Windows 컴퓨터 를 잠재적으로 크게 변경하기 전에 시스템 복원 지점(System Restore Point) 을 만들도록 경고하는 여러 문제 해결 기사를 읽었을 것입니다 . 시스템 복원 지점(System Restore Point) 이 무엇을 의미하는지 모르는 경우 PC 설정 및 기타 중요한 시스템 파일의 백업 복사본으로 생각하십시오.
(Say)악성 프로그램을 설치했거나 실수로 레지스트리 파일을 삭제했는데 컴퓨터가 오작동하기 시작했다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 시스템 복원을 수행하여 이러한 (원치 않는) 변경 사항을 쉽게 취소할 수 있습니다(System Restore) . 이를 통해 일이 원활하게 작동했을 때 컴퓨터를 초기 상태( 복원점 이라고 함)로 되돌릴 수 있습니다.(Restore Point)

이 가이드에서는 Windows 10 에서 (Windows 10)시스템 복원(System Restore) 이 작동 하는 방식을 설명 하고 시스템 복원 지점을 수동으로 만드는 여러 방법을 알려줍니다.
Windows에서 시스템 보호 활성화
시스템 보호(Protection) 는 복원 지점이 생성되고 관리되는 Windows OS 섹션입니다 . 복원 지점을 만들려면 먼저 장치에서 시스템 보호를 활성화해야 합니다(System Protection enabled on your device) . 일부 컴퓨터에는 이 기능이 기본적으로 활성화되어 있지만 다른 컴퓨터에서는 수동으로 켜야 할 수도 있습니다.
PC에서 시스템 보호(Protection) 가 활성화되어 있는지 확인하려면 Windows 검색 창 에 "복원 지점"을 입력 하고 결과에서 복원 지점 만들기(Create a restore point) 를 클릭 합니다.
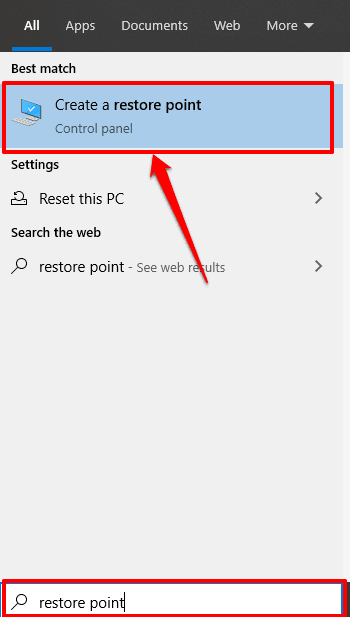
그러면 장치에서 시스템 복원 을 구성할 수 있는 (System Restore)시스템 보호(System Protection) 창으로 리디렉션됩니다 . 이 지점에 대한 대체 경로는 제어판(Control Panel) > 시스템( System) > 시스템 보호(System protection) 를 통하는 것 입니다.
시스템 복원(System Restore) 및 만들기(Create) 버튼이 회색으로 표시되고 시스템(System) 디스크 옆 의 보호 상태가 (Protection)꺼짐 이면 컴퓨터에서 (Off)시스템 보호(System Protection) 가 비활성화되어 있음을 의미 합니다.

시스템 보호(System Protection) 를 활성화하려면 시스템(System) 드라이브를 선택하고 구성(Configure) 을 클릭 합니다.

시스템 보호 켜기를(Turn on system protection) 선택 하고 확인(OK) 을 클릭 합니다.

Windows 는 (Windows)시스템 보호(System Protection) 를 위해 하드 드라이브의 약 3~10%를 자동으로 할당합니다 . 최대 사용(Max Usage) 슬라이더 를 조정하여 이를 변경할 수 있습니다 . 그러나 예약된 디스크 공간이 1GB 미만인 경우 시스템 보호(System Protection) 기능이 실행되지 않으므로 최소 1GB(또는 그 이상)를 할당해야 합니다 .
예약된 공간이 점유되면 Windows 는 새 복원 지점을 위한 공간을 만들기 위해 이전 복원 지점을 삭제합니다. Windows 에서 권장 하는 기본 디스크 공간으로 진행하는 것이 좋습니다.
기본 할당은 가능한 한 많은 복원 지점을 수용하기에 충분해야 합니다. 복원 지점이 많을수록 컴퓨터에 문제가 발생할 경우 파일, 설정 및 기타 구성을 복구할 가능성이 높아집니다.
시스템 보호(System Protection) 를 설정하면 이제 수동으로 복원 지점을 만들 수 있습니다 .
수동 으로 시스템 복원(System Restore) 지점 만들기(Create)

(Windows)시스템 보호 를 활성화하면 (Protection)Windows 에서 자동으로 복원 지점을 생성합니다 . 매주 한 번 또는 Windows 업데이트, 드라이버 설치 등과 같은 중요한 이벤트가 발생하기 전에 수행합니다. 컴퓨터에 시스템 변경 사항을 적용하는 경우 수동으로 복원 지점을 만들 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어 Windows 레지스트리를 변경하기 전에 항상 수동으로 복원 지점을 만드는(making changes to the Windows Registry) 것이 좋습니다 .
복원 지점을 수동으로 생성하려면 시스템 보호(System Protection) 창( 제어판(Control Panel) > 시스템( System) > 시스템 보호(System protection) )으로 이동하여 생성 을 클릭 하십시오(Create) .

대화 상자에 설명을 입력하고 만들기(Create) 를 클릭하여 계속 진행합니다.

Windows는 복원 지점을 만들고 완료되면 성공 메시지를 표시합니다.
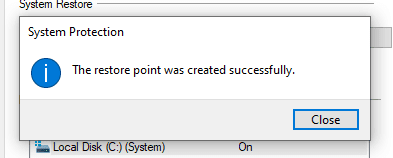
생성 프로세스는 복원 지점의 파일 크기와 드라이브 성능에 따라 몇 분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.
Windows PowerShell을 사용하여 복원 지점(Restore Point Using Windows PowerShell) 만들기
일반적으로 Windows(Windows) 에서 작업을 수행하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다 . Windows PowerShell 을 사용하여 몇 초 만에 복원 지점을 신속하게 만들 수 있습니다 . PowerShell 콘솔 에 몇 가지 명령을 붙여넣기만 하면 됩니다. 방법을 알려드리겠습니다.
Windows 검색 창 에 "PowerShell"을 입력 하고 결과에서 관리자 권한으로 실행을(Run as Administrator) 클릭 합니다.

PowerShell 콘솔 에 아래 명령을 붙여넣고 Enter 키를 누릅니다 .
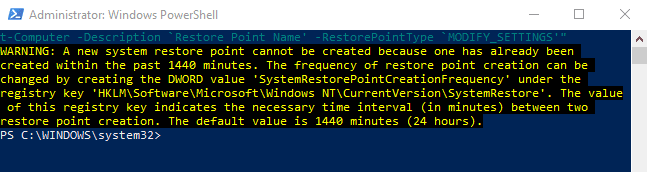
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoExit -Command "Checkpoint-Computer - 설명 '복원 지점 이름' -RestorePointType 'MODIFY_SETTINGS'"(powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoExit -Command “Checkpoint-Computer -Description ‘Restore Point Name’ -RestorePointType ‘MODIFY_SETTINGS’”)
참고:(Note:) 명령의 "복원 지점 이름" 자리 표시자를 원하는 설명으로 바꿀 수 있습니다.

진행률 표시줄이 100%에 도달하면 Windows에서 복원 지점을 만듭니다.

기본적으로 PowerShell 로 24시간에 한 번만 복원 지점을 만들 수 있습니다. Windows 에 "지난 1440분 이내에 이미 생성되었기 때문에 새 시스템 복원 지점을 생성할 수 없습니다."라는 오류가 표시 되면 Windows 가 지난 24시간 동안 자동으로 복원 지점을 생성했음을 의미합니다.
시스템 복원을 사용하여 변경 사항(Changes Using System Restore) 을 복구하는 방법
복원 지점을 생성했으므로 PC에 문제가 발생할 경우 복원 지점을 어떻게 사용하여 이전 지점으로 되돌릴 수 있습니까? 아마도 최근에 인터넷 연결을 엉망 으로 만든 Windows 업데이트 또는 네트워크 드라이버를 설치했을 것입니다. (Windows)시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 사용하여 시스템 변경 사항을 실행 취소하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다 .
시스템 보호(System Protection) 창( 제어판(Control Panel) > 시스템( System) > 시스템 보호(System protection) )을 시작 하고 시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 클릭합니다 .

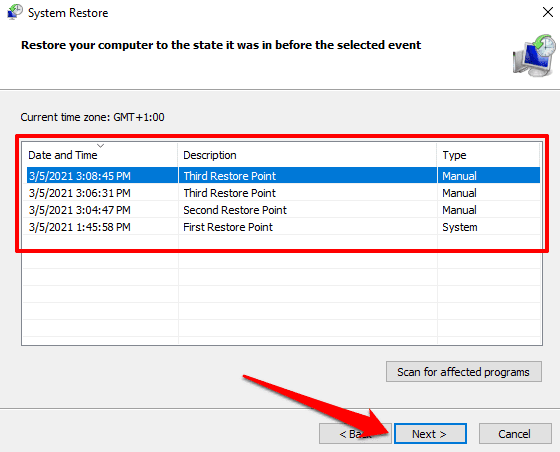
다음(Click Next) 을 클릭하여 시스템 복원(System Restore) 창을 시작합니다. 이 페이지에서 모든 복원 지점 목록, 설명, 생성 날짜 및 시간을 찾을 수 있습니다. Windows 는 또한 "유형"별로 복원 지점에 레이블을 지정합니다. 수동(Manual) 복원 지점은 사용자가 직접 만든 것이고 시스템 은 (System)Windows 에서 자동으로 생성된 복원 지점을 설명합니다 .

복원 지점을 선택하고 다음(Next) 을 클릭하여 계속 진행합니다. 수정하려는 문제를 트리거한 이벤트 직전에 복원 지점을 선택했는지 확인합니다.
전문가 팁: (Pro Tip:)영향을 받는 프로그램 검색(Scan for affected programs) 버튼을 클릭 하면 시스템 복원 프로세스 중에 Windows 에서 삭제할 앱 목록을 볼 수 있습니다.
복원 지점의 설명이 기억나지 않거나 유사한 설명을 가진 항목이 목록에 여러 개 있는 경우 날짜/시간을 확인하고 가장 최근 항목을 선택합니다.
다음 페이지에서 마침(Finish) 을 클릭 하여 선택을 확인합니다. Windows 가 컴퓨터를 다시 시작하므로 저장하지 않은 파일 및 데이터가 손실되지 않도록 활성 앱을 모두 닫아야 합니다.

시스템 복원(System Restore) 창 에서 복원 지점을 찾을 수 없습니까 ? Windows에서 누락된 복원 지점 수정에 대한(troubleshooting guide on fixing missing restore points on Windows) 이 문제 해결 가이드를 참조하십시오 .
Windows가 부팅(Boot) 되지 않습니까? 시스템 복원(System Restore) 을 수행하는 방법(How) 은 다음과 같습니다 .
위의 기술 은 컴퓨터가 켜져 있을 때 시스템 복원(System Restore) 으로 변경 사항을 실행 취소하는 방법을 보여줍니다 . 하지만 컴퓨터가 전혀 시작되지 않는다면 어떻게 될까요? 또는 Windows 가 올바르게 부팅되지만 (Windows)시스템 복원(System Restore) 창 에 도달하기 전에 충돌이 발생 합니까? 그런 다음 장치를 어떻게 복원합니까?
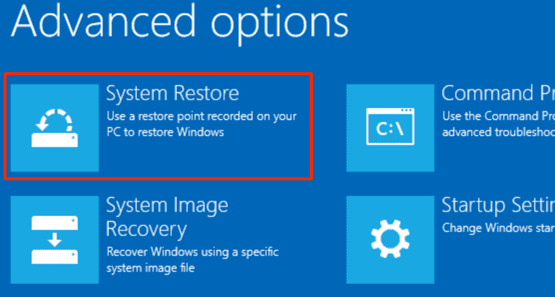
앞에서 언급했듯이 Windows 는 작업을 수행하는 여러 가지 방법을 제공합니다. 따라서 PC가 Windows 를 제대로 로드하지 못하는 경우 (Windows)고급 시작 (Advanced Startup) 옵션(Options) 메뉴 에서 시스템 복원을 시작할 수 있습니다 .
PC의 전원을 껐다가 다시 켭니다. Windows 로고가 화면에 나타나면 전원 버튼을 길게 눌러 PC를 다시 종료합니다. 이 작업을 세 번 반복하면 PC가 Windows 복구 환경(Windows Recovery Environment) 으로 부팅됩니다 .
Windows는 컴퓨터를 진단하고 " 자동 복구(Automatic Repair) 로 PC를 복구할 수 없습니다." 또는 "PC가 올바르게 시작되지 않았습니다 ."라는 오류 메시지 중 하나를 표시 합니다. ” 오류 메시지를 무시 하고 (” Ignore)고급 옵션(Advanced options) 을 클릭 하여 고급(Advanced) 옵션 메뉴로 들어갑니다.

그런 다음 문제 해결(Troubleshoot ) > 고급 옵션( Advanced Options ) > 시스템 복원( System Restore) 을 클릭하고 다음 페이지에서 사용자 이름을 선택합니다.
계속하려면 계정 비밀번호를 입력하세요. 계정이 암호로 보호되어 있지 않으면 암호 상자를 비워 두고 계속(Continue) 을 클릭 합니다. 목록에서 복원 지점을 선택하고 다음(Next) 을 클릭하여 계속 진행합니다.
중요한 파일 및 설정 (Settings)을 잃지(Lose Important Files) 마십시오
시스템 복원 지점을 수동으로 만드는 방법과 컴퓨터가 부팅되지 않는 경우에도 시스템 복원을 수행하는 방법을 배웠습니다. 그러나 시스템 복원은 백업 솔루션이 아닙니다. 개인 데이터가 아닌 시스템 파일과 설정만 저장합니다.
수동으로 복원 지점을 만드는 것 외에도 시스템 이미지 백업(creating a System Image Backup) 또는 recovery CD/USB drive 를 만드는 것이 좋습니다 . 이를 통해 PC가 Windows(Windows) 를 로드하지 못할 정도로 손상되었을 경우 컴퓨터(설치된 모든 프로그램, 설정, 파일 등 포함)를 이전 상태로 복원할 수 있습니다 .
How to Manually Create a System Restore Point in Windows 10
You’ve probably read severаl troubleshooting articles that warn you to crеate a Syѕtem Restore Point before making potentially drastic changes to your Windows computer. If you have no idea what a System Restore Point means, think of it аs a backup cорy of your PC’s settіngѕ and othеr vital system files.
Say you installed a malicious program or deleted a registry file by accident, and your computer begins to malfunction, you can easily undo these (unwanted) changes by performing a System Restore. That allows you to revert your computer to an initial state (called Restore Point) when things were working smoothly.

In this guide, we’ll explain how System Restore works in Windows 10 and teach you several ways to manually create a system restore point.
Enable System Protection on Windows
System Protection is a section of the Windows OS where restore points are created and managed. To create restore points, you need to first have System Protection enabled on your device. Although some computers have this feature activated by default out-of-the-box, others may require you to manually turn it on.
To check if you have System Protection enabled on your PC, type “restore point” in the Windows search bar and click Create a restore point in the results.

That’ll redirect you to the System Protection window where you can configure System Restore on your device. An alternative route to this point is through Control Panel > System > System protection.
If the System Restore and Create buttons are grayed out, and the Protection status next to the System disk reads Off, that means System Protection is disabled on your computer.

To enable System Protection, select the System drive and click Configure.

Select Turn on system protection and click OK.

Windows automatically assigns about 3 – 10 percent of your hard drive for System Protection. You can change this by adjusting the Max Usage slider. However, make sure you assign at least 1GB (or more) because the System Protection feature won’t run if the reserved disk space is below 1GB.
If the reserved space gets occupied, Windows will delete older restore points to make room for new ones. We recommend that you proceed with the default disk space that Windows recommends.
The default allocation should be enough to accommodate as many restore points as possible. The more restore points you have, the higher the chances of recovering files, settings, and other configurations should your computer ever run into a problem.
With System Protection set up, you can now manually create restore points.
Manually Create a System Restore Point

Windows automatically creates restore points when you enable System Protection. It does so once every week or prior to significant events like a Windows update, driver installation, etc. You can also manually create a restore point if you’re making system-altering changes to your computer. For example, it’s always recommended to manually create a restore point before making changes to the Windows Registry.
To manually create a restore point, head to the System Protection window (Control Panel > System > System protection) and click Create.

Type a description in the dialog box and click Create to proceed.

Windows will create the restore point and display a success message when done.

The creation process may take a couple of minutes, depending on the sizes of files in the restore point as well as your drive’s performance.
Create a Restore Point Using Windows PowerShell
There are usually many ways to get things done on Windows. You can swiftly create a restore point in seconds using the Windows PowerShell. All you need to do is paste some commands in the PowerShell console; we’ll show you how.
Type “PowerShell” in the Windows search bar and click Run as Administrator on the results.

Paste the command below in the PowerShell console and press Enter.
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoExit -Command “Checkpoint-Computer -Description ‘Restore Point Name’ -RestorePointType ‘MODIFY_SETTINGS’”
Note: You can replace the “Restore Point Name” placeholder in the command with any description of your choice.

Windows will create the restore point when the progress bar hits 100%.

By default, you can only create one restore point with PowerShell once in 24 hours. If Windows displays an error that reads “A new system restore point cannot be created because one has already been created within the past 1440 minutes,” that means Windows has automatically created a restore point for you in the past 24 hours.

How to Recover Changes Using System Restore
Now that you’ve created a restore point, how do you use it to revert to an earlier point if your PC runs into issues? Perhaps, you recently installed a Windows update or network driver that messed up your internet connectivity. Here’s how to undo system changes using System Restore.
Launch the System Protection window (Control Panel > System > System protection) and click System Restore.

Click Next to launch the System Restore window. On this page, you’ll find a list of all restore points, their description, as well as the date & time they were created. Windows also labels restore points by “Types”—Manual restore points are those you created yourself while System describes a restore point automatically generated by Windows.

Select the restore point and click Next to proceed. Make sure you select the restore point just before the event that triggered the issue you’re trying to fix.
Pro Tip: Click the Scan for affected programs button to see a list of apps that Windows will delete during the system restore process.
If you cannot remember the restore point’s description, or there are multiple items on the list with similar descriptions, check the date/time and select the most recent entry.
Click Finish on the next page to confirm your selection. Windows will restart your computer, so make sure you close all active apps to avoid losing unsaved files & data.

Can’t find a restore point in the System Restore window? Refer to this troubleshooting guide on fixing missing restore points on Windows.
Windows Won’t Boot? Here’s How to Perform a System Restore
The technique above shows you how to undo changes with System Restore when your computer is on. But what if your computer won’t start up at all? Or perhaps Windows boots correctly but crashes before you get to the System Restore window? How then do you restore your device?
Like we mentioned earlier, Windows often provides multiple ways to get things done. So, if your PC won’t properly load Windows, you can initiate a system restore from the Advanced Startup Options menu.
Power off your PC and turn it back on. Press and hold the power button as soon as the Windows logo appears on the screen to shut down your PC again. Repeat this three times and your PC should boot into the Windows Recovery Environment.
Windows will diagnose your computer and display either of these error messages: “Automatic Repair couldn’t repair your PC” or “Your PC did not start correctly.” Ignore the error message and click Advanced options to enter the Advanced options menu.

Next, click Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > System Restore and select your username on the next page.

Enter your account password to continue. If your account isn’t password-protected, leave the password box empty and click Continue. Select a restore point from the list and click Next to proceed.

Never Lose Important Files & Settings
You’ve learned how to manually create a system restore point and how to perform a system restore, even when your computer won’t boot. However, you should note that a system restore isn’t a backup solution; it only saves system files and settings, not your personal data.
In addition to manually creating a restore point, we also recommend creating a System Image Backup or a recovery CD/USB drive. With these, you can restore your computer (including all installed programs, settings, files, etc.) to a previous state should your PC get corrupted to the point where it won’t load Windows.



















