특정 시간에 프로세서의 전력이 얼마나 사용되고 있는지 알고 싶었던 적이 있습니까? 아니면 좋아하는 게임에 사용할 수 있는 RAM 이 얼마나 남았습니까? 비디오 카드의 전력이 얼마나 사용됩니까? 이 모든 것은 앱과 게임(apps and games) 이 제대로 실행되지 않는 필수 시스템 리소스입니다. 통계 및 실시간 정보를 보려면 Windows 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 통해 사용자가 현재 프로세서( CPU ) 및 메모리 사용률(memory utilization) 을 모니터링 하고 비디오 카드(video card) ( GPU ) 사용량 및 기타 시스템 리소스. 시스템 리소스에 대한 탭을 유지하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
참고:(NOTE:) 이 가이드는 Windows 10 및 Windows 8.1 용으로 작성되었으며 우리가 보여주는 일부 기능은 최신 버전의 (Windows 8.1)Windows 10 에서만 사용할 수 있습니다 .
시스템 리소스를 모니터링할 수 있는 도구를 찾을 수 있는 위치: 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 의 성능 탭 에 액세스(Performance tab)
리소스 소비(resource consumption) 를 보려면 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 시작해야 합니다 . 이를 수행하는 방법은 여러 가지가 있지만 속도와 편의성 을 위해 (speed and ease)키보드 단축키 (keyboard shortcut) "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." 를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다 . 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 가 압축 보기로 열리면 "자세히" 를 ("More Details")클릭하거나 탭(click or tap) 하여 전체 보기로 확장합니다.
그런 다음 성능(Performance) 탭 을 클릭하거나 탭합니다. 아래 스크린샷과 거의 비슷해야 합니다. 모양과 내용은 사용하는 Windows 버전 과 하드웨어에 따라 다릅니다.

작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)성능(Performance) 탭 을 사용하여 CPU , GPU 및 메모리 사용률(memory utilization) 과 같은 필수 하드웨어 구성 요소의 성능을 모니터링하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다 .
1. 작업 관리자(Manager) 를 통해 사용자는 현재 프로세서 사용률 을 모니터링할 수 있습니다.(processor utilization)
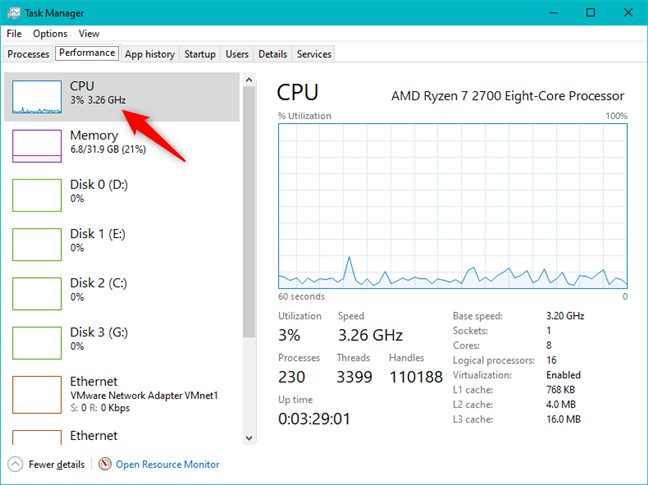
기본적 으로 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)성능(Performance) 탭은 먼저 프로세서로 알려진 CPU 사용량을 표시합니다 . 아직 선택하지 않은 경우 창 왼쪽에 있는 CPU 를 클릭하거나 탭하여 수동으로 선택할 수 있습니다.(CPU)
창(window and choosing) 안의 아무 곳이나 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭 하고 "View -> CPU."CPU 사용량 을 볼 수도 있습니다 .

프로세서를 선택하고 나면 창 오른쪽에 지난 60초 동안 CPU 사용량 의 백분율을 보여주는 그래프가 표시되어야 합니다. (CPU usage)리소스 (Notice)보기(resource view) 의 오른쪽 상단 모서리(right corner) 에 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 가 프로세서의 정확한 모델을 표시합니다.

그래프 아래에는 현재 CPU 사용률 및 속도(CPU utilization and speed) 에 대한 자세한 정보는 물론 기본 속도, (Base speed,)소켓(Sockets) 및 코어(Cores) 수 , 논리 프로세서(Logical processors) (스레드), 가상화(Virtualization) 기능이 켜져 있는지 여부와 같은 프로세서 사양에 대한 정보가 있습니다. , 그리고 사용 가능한 레벨 1(Level 1) , 2, 3 캐시 메모리(cache memory) 의 양 .
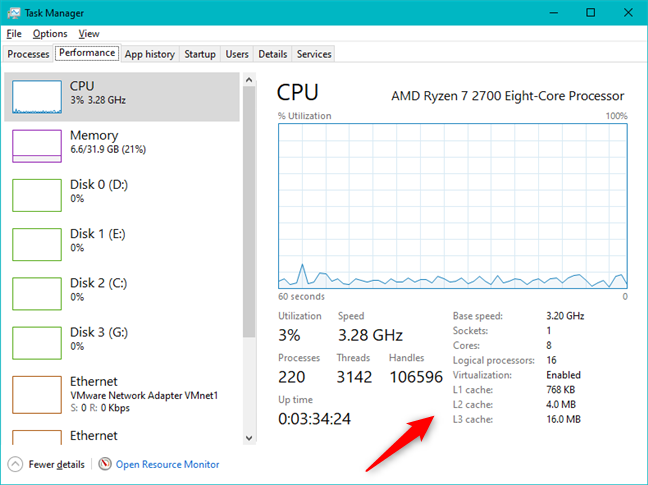
기본적으로 PC의 각 물리적 프로세서에 대한 그래프가 표시됩니다. 이해가 되지만 일부 사용자가 원하는 것은 아닐 수도 있습니다. 프로세서 사용량(processor usage) 에 대한 더 자세한 그림을 보려면 그래프를 논리 프로세서로 분할할 수 있습니다. CPU 그래프를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "그래프 변경" 위로 마우스를 가져간 다음 ("Change graph to")"논리 프로세서"("Logical processors.") 를 클릭하거나 탭합니다 .
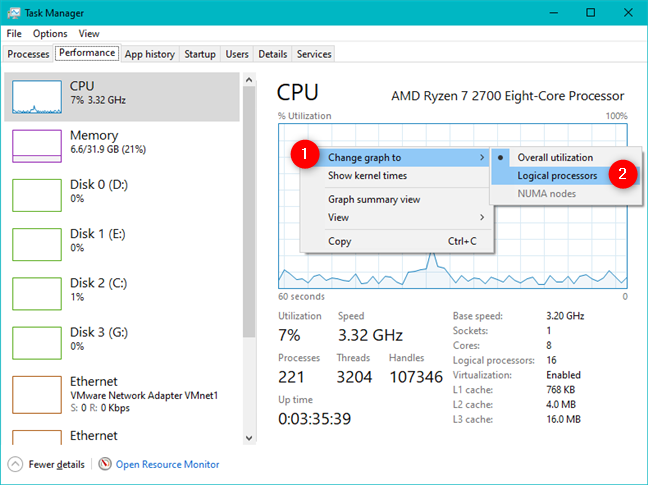
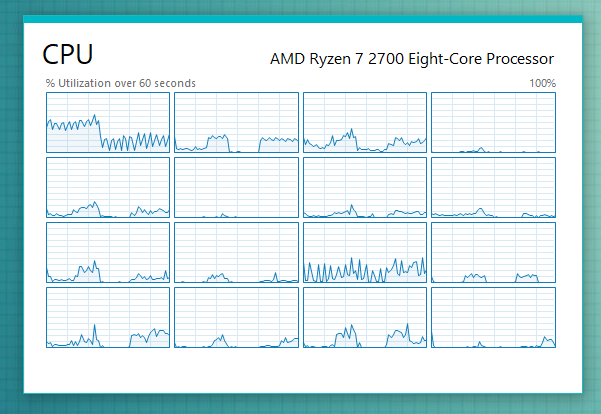
이제 각 CPU 의 논리적 프로세서에 대해 더 작은 그래프가 표시되어야 합니다. AMD Ryzen 7 2700 프로세서 의 경우 각 스레드에 대해 하나씩 16개의 차트가 제공됩니다. 컴퓨터의 프로세서에 따라 더 많이 또는 더 적게 보일 수 있습니다.

CPU 주기가 할당되는 방식에 대한 더 많은 정보를 보려면 커널 시간 표시를 고려할 수 있습니다. 내부 시스템 기능을 담당하는 커널이 얼마나 많은 CPU 사이클을 사용하고 있는지, 사용자 프로세스가 얼마나 사용하고 있는지 보여줍니다.(CPU)
커널 시간을 활성화하려면 CPU 그래프를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "커널 시간 표시"를 클릭하거나 탭합니다.("Show kernel times.")

그래프 의 어두운 영역은 커널 시간(graph represent kernel time) 을 나타내는 반면 밝은 영역은 다른 유형의 사용을 나타냅니다.

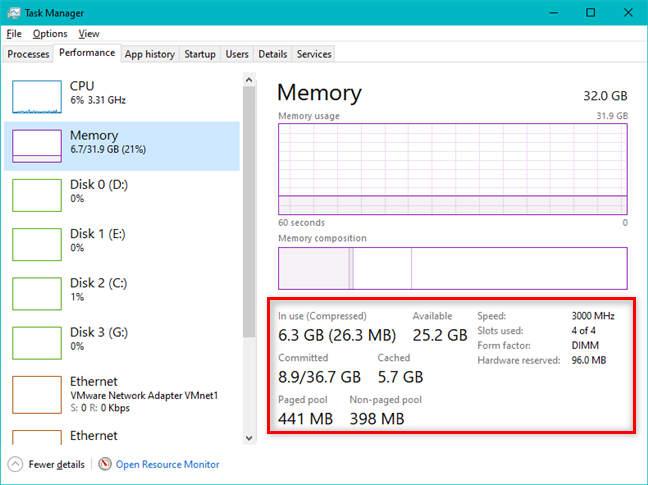
2. 작업 관리자(Manager) 를 통해 사용자는 현재 메모리 사용률(memory utilization) ( RAM ) 을 모니터링할 수 있습니다.
특히 속도가 느려지는 동안 계속 주시해야 할 또 다른 리소스는 RAM ( Random Access Memory )입니다. 성능(Performance) 탭 의 왼쪽에 있는 리소스 목록에서 메모리(Memory) 를 선택하여 메모리 사용량(memory usage) 을 볼 수 있습니다 .

메모리(Memory) 그래프 로 전환하려면 창 내부의 아무 곳이나 마우스 오른쪽 버튼을 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "View -> Memory."

메모리(Memory) 섹션에는 두 개의 그래프가 표시됩니다. 맨 위 그래프는 마지막 1분 동안 사용된 메모리의 백분율을 표시합니다. 아래 그래프는 메모리 할당 방법을 보여줍니다. 아래 그래프의 각 섹션에 마우스를 가져가면 무엇이 무엇인지 볼 수 있습니다.

RAM 사용량(RAM usage) 은 4가지 사용 유형으로 나뉩니다.
- 사용(In Use) 중 - 현재 앱, 드라이버 또는 Windows 자체에서 사용 중인 메모리입니다.
- 수정(Modified) 됨 - 다른 용도로 사용하기 전에 디스크에 내용을 기록해야 하는 메모리입니다.
- 대기(Standby) - 현재 사용되지 않는 캐시된 데이터와 코드가 포함된 메모리입니다.
- 여유(Free) - 현재 사용하지 않고 사용 가능한 여유 메모리입니다.
그래프 아래에는 사용된 메모리, 사용 가능한 메모리, 속도, 사용된 슬롯 및 폼 팩터, 페이징 및 비페이징 메모리 풀 크기 등을 포함하여 (memory pool size)RAM 에 대한 자세한 정보가 있습니다. 표시되는 메모리 풀은 실제 메모리에 상주하거나 필요에 따라 디스크에서 앞뒤로 스왑할 수 있습니다. 또한 캐시에 사용된 총 메모리와 총 커밋된 메모리도 확인해야 합니다. 표시되는 데이터의 양은 또한 컴퓨터의 하드웨어 구성(hardware configuration) 에 따라 다릅니다 .
3. 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 통해 사용자가 현재 비디오 카드 사용률(video card utilization) ( GPU ) 을 모니터링할 수 있습니다.
2019년 5월 (May 2019)업데이트 및 Fall Creators Update(Update and Fall Creators Update) 를 포함한 최신 버전의 Windows 에서는 작업 관리자 를 통해 (Task Manager)GPU 사용량(GPU usage) 도 확인할 수 있습니다 . 이 기능은 이전 버전의 Windows 10 이나 이전 버전의 Windows 에는 없습니다 .
작업 관리자(Task Manager) 창의 왼쪽에 있는 목록에서 선택하여 모든 그래픽 카드의 성능을 모니터링할 수 있습니다 . 장치에 두 개 이상의 비디오 카드(video card) 가 설치되어 있으면 각각에 대한 항목이 있어야 합니다.

모니터링할 비디오 카드(video card) 를 선택하면 창의 오른쪽이 그래프와 해당 활동에 대한 정보로 채워집니다. 선택한 비디오 카드(video card) 유형에 따라 3D, 복사, 비디오 인코딩(3D, Copy, Video Encode) 및 비디오 디코딩(Video Decode) 에 소비되는 전력량에 대한 그래프가 표시되어야 합니다 .

기본적으로 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 에는 4개의 다른 그래프만 표시할 수 있는 충분한 공간이 있습니다. 그러나 그 중 하나를 변경하고 다른 기능을 모니터링하려면 그래프의 왼쪽 상단 모서리에 있는 작은 화살표 버튼을 클릭하거나 탭하고 시청할 항목을 선택할 수 있습니다. 해당 비디오 카드(video card) 에서 제공하는 실제 기능에 따라 비디오 처리, 레거시 오버레이, 보안, Cuda, VR(Video Processing, Legacy Overlay, Security, Cuda, VR,) 등과 같은 항목 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다 .

4개의 기능 그래프에서 작업 관리자 는 (Task Manager)비디오 메모리(video memory) 가 어떻게 사용되는지도 보여줍니다 . "공유 GPU 메모리 사용량"("Shared GPU memory usage") 에 대한 그래프가 있어야 하며 비디오 카드(video card) 에도 전용 메모리가 있는 경우 "전용 GPU 메모리 사용량"이라는 그래프도 있어야 합니다. ("Dedicated GPU memory usage.")각 그래프의 오른쪽 상단에서 시스템에서 사용 가능한 총 비디오 메모리 양을 확인할 수 있습니다.
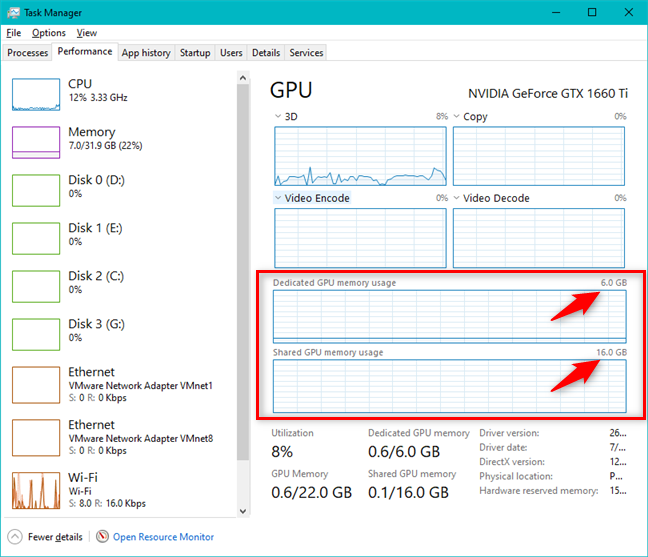
그래프 아래에는 기타 유용한 정보가 많이 있습니다. 비디오 카드 의 총 사용률 , 사용된 (Utilization)GPU 메모리(GPU Memory) 양 및 사용 가능한 양은 물론 전용 GPU 메모리,(Dedicated GPU memory,) 사용 된 공유 GPU 메모리(Shared GPU memory) 및 사용 가능한 양을 볼 수 있습니다. 사용 된 드라이버 버전 , (driver version)드라이버 날짜(driver date) , DirectX 버전 , (DirectX version)하드웨어 예약 메모리(Hardware reserved memory) 의 양(있는 경우), 컴퓨터 내부 에서 비디오 카드 가 연결된 (video card)PCI 버스(PCI bus) 를 보여주는 물리적 위치 에 대한 세부 정보도 있습니다.(Physical location)

4. 작업 관리자(Manager) 를 통해 사용자는 현재 네트워크 사용률(network utilization) ( Wi-Fi , 이더넷(Ethernet) , Bluetooth ) 을 모니터링할 수 있습니다.
네트워크 사용(network usage) 을 모니터링하려면 먼저 모니터링할 네트워크 인터페이스를 선택합니다. 작업 관리자 (Task Manager)성능(Performance) 탭 의 왼쪽에 있는 리소스 목록(resource list) 에서 이 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다 . 원하는 경우 성능(Performance) 탭 의 아무 곳이나 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "View -> Network."

이더넷 및 Wi-Fi 연결(Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections) 은 가상 머신 또는 Bluetooth 어댑터 에 사용할 수 있는 가상 네트워크 어댑터(network adapter) 와 함께 별도로 나열됩니다 . 모니터링할 인터페이스를 선택합니다. 그래프는 지난 1분 동안의 총 사용량을 표시하고 아래 차트는 데이터 송수신 속도(sending and receiving speeds) , 연결 유형(connection type) 및 IP 주소(IP address) 에 대한 정보를 보여줍니다 . 또한 각 네트워크 어댑터(network adapter) 아래 창 왼쪽의 목록에서 평균 보내기 및 받기 속도(send and receive speeds) 를 볼 수 있습니다 .

네트워크 사용(network usage) 에 대한 자세한 정보를 보려면 그래프를(graph and click) 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "네트워크 세부 정보 보기"("View network details.") 를 클릭 하거나 탭 하세요.

결과 창에는 총 네트워크 사용률(network utilization) , 링크 상태 및 속도, 전송/수신된 바이트, 전송 및 수신된 유니캐스트 및 비유니캐스트 패킷 수를 포함하여 안목 있는 네트워크(discerning network) 기술자 에게 유용한 정보가 많이 표시됩니다.

5. 작업 관리자(Manager) 를 통해 사용자는 현재 스토리지 사용률(storage utilization) ( HDD 또는 SSD(HDD or SSD) ) 을 모니터링할 수 있습니다.
모니터링할 수 있는 또 다른 리소스는 디스크(Disk) 사용량입니다. 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)성능(Performance) 탭 왼쪽에 있는 목록에서 선택하여 액세스할 수 있습니다 . 또는 원하는 경우 창 내부의 아무 곳이나 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭(또는 길게 누름)하고 "View -> Disk."

이 섹션에서는 하드 드라이브 또는 솔리드 스테이트 드라이브의 활동을 볼 수 있습니다. 상단 그래프는 지난 60초 동안의 디스크 사용량을 표시하고 하단 그래프는 데이터 전송 속도를 표시합니다.

그래프 아래에는 드라이브가 활성화된 시간의 백분율, 요청에 응답하는 평균 속도, 평균 읽기 및 쓰기 속도, 드라이브 용량 등의 추가 정보가 있습니다.

6. 시스템 리소스(system resource) (프로세서, 그래픽, 메모리, 네트워크 또는 스토리지(network or storage) ) 활용 요약 보기
장기간에 걸쳐 리소스 사용량을 모니터링하려는 경우 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 창에 표시되는 정보의 양을 최소화할 수 있습니다. 결국 창을 최소화하면서 동시에 볼 수는 없습니다. 화면 공간을 보존하기 위해 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 는 현재 차트만 표시하고 다른 것은 표시하지 않는 그래프 요약 보기를 제공합니다. 그것을 시도하려면 모니터링하려는 시스템 리소스 의 그래프를 두 번 클릭(더블 탭)하십시오. (system resource)또는 시스템 리소스 그래프(system resource graph) 를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누른 다음 "그래프 요약 보기"("Graph summary view.") 를 클릭하거나 탭할 수도 있습니다.

결과 창은 더 작고 덜 복잡합니다. 이것은 프로세서( CPU(CPU) ) 에 대해 얻을 수 있는 것입니다 .
또한 이것은 무선 카드에 대해 얻을 수 있는 것입니다.

다른 시스템 리소스에 대해 얻을 수 있는 미니 그래프는 위와 유사합니다.
7. 하나의 작은 창에서 동시에 모든 필수 시스템 리소스의 활용도 요약 보기
모든 리소스 사용량을 빠르게 보려면 리소스 목록을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 "요약 보기" 를 ("Summary View.")클릭하거나 탭할 수 있습니다.(click or tap)

작업 관리자(Task Manager) 창이 축소되어 각 리소스와 총 사용량의 백분율을 표시하므로 화면 공간을 너무 많이 차지하지 않고 모니터링하기가 더 쉽습니다.

최신 버전의 Windows 10 에서는 기본적으로 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 창의 왼쪽 열에 각 리소스 사용량(resource usage) 에 대한 미니 그래프가 표시 됩니다. 기본적으로 요약 보기(Summary view) 에도 표시됩니다 . 그러나 이전 버전의 Windows 에서는 기본적으로 표시되지 않을 수 있습니다. 이 경우 목록을 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 (list and select) "그래프 표시"("Show graphs") 를 선택하여 표시하십시오.

시스템 리소스 사용에 대한 정보를 복사하여 붙여넣는 방법
이제 시스템 리소스에 대한 모든 유용한 정보를 보는 방법을 알았으므로 일부 데이터를 기록할 수 있습니다. 스크린샷을 찍을 수는 있지만 이미지만 남게 되므로 해당 정보로 작업해야 하는 경우 유용하지 않습니다. 다행히 필요한 데이터를 복사하여 붙여넣을 수 있습니다. 리소스(resource and click) 의 데이터 차트를 마우스 오른쪽 버튼으로 클릭하거나 길게 누르고 복사(Copy.) 를 클릭 하거나 탭 합니다.

워드 프로세서나 스프레드시트 응용 프로그램(word processor or spreadsheet application) 을 열고 프레젠테이션이나 기록에 사용할 수 있는 올바른 형식의 정보 덤프(info dump) 용 데이터를 붙여넣습니다 .

CPU , RAM , GPU 및 기타 시스템 리소스 의 사용량을 확인하려는 이유는 무엇 입니까?
이제 Windows 10 및 Windows 8.1 에서 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 를 사용 하여 시스템 성능을 모니터링하는 방법을 알게 되었습니다. 각 리소스에 대한 데이터 차트는 많은(resource share plenty) 정보를 공유하며 기술자와 일반 사용자 모두 작업 관리자 의 (Task Manager)성능(Performance) 탭 에서 수집할 수 있는 데이터를 높이 평가합니다 . 작업 관리자(Task Manager) 는 현재 CPU 및 메모리 사용률 을 모니터링하고 (CPU and memory utilization)GPU 사용률(GPU usage) 을 확인할 수 있는 깔끔한 도구입니다., 또는 네트워크 인터페이스 또는 스토리지 드라이브와 같은 기타 중요한 리소스의 사용. 이 주제에 대해 질문이 있는 경우 주저하지 말고 아래에 의견을 남겨주세요.
7 ways to keep tabs on your systems' performance with the Task Manager
Have you ever wanted tо know how muсh of your processor's power is being used at a partіcular time? Or maybe how much free RAM was left for your favorite game to uѕe? How about how much of your video card's power is uѕed? All these are eѕsential system resources without which apps and games сannot run well. If you want to see statistics as well as real-time information, you should know that the Windows Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current processor (CPU) and memory utilization, check the video card (GPU) usage, as well as other system resources. Here's how to keep tabs on your system resources:
NOTE: This guide is created for Windows 10 and Windows 8.1, and some of the features we show are available only in the latest versions of Windows 10.
Where to find the tools that let you monitor the system resources: access the Task Manager's Performance tab
To get a look at resource consumption, you must launch the Task Manager. While there are many methods to do that, for speed and ease we recommend using the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." If the Task Manager opens in its compact view, click or tap on "More Details" to expand to full view.

Then, click or tap on the Performance tab. It should look more or less like in the screenshot below. Its looks and contents depend on the version of Windows that you use and on the hardware you have.

Let's see how to use the Performance tab from Task Manager to monitor the performance of the essential hardware components such as your CPU, GPU, and memory utilization.
1. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current processor utilization
By default, the Performance tab of Task Manager first shows you the usage of CPU, otherwise known as the processor. If it is not already selected, you can do so manually by clicking or tapping on CPU on the left side of the window.

You can also choose to view the CPU usage by right-clicking anywhere inside the window and choosing "View -> CPU."

Once you have selected the processor, on the right side of the window, you should see a graph that shows the percentage of the CPU usage during the last 60 seconds. Notice that in the upper right corner of the resource view, Task Manager shows you the exact model of your processor.

Below the graph, there is detailed information about the current CPU utilization and speed, as well as information about your processor's specifications such as its Base speed, number of Sockets and Cores, Logical processors (threads), whether the Virtualization feature is on or off, and the amounts of Level 1, 2, and 3 cache memory available on it.

By default, you get a graph for each physical processor in your PC. It makes sense, but it may not be what some users are looking for: to get a more detailed picture of your processor usage, you can split the graph into logical processors. Right-click or press-and-hold on the CPU graph, hover over "Change graph to" and then click or tap on "Logical processors."

You should now see smaller graphs for each of the CPU's logical processors. For our AMD Ryzen 7 2700 processor, we get 16 charts, one for each of its threads. You may see more or less, depending on your computer's processor.

If you want to see even more information about how CPU cycles are being allotted, you might want to consider showing kernel times. They show how many of your CPU cycles are being used by the kernel, which is responsible for internal system functions, and how much is getting used by user processes.
To enable kernel times, right-click or press-and-hold the CPU graph and click or tap "Show kernel times."

The darker areas of the graph represent kernel time, while the lighter areas represent other types of usage.

2. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current memory utilization (RAM)
Another resource that you probably want to keep a close eye on, especially during slowdowns, is your RAM (Random Access Memory). You can view memory usage by choosing Memory from the list of resources on the left side of the Performance tab.

To switch to the Memory graph, you can also right-click or press-and-hold anywhere inside the window and go to "View -> Memory."

The Memory section displays two graphs. The top graph displays the percentage of memory used during the last minute. The lower graph shows how memory is allocated. Hover your mouse over each section of the lower graph to see what is what.

The RAM usage is split into four usage types:
- In Use - Memory currently being used by apps, drivers, or Windows itself.
- Modified - Memory whose contents must be written to disk before it can be used for other purposes.
- Standby - Memory that contains cached data and code that is not currently in use.
- Free - Memory that is not currently in use and free for use.
Below the graphs, there's more detailed information about the RAM, including used memory, available memory, its speed, slots used and form factor, paged and nonpaged memory pool size, and so on. The pools of memory that you see are either guaranteed to reside in physical memory or can be swapped back and forth to the disk, as needed. You should also see the total memory used for cache and the total committed memory. The amount of data displayed also depends on your computer's hardware configuration.

3. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current video card utilization (GPU)
In the last versions of Windows, including the May 2019 Update and Fall Creators Update, the Task Manager also lets you check GPU usage. This feature is not present in older versions of Windows 10, nor older versions of Windows.
You can monitor the performance of all your graphics cards by selecting them from the list on the left of the Task Manager window. If you have more than one video card installed on your device, you should have an entry for each of them.

When you select a video card that you want to monitor, the right side of the window fills up with graphs and information about its activity. Depending on the type of video card you select, you should see graphs for how much of its power is spent on 3D, Copy, Video Encode, and Video Decode.

By default, the Task Manager has enough room to display only four different graphs. However, if you want to change one of them and monitor some other feature, you can click or tap on the small arrow button on the top-left corner of a graph and select what to watch. You can choose from things like Video Processing, Legacy Overlay, Security, Cuda, VR, and so on, depending on the actual features offered by that video card.

Under the four feature graphs, the Task Manager also shows how the video memory is used. You should have a graph for the "Shared GPU memory usage" and, if your video card also has dedicated memory, you should also have one called "Dedicated GPU memory usage." On the top-right corner of each graph, you can find out the total amount of video memory available on your system.

Below the graphs, there's plenty of other useful information. You can see the total Utilization percentage of your video card, the amount of GPU Memory used and the amount available, as well as the Dedicated GPU memory, and the Shared GPU memory used and the amounts available. There are also details about the driver version used, the driver date, DirectX version, the amount of Hardware reserved memory, if any, and the Physical location, which shows you the PCI bus to which the video card is connected inside your computer.

4. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current network utilization (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth)
To monitor your network usage, first, select which of your network interfaces you want to monitor. You can do that from the resource list on the left side of the Task Manager Performance tab. If you prefer, you can also right-click or press-and-hold anywhere in the Performance tab and choose "View -> Network."

The Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections are listed separately, along with any virtual network adapters you might use for virtual machines or Bluetooth adapters. Choose the interface that you want to monitor. The graph displays the total usage for the last minute, and the chart below shows information about the data sending and receiving speeds, the connection type, and the IP address. You can also see the average send and receive speeds in the list from the left side of the window, under each network adapter.

For a greater level of details about your network usage, right-click or press-and-hold the graph and click or tap on "View network details."

The resulting window displays tons of useful information for the discerning network technician including the total network utilization, link-state and speed, bytes sent/received and the number of unicast and non-unicast packets sent and received.

5. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current storage utilization (HDD or SSD)
Another resource that you may want to monitor is Disk usage. You can get to it by selecting it in the list from the left of the Performance tab in Task Manager. Or, if you prefer, right-click (or press-and-hold) somewhere inside the window and go to "View -> Disk."

This section allows you to see the activity of your hard drives or solid-state drives. The top graph displays disk usage over the past 60 seconds, while the bottom graph displays how fast your data is getting transferred.

Below the graphs, there is more information, including the percentage of time your drives have been active, the average speed with which they respond to requests, the average read and write speeds and the drives' capacities.

6. View a summary of the utilization of a system resource (processor, graphics, memory, network or storage)
If you plan to monitor resource usage over an extended period, you may want to minimize the amount of information displayed in the Task Manager window. After all, you cannot minimize the window and watch it at the same time. To preserve screen space, the Task Manager offers a graph summary view that shows only the current charts and nothing else. To try it out, double-click (double-tap) on the graph of the system resource you want to monitor. Alternatively, you can also right-click or press-and-hold on the system resource graph and then click or tap on "Graph summary view."

The resulting window is smaller and less cluttered. This is what you get for the processor (CPU):

Also, this is what you get for a wireless card:

The mini-graphs you get for the other system resources are similar to the ones above.
7. View a summary of the utilization of all the essential system resources at the same time, in a single small window
If you would rather get a quick view of all your resources usage, you can right-click or press-and-hold the list of resources and click or tap "Summary View."

The Task Manager window shrinks down to show you each resource and its percentage of total usage, making it easier to monitor without taking up too much screen real estate.

In the latest versions of Windows 10, the column from the left side of the Task Manager windows shows mini-graphs for each resource usage, by default. They're also shown in the Summary view by default. However, in older versions of Windows, you might not see them by default. If that is the case for you, right-click or press-and-hold the list and select "Show graphs" to display them.

How to copy and paste information about the use of your system resources
Now that you know how to view all that useful information about your system's resources, you may want to record some of the data. While you could take a screenshot, you would only end up with an image, which is not useful if you need to work with that information. Fortunately, you can copy and paste the data that you need. Right-click or press-and-hold on the data chart from any resource and click or tap Copy.

Open a word processor or spreadsheet application and paste the data for a well-formatted info dump that you can use for presentations or records.

Why did you want to check the usage of your CPU, RAM, GPU, and other system resources?
Now you know how to use the Task Manager in Windows 10 and Windows 8.1, to keep tabs on your system's performance. The data charts for each resource share plenty of information, and both techies and home users alike appreciate the data they can gather from the Performance tab of Task Manager. You know that the Task Manager is a neat tool that allows you to monitor the current CPU and memory utilization, as well as check the GPU usage, or the usage of other important resources such as your network interfaces or storage drives. If you have any questions on this subject, do not hesitate to leave a comment below.


































