev/vdc

To set the partition table, type GPT, then Yes to accept it. You should only do this on partitions that contain no data you want to keep.

Review your partition table to show information about the storage device with the following command:
(parted) print
To see instructions on how to make a new partition, type (parted) help mkpart.

For this article, we will create a new Linux disk partition using the command below:
(parted) mkpart primary 0 1396MB
The 0 means you want to start the partition at the beginning of the drive. We know from the screenshot above that the drive has 1396MB. The command above tells your system to start the partition at 0 and end it at 1396MB.
To be able to use the partition, it must be formatted. First, you need to exit parted by typing quit. Then, using the ext4 file system, type the command below to format the disk:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdc
Verify by typing sudo parted /dev/vdc. To exit parted, type quit. When you exit parted, the changes save automatically.
In command mode, use a single letter command to show you a list of the actions you can take. Type m and press Enter.

Create Disk Partitions Using cfdisk
Cfdisk is a Linux utility program used to create, delete, and modify partitions on a disk device. To use it to create a partition, enter the following command:
# cfdisk /dev/sda
The name of the drive for this example is sda.

In the screenshot above, you can see summary information for the disk device. The middle of the window shows the partition table. The brackets on the bottom show selectable commands.
To select a partition from the list, use the up and down arrow keys. Select a command by using the right and left arrows.
The example above shows three primary partitions (1,2 & 3). Notice the free space partition type.
Create a new partition by selecting New from the bottom window. We will call this partition /dev/sdb. Type the command # cfdisk /dev/sdb. Next select primary as the partition type from the next screen.
On the next screen you will specify the size of the partition. We will create a partition that is 800 KB. Now you will be asked to determine where to start the partition. Choose the beginning of free space.
From the next screen, select Write to save your changes and write the partition data to disk. Verify the new partition by printing it using the following command:
fdisk -l /dev/sdb

Concluding Tips for Creating Linux Disk Partitions
You should always back up your data. Even the smallest mistake can destroy the partition of a critical drive.
Also, be sure to verify and re-verify that you are using the correct drive when creating your partition. Otherwise, you could lose data.
Let us know your questions in the comments below.










