모든 무선 라우터(wireless router) 에는 이름에 AC가 있고 그 뒤에 숫자가 옵니다. 예를 들어 Tenda AC9 AC1200 , TP-Link Archer C7 AC1750 , NETGEAR Nighthawk XR500 AC2500 또는 ASUS RT-AC88U AC3100 이라는 라우터가(ASUS RT-AC88U AC3100) 있습니다. 숫자 가 뒤에 오는 이 AC는 무엇을 의미(number mean) 합니까? AC 뒤에 오는 숫자가 라우터의 속도를 알려줍니까? AC1900 라우터가 AC1200 라우터보다 빠릅(AC1200 router) 니까? 이론적으로 제조업체는 그렇다고 말합니다. 실제로는 진실이 다릅니다. 이 AC 명명 규칙이 소비자에게 거의 가치가 없는 마케팅인 이유와 무선 라우터(wireless router) 를 구입할 때 자신을 속이지 않는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
라우터와 관련하여 AC1200(AC1200) , AC1750 , AC1900 , AC2900 , AC3200 및 기타 유사한 이름은 무엇을 의미합니까 ?
무선 라우터(wireless router) 를 구입할 때 이름 어딘가에 AC라는 용어 뒤에 숫자가 오는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 최신(Newer) 모델에는 AX라는 용어 뒤에 더 큰 숫자가 올 수 있습니다. AC는 라우터가(AC means that the router has support for the) 5GHz 주파수에서 빠른 WiFi 네트워크(WiFi network) 연결을 제공하는 802.11ac(또는 Wi-Fi 5) 무선 네트워킹 표준 을 지원한다는 의미입니다. (wireless networking standard)AX는 라우터가 802.11ax(또는 Wi-Fi 6 ) 무선 네트워킹 표준을 지원한다는 의미입니다.

AC 또는 AX 뒤에 오는 숫자(The number that comes after AC or AX represents the maximum THEORETICAL bandwidth) 는 라우터의 최대 이론적 대역폭을 나타냅니다. 1200은 1200Mbps를 의미 하고(Mbps) , 1900은 1900Mbps(Mbps) 를 의미하고, 3200은 3200Mbps를 의미 하는(Mbps) 식 입니다. 공유기 이름으로 AC2300을(AC2300 in the name of a router, it means) 읽을 때는 총 이론상 최대 대역폭이(a total maximum theoretical bandwidth of 2300 Mbps.) 2300Mbps인 802.11ac( Wi-Fi 5 ) 표준을 사용하여 무선 네트워크(wireless network) 를 제공하는 WiFi 공유기(WiFi router) 를 다루고 있음을 의미합니다.
AC3200 라우터 가 (AC3200 router)3200Mbps(Mbps) 에서 작동 하는 무선 네트워크(wireless network) 를 제공 한다고 믿고 싶을 수도 있습니다 . 그것은 놀라운 일이지만 불행히도 그것은 거짓입니다. 진실은 이 명명 규칙이 구매 결정(purchasing decision) 을 내리는 데 유용하지 않다는 것 입니다. 라우터가 실제보다 더 빠르다고 믿게 만드는 마케팅 전술(marketing tactic) 일 뿐입니다 .
AC1200 , AC1750 , AC1900 등은 라우터 의 실제 속도가 아니라 라우터가 WiFi 신호(WiFi signal) 를 내보내는 모든 대역의 합입니다.
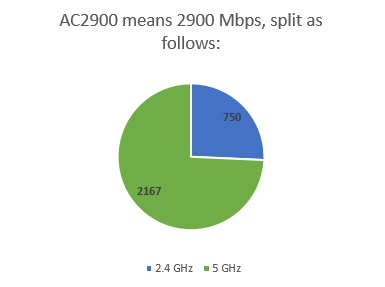
AC 또는 AX 이름(AC or AX naming) 을 지정 하는 계산의 한 가지 주요 측면은 라우터가 무선 신호를 방출하는 대역 또는 주파수의 수입니다. ASUS RT-AC86U AC2900 과 같은 현대적이고 인기 있는 라우터를 예로 들어 보겠습니다 .

이 라우터에는 각각 고유한 최대 이론 대역폭이 있는 두 개의 대역이 있습니다.
- 첫 번째 대역(가장 느린 대역)은 2.4GHz 무선(GHz wireless) 대역입니다. 최대 이론적 대역폭은 750Mbps(Mbps) 입니다.
- 두 번째 대역(가장 빠른 대역)은 5GHz 무선(GHz wireless) 대역입니다. 최대 이론적 대역폭은 2167Mbps 입니다(Mbps) .
따라서 AC2900 은 하나의 (AC2900)무선 대역이나 주파수(wireless band or frequency) 에서 얻을 수 있는 최대 대역폭이 아니라 사용 가능한 모든 무선 대역 또는 주파수의 합계입니다. 얻을 수 있는 최대 속도는 실험실 조건에서만 가장 빠른 대역( 5GHz 무선(GHz wireless) 대역 에서 2167Mbps(Mbps) )이며 이 기사의 뒷부분에서 설명합니다.
더 나은 이해를 돕기 위해 대역 또는 주파수와 관련하여 무선 라우터를 분류하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다.
- 단일 대역 및 하나의 무선 주파수에서만 WiFi(Single-band and emit WiFi only on one wireless frequency) 를 방출합니다. 즉, 하나의 무선 네트워크(wireless network) 만 방출합니다 . 대부분의 경우 2.4GHz 주파수(GHz frequency) 에서 방출하며 이름에 최대 AC1000 이 있습니다. 일부 제조업체는 이러한 라우터 생산을 중단했습니다. 그들은 엄청나게 저렴한 가격을 가지고 있지만 전력이 부족하고 Full HD 영화(Full HD movie) 스트리밍, 온라인 게임 등에 적합하지 않은 오래된 무선 네트워크 표준을 사용하기 때문에 현대 스마트 홈에는 올바른 선택이 아닙니다.(wireless network)
- 듀얼 밴드 및 두 개의 무선 주파수에서 WiFi를 방출합니다.(Dual-band and emit WiFi on two wireless frequencies:) 2.4GHz (느리지만 적용 범위는 더 큼 ) (coverage area)및 5GHz(GHz) ( 더(GHz) 빠르지만 적용 영역(coverage area) 은 더 작음 ). 이름이 다른 두 개의 무선 네트워크가 브로드캐스트되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 동일한 네트워크 이름(network name) 을 사용하도록 두 대역의 설정을 변경할 수도 있습니다 . 최신 라우터의 대부분은 이중 대역입니다. 가격은 매우 다양하지만 대부분의 사람들이 이용할 수 있는 경향이 있습니다. 그러나 AC 명명(AC naming) 규칙 이후의 숫자 가 낮을수록 가격이 낮아집니다. 따라서 (Therefore)AC1750 무선(AC1750 wireless) 라우터 는AC2900 무선(AC2900 wireless) 라우터.
- 트라이 밴드 및 3가지 무선 주파수 ( (Tri-band and emit on three wireless frequencies:)2.4GHz 주파수(GHz frequency) 1 개 및 5GHz(GHz) 주파수 2개 )에서 방출 합니다. 세 개의 무선 네트워크가 브로드캐스트되는 것을 볼 수 있지만 동일한 이름을 사용하도록 설정할 수 있습니다. 가장 비싼 무선 라우터는 트라이 밴드이며 이름에 AC3200 이상이 있습니다. 일부 최신 라우터에는 이름에 AC5400 이 포함 되어 있기 때문에 무선 네트워크를 5400Mbps로 방출한다고 믿게 되지만(Mbps) 이는 사실과 거리가 멉니다.
밴드 수와 밴드가 AC 명명(AC naming) 규칙 과 어떻게 관련되어 있는지 이해하기 위해 마지막 예를 하나 들어보겠습니다. TP-Link Archer C5400X . 아래 그래픽과 같이 이론적인 최대 대역폭 분할(bandwidth split) 이 있는 3개의 대역 이 있는 AC5400 무선 라우터입니다.(AC5400 wireless)
- 2.4GHz 무선(GHz wireless) 대역 의 경우(Mbps) 1000Mbps
- 2개의 5GHz (Mbps)무선(GHz wireless) 대역 각각에 대해 2167Mbps

WiFi 에서 이 라우터에서 얻을 수 있는 최대 속도 는(Mbps) 실험실 조건에서 두 개의 5GHz 무선 대역 각각에서 2167Mbps(GHz wireless) 입니다 .
AC 명명 규칙이 잘못된(convention misleading) 이유는 무엇 입니까?
무선 라우터(wireless router) 제조업체에서 사용 하는 AC 명명(AC naming) 규칙은 무선 라우터(wireless router) 에서 브로드캐스트하는 모든 무선 대역의 이론상 최대 대역폭을 합산하기 때문에 오해의 소지가 있습니다. 그것이 우리가 AC5400 과 같은 미친 숫자로 끝나는 방법 입니다. 실제로 AC5400 무선 라우터(wireless router) 를 사용할 때 WiFi 에서 (WiFi)5400Mbps(Mbps) 를 얻지는 못합니다 . 네트워크 장치는 한 번에 모든 대역이 아니라 한 번에 하나의 대역에만 연결할 수 있기 때문입니다. 더 잘 이해하려면 아래 그림을 보십시오. 세 가지 네트워크 장치(iPhone, Surface Pro 및 Xbox One )가 있으며 각각 다른 장치에 연결되어 있습니다. (WiFi band)TP-Link Archer C5400X 라우터(TP-Link Archer C5400X router) 에서 사용할 수 있는 3가지 WiFi 대역 .

이러한 장치가 얻는 속도는 연결된 무선 대역(wireless band) 의 이론상 최대 대역폭보다 크지 않습니다 . 따라서 iPhone은 1000Mbps(Mbps) 이상의 속도 를 얻지 못하고 다른 두 장치는 2167Mbps 이상의 속도를 얻지 못합니다(Mbps) .
제조업체의 실험실에서 최대 무선 대역폭 은 어떻게 측정됩니까?(wireless bandwidth)
앞서 우리는 트라이 밴드 라우터의 예를 들었고 AC5400과 같은 이름이 5400Mbps (Mbps)에서 (AC5400)무선 네트워크(wireless network) 를 제공한다는 의미는 아니라고 설명했습니다 . WiFi 에서 얻을 수 있는 최고 속도 는 2167Mbps 로 가정할 수 있습니다 . 이는 라우터에서 제공 하는 2개의 5GHz(GHz) 대역 에 대한 이론상 최대 대역폭입니다 . (Mbps)불행히도 이 또한 거짓입니다. 이는 WiFi 와 같은 네트워킹 장비의 모든 제조업체가(ALL)라우터는 사람의 집과 아파트와 같은 실제 측정 환경을 사용하지 마십시오. 그들은 가능한 최대 속도를 주장할 수 있도록 전문 실험실에서 측정을 수행합니다. 총 최대 대역폭을 계산하기 위해 라우터 제조업체가 수행하는 작업은 다음과 같습니다.
- 측정은 무선 신호를 흡수하는 두꺼운 벽이 없는 실험실에서 이루어지며 계산에 사용되는 네트워크 클라이언트와 라우터 사이의 직접적인 가시선이 있습니다.
- 그들은 대역폭을 측정하는 데 사용하는 장치를 2~3미터(6~10피트)의 최적 거리에 배치합니다. 그들은 집이나 아파트(home or apartment) 의 먼 구석 이나 두꺼운 벽(thick wall) 으로 라우터와 분리된 방에서 대역폭을 측정하는 데 관심이 없습니다 .
- 여러 번 그들은 서로 연결된 두세 개의 동일한 라우터를 사용하여 데이터를 전송할 때 최대 대역폭을 측정합니다. 회사의 라우터는 PC, 랩톱, 태블릿 또는 스마트폰에 포함된 네트워크 카드보다 무선 기술을 더 잘 지원하기 때문에 사용자처럼 일반 컴퓨터나 스마트폰을 사용하지 않습니다. 결과적으로 예를 들어 랩톱을 사용할 때보다 전송이 더 빠릅니다.
- 제조업체가 최대 대역폭을 측정하기 위해 컴퓨터를 사용할 때 라우터에서 사용하는 네트워크 표준에 대해 가능한 최고의 프로세서, RAM 및 가장 빠른 네트워크 카드(network card) 를 갖춘 고가의 고급 PC를 사용합니다. 대부분의 사용자는 유사한 고급 컴퓨터에 투자할 동일한 예산이 없습니다. ASUS PCE-AC88 과 같은 고급 무선 네트워크 카드(wireless network card) 를 구입하시겠습니까 ? 대부분의 사람들은 그렇지 않을 것입니다.
- 네트워킹 회사 는 최신 표준 및 WiFi 기술 과 함께 작동하도록 최적화된 전문 네트워킹 소프트웨어 및 드라이버 를 사용하여 (networking software and drivers)무선 대역폭 을 측정합니다. (wireless bandwidth)많은 컴퓨터와 장치는 종종 최신 WiFi 네트워킹(WiFi networking) 기술과 잘 작동하지 않는 오래된 소프트웨어와 운영 체제를 사용합니다. 종종(Often) 드라이버, 특히 대부분의 소비자 랩톱에 있는 네트워크 카드 드라이버도 구식입니다.
- 제조업체 는 라우터에서 브로드캐스트하는 WiFi(WiFi broadcast) 에 가능한 한 적은 수의 장치를 연결하여 최대 대역폭을 측정합니다. 집이나 직장(home or workplace) 에서 동시에 연결하는 것보다 훨씬 많은 장치를 연결하여 사용 가능한 무선 대역폭을 놓고 싸우게 됩니다(wireless bandwidth) .
- 최대 무선 처리량(wireless throughput) 을 보장하는 위치에 라우터의 안테나를 배치합니다 . 집에서는 라우터가 방해가 되거나 어린이가 쉽게 접근할 수 없도록 라우터와 안테나를 덜 최적의 위치에 배치할 수 있습니다.
- 회사는 최대 속도를 위해 펌웨어 설정을 최적화합니다. 예를 들어, 일부 WiFi 라우터에서 USB 포트(USB port) 는 위치 및 기본 설정 에 따라 최대 (positioning and default settings)무선 처리량(wireless throughput) 을 낮출 수 있습니다 . 따라서 네트워킹 회사는 무선 대역폭 을 측정하면서 (wireless bandwidth)USB 처리량(USB throughput) 을 낮추고 간섭을 최소화하기 위해 펌웨어 설정을 변경합니다 . 실시간 바이러스 백신 검사(antivirus scanning) 또는 자녀 보호 기능 과 같이 WiFi 속도(WiFi speed) 를 줄이는 보안 기능을 비활성화할 수도 있습니다 .
AC 명명 규칙과 현실의 차이는 얼마나 됩니까?
AC 명명(AC naming) 규칙과 실생활에서 얻는 속도 의 차이는 매우 클 수 있습니다. 그것들은 또한 매우 다양하며, 많은 경우에 AC 이름(AC naming) 에서 높은 번호를 가진 라우터 가 낮은 번호를 가진 라우터보다 반드시 더 빠른 것은 아닙니다. 더 나은 관점을 제공하기 위해 몇 가지 예를 살펴보겠습니다.
Tenda AC9 와 같은 저렴한 AC1200 라우터 는 일반 (AC1200 router)Windows 10 노트북 을 사용할 때 5GHz 대역(GHz band) 에서 최대 다운로드 속도(download speed) 224.09Mbps 를 제공 합니다 . (Mbps)해당 대역에 대한 이론적인 최대 대역폭(maximum bandwidth) 은 867Mbps 입니다(Mbps) . 실제 속도는 광고된 최대 대역폭(maximum bandwidth) 보다 2.86배 낮습니다 .

Linksys EA7500 v2 와 같은 (Linksys EA7500 v2)AC1900 무선(AC1900 wireless) 라우터 는 5GHz 대역(GHz band) 에 대해 이론상 최대 대역폭이 1300Mbps(Mbps) 입니다. 일반 Windows 10(Windows 10) 노트북 을 사용할 때 최대 다운로드 속도 (download speed)는(Mbps) 539.86Mbps 입니다. 실제 속도는 광고된 최대 대역폭보다 2.4배 낮습니다.

다음으로 ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AC2900 과 같은 (ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AC2900)AC2900 무선(AC2900 wireless) 라우터를 살펴보겠습니다 . 5GHz 대역(GHz band) 에서 이론상 최대 대역폭(maximum bandwidth) 은 2167Mbps(Mbps) 입니다. 실제 생활에서는 ASUS PCE-AC88 과 같은 고가의 네트워크 카드(network card) 를 사용하여 라우터가 있는 방에서만 다운로드 속도 가 (download speed)701.60Mbps(Mbps) 에 도달할 수 있습니다 . 이는 광고된 최대 대역폭(maximum bandwidth) 보다 3배 낮습니다 .

ASUS Blue Cave 와 같은 AC1900 라우터(AC1900 router) 로 돌아가기 . 동일한 값비싼 네트워크 카드(network card) 를 사용하여 훨씬 더 빠른 다운로드 속도 (download speed)인(Mbps) 741.54Mbps 를 얻었 습니다. 재미있는(fun bit) 점은 이 라우터의 이론상 최대 대역폭이 5GHz 대역(GHz band) 에 대해 1734Mbps 로 더 비싼 (Mbps)AC2900 무선(AC2900 wireless) 라우터 보다 낮다는 것입니다 . 그럼에도 불구하고 실제 속도는 광고된 최대 대역폭보다 2.33 낮습니다.

이 모든 데이터는 무선 라우터 에 사용되는 (wireless router)AC 명명(AC naming) 규칙 이 비현실적인 추정임을 증명합니다. 이는 다음 라우터를 선택할 때 문제가 되지 않습니다. 다른 기준이 훨씬 더 중요합니다. 무선 라우터(wireless router) 를 구입할 때 고려해야 할 8가지 사항 (초보자용)
무선 라우터(wireless router) 에서 얻을 수 있는 실제 속도를 알고 싶다면 구입하기 전에 온라인에서 자세한 리뷰를 읽어야 합니다. Digital Citizen 과 같은 많은 웹사이트는 값비싼 실험실 장비 없이도 (lab equipment)무선 라우터(wireless router) 를 테스트 하고 일상적인 상황에서 얻을 수 있는 것을 보여주는 데 많은 시간을 할애합니다 .
무선 라우터와 관련하여 이 AC 명명 규칙을 어떻게 해석해야 합니까?
AC 명명 규칙은 하나의 라우터 또는 다른 라우터를 구입할 때 얻는 무선 네트워크(wireless network) 의 실제 속도를 알려주지 않습니다 . 이 명명 규칙은 다음과 같은 다른 사항을 알려줍니다.
- 라우터가 비싸거나 저렴한지 여부. (Whether the router is expensive or affordable.)최대 AC1750 및 때로는 AC1900 까지의 무선 라우터 는 대부분의 사람들에게 저렴한 경향이 있습니다. AC3200 이상의 라우터 는 항상 많은 비용을 지불하는 프리미엄 모델입니다.
- 라우터가 단일 대역, 이중 대역 또는 삼중 대역인지 여부:(Whether the router is single band, dual-band or tri-band:) 최대 AC1000 라우터 는 항상 단일 대역이며 느린 2.4GHz 주파수 에서 (GHz frequency)WiFi 신호(WiFi signal) 를 방출합니다 . AC1200 라우터부터 AC3200 까지의 라우터는 (AC3200)2.4GHz(GHz) 및 5GHz(GHz) 주파수 모두에서 신호를 방출하는 듀얼 밴드 라우터입니다 . AC3200 이상의 명명 규칙을 가진 라우터 는 트라이 밴드 무선 라우터입니다.
- 얻을 수 있는 기능:(The features you get:) 최대 AC1750 라우터 는 저렴한 경향이 있으며 사람들이 필요로 하는 기본 기능만 갖추고 있습니다. 위의 라우터는 포함된 안티바이러스 보호(antivirus protection) , 고급 자녀 보호 또는 게임 중심 서비스 와 같은 점점 더 고급 기능을 제공하는 경향이 있습니다.
- 하드웨어가 얼마나 강력한지:(How powerful their hardware is:) 최대 AC1750 라우터 에는 하드웨어 리소스가 제한된 단일 코어 프로세서가 있습니다. 최대 AC3200 으로 이동하면 라우터에 듀얼 코어 프로세서와 더 많은 RAM 및 저장 공간(RAM and storage space) 이 제공 됩니다. AC5400 에 가까워 지면 쿼드 코어 프로세서와 많은 RAM 이 제공 됩니다. 기억해야 할 한 가지 규칙은 라우터의 하드웨어가 좋을수록 더 나은 품질과 속도(quality and speed) 로 더 많은 네트워크 클라이언트를 제공할 수 있다는 것 입니다.
결론을 요약하기 위해 AC 명명(AC naming) 규칙이 사용되는 방식을 기억하는 데 도움이 되도록 아래 그림을 만들었습니다 .

(Are)답변되지 않은 다른 질문이 있습니까 ?
Digital Citizen 은 ASUS , TP-Link , Netgear , Tenda , D-Link , Linksys , Synology 등 많은 제조업체의 무선 라우터를 테스트 했습니다. 이 기사는 이 분야에서 수년간의 작업을 기반으로 작성되었습니다. 이 업계의 현실을 명확히 하고 이제 이 명명 규칙과 사용 방법에 대해 더 많이 알게 되었기를 바랍니다. 답변되지 않은 질문이 있으면 아래에 댓글을 달고 토론해 보겠습니다.
What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 or more, mean and what's the difference?
All wireless rоuters haνe AC in their name, followed by a number. For example, you have routers that are called: Tenda AC9 ΑC1200, TP-Link Archer C7 AC1750, NETGEAR Nighthаwk XR500 AC2500, or ASUS RT-AC88U AC3100. What does this AC followed by a number mean? Does the number followіng AC tell you how fast the router is? Is an AC1900 router faster than an AC1200 router? In theory, mаnufacturers say that it is. In reality, the truth is different. Here is why this AC naming convention is marketing with little value for consumerѕ, and how not to fool yourself when purсhasing a wirelеss router:
What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900, AC2900, AC3200, and other similar naming means, when it comes to routers?
When you purchase a wireless router, you see the term AC followed by a number, somewhere in its name. Newer models may have the terms AX followed by an even larger number. AC means that the router has support for the 802.11ac (or Wi-Fi 5) wireless networking standard, which offers fast WiFi network connections on the 5GHz frequency. AX means that the router has support for the 802.11ax (or Wi-Fi 6) wireless networking standard.

The number that comes after AC or AX represents the maximum THEORETICAL bandwidth of the router. 1200 means 1200 Mbps, 1900 means 1900 Mbps, 3200 means 3200 Mbps, and so on. When reading AC2300 in the name of a router, it means that you are dealing with a WiFi router that offers a wireless network using the 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) standard, with a total maximum theoretical bandwidth of 2300 Mbps.
You might be tempted to believe that an AC3200 router provides a wireless network that works at 3200 Mbps. That would be amazing, but, unfortunately, it is false. The truth is that this naming convention is not useful for making a purchasing decision. It is just a marketing tactic that tries to make you believe that a router is faster than it really is.
AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 and so on, is a sum of all the bands on which the router emits WiFi signal, not the real speed of the router
One key aspect of the calculation that results in an AC or AX naming is the number of bands or frequencies on which the router emits the wireless signal. Let's take a modern and popular router as an example: ASUS RT-AC86U AC2900.

This router has two bands, each of them with its own maximum theoretical bandwidth:
- The first band (and the slowest) is the 2.4 GHz wireless band. It has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 750 Mbps.
- The second band (and the fastest) is the 5 GHz wireless band. It has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 2167 Mbps.
Therefore, AC2900 is not the maximum bandwidth you get on one wireless band or frequency, but the sum of all the available wireless bands or frequencies. The maximum speed you could get is that of the fastest band - 2167 Mbps on the 5 GHz wireless band - only in laboratory conditions, which we are going to explain later in this article.

To give you an even better understanding, here's how wireless routers are categorized when it comes to bands or frequencies:
- Single-band and emit WiFi only on one wireless frequency, meaning that they emit only one wireless network. In most cases, they emit on the 2.4 GHz frequency, and they have up to AC1000 in their name. Some manufacturers have stopped producing such routers. They have incredibly low prices, but are not the right choice for modern smart homes, because they are underpowered, and use an old wireless networking standard that is not suitable for Full HD movie streaming, online gaming, and so on.
- Dual-band and emit WiFi on two wireless frequencies: 2.4 GHz (which is slower but with a larger coverage area) and 5 GHz (which is faster but with a smaller coverage area). You see two wireless networks being broadcast, with different names. You can also change the settings for both bands to use the same network name. The majority of modern routers are dual-band. Their pricing varies a lot, but it tends to be accessible for most people. However, one observation is that the lower the number after the AC naming convention, the lower the price. Therefore, an AC1750 wireless router should be cheaper than an AC2900 wireless router.
- Tri-band and emit on three wireless frequencies: one 2.4 GHz frequency and two 5 GHz frequencies. You see three wireless networks being broadcast, but they can be set to use the same name. The most expensive wireless routers are tri-band, and their names have AC3200 or more in their name. Some of the latest routers even have AC5400 in their name, making you believe that they emit wireless networks at 5400 Mbps, which is far from the truth.
To make sure that you understand the number of bands and how they are related to the AC naming convention, let's take one final example: TP-Link Archer C5400X. It is an AC5400 wireless router with three bands, having their maximum theoretical bandwidth split like in the graphic below:
- 1000 Mbps for the 2.4 GHz wireless band
- 2167 Mbps for each of the two 5 GHz wireless bands

The maximum speed you could get from this router, on WiFi, is 2167 Mbps on each of its two 5 GHz wireless bands, in laboratory conditions.
Why is the AC naming convention misleading?
The AC naming convention used by wireless router manufacturers is misleading, because it sums up the maximum theoretical bandwidth of all the wireless bands that are broadcast by the wireless router. That's how we end-up with crazy numbers like AC5400. In reality, you do not get 5400 Mbps on WiFi, when using an AC5400 wireless router, because network devices can connect to only one band at a time, not all bands at once. To better understand, look at the picture below. There are three network devices (an iPhone, a Surface Pro, and an Xbox One), each connected to a different WiFi band, from the three made available by the TP-Link Archer C5400X router.

The speed these devices get is never bigger than the theoretical maximum bandwidth of the wireless band that they are connected to. Therefore, the iPhone won't get a speed that is higher than 1000 Mbps, while the other two devices won't get a speed that is higher than 2167 Mbps.
How is the maximum wireless bandwidth measured in manufacturer's labs?
Earlier we gave an example of a tri-band router and explained that a naming like AC5400 did not mean that it offers a wireless network at 5400 Mbps. You could assume that the top speed you get on WiFi is 2167 Mbps - the maximum theoretical bandwidth for the two 5 GHz bands offered by the router. Unfortunately, this is also false. This is because ALL manufacturers of networking equipment such as WiFi routers, do not use real-life measuring environments, like people's homes and apartments. They do their measurements in specialized labs so that they can claim the maximum possible speed. Here is what router manufacturers tend to do, to calculate the total maximum bandwidth:
- The measurements are made in labs without thick walls that absorb the wireless signal, and with a direct line of sight between the router and the network clients used to make the calculations.
- They place the devices that they use for measuring the bandwidth at an optimal distance of two to three meters (6 to 10 feet). They have no interest in measuring the bandwidth in the far corner of a home or apartment, or in a room separated from the router by a thick wall.
- Many times, they use two or three identical routers connected to each other to measure the maximum bandwidth when transferring data between them. Companies do not use regular computers or smartphones, like users do, because their routers have better support for wireless technologies than the network cards included in PCs, laptops, tablets or smartphones. As a result, their transfers are faster than when using a laptop, for example.
- When manufacturers use computers for measuring the maximum bandwidth, they use expensive high-end PCs, with the best possible processor, RAM, and the fastest network card for the network standards that they are using on their routers. Most users do not have the same budget to invest in similar high-end computers. Would you buy a high-end wireless network card like ASUS PCE-AC88? Most people would not.
- Networking companies measure the wireless bandwidth using specialized networking software and drivers, that are optimized to work with the latest standards and WiFi technologies. Many computers and devices often use older software and operating systems, that do not work as well with modern WiFi networking technologies. Often, drivers are also outdated, especially those of the network cards on most consumer laptops.
- Manufacturers connect the smallest possible number of devices to the WiFi broadcast by their routers, so that they measure its maximum bandwidth. In your home or workplace, you connect a lot more devices than they do, at the same time, causing them to fight over the available wireless bandwidth.
- They place the router's antennas in a position that guarantees the maximum wireless throughput. In your home, you are likely to place the router and its antennas in a less optimal way, to make sure the router is not in your way or easily reached by children.
- Companies optimize their firmware settings for maximum speed. For example, on some WiFi routers, the USB port, depending on its positioning and default settings, can lower the maximum wireless throughput. Therefore, networking companies change the firmware settings to lower the USB throughput and minimize interference, while measuring the wireless bandwidth. They may also disable security features that reduce the WiFi speed, like real-time antivirus scanning or parental controls.
How big is the difference between AC naming conventions and reality?
The differences between AC naming conventions and the speeds you get in real life can be depressingly high. They also vary wildly, and, many times, routers with high numbers in their AC naming are not necessarily faster than others with lower numbers. To give you a better perspective, let's discuss some examples:
An affordable AC1200 router like Tenda AC9, delivers a maximum download speed of 224.09 Mbps, on the 5 GHz band, when using a regular Windows 10 laptop. Its theoretical maximum bandwidth for that band is of 867 Mbps. The real-life speed you get is 2.86 times lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

An AC1900 wireless router like Linksys EA7500 v2 has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 1300 Mbps for the 5 GHz band. When you use a normal Windows 10 laptop, you get a maximum download speed of 539.86 Mbps. The real-life speed you get is 2.4 times lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

Next, let's look at an AC2900 wireless router, like ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AC2900, with a theoretical maximum bandwidth of 2167 Mbps for the 5 GHz band. In real life, you can reach 701.60 Mbps for the download speed, only in the room where the router is placed, using an expensive network card like ASUS PCE-AC88. That's three times lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

Getting back to an AC1900 router, like ASUS Blue Cave. With the same expensive network card, it obtained an even higher download speed: 741.54 Mbps. The fun bit is that this router has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 1734 Mbps for the 5 GHz band, which is lower than that of the more expensive AC2900 wireless router. Even so, the real-life speed is 2.33 lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

All this data proves that the AC naming conventions used for wireless routers are unrealistic estimations, that should not matter when you choose your next router. Other criteria are a lot more important: 8 things to consider when buying a wireless router (for beginners)
If you want to know the real-life speed you get from a wireless router, before purchasing it, you should read in-depth reviews online. Many websites, like Digital Citizen, spend a lot of time testing wireless routers and showing what you get in normal, day-to-day situations, without expensive lab equipment.
How should I interpret this AC naming convention, when it comes to wireless routers?
The AC naming convention does not tell you the real-life speed of the wireless network that you get when buying one router or another. This naming convention tells you other things like:
- Whether the router is expensive or affordable. Wireless routers up to AC1750 and sometimes even AC1900, tend to be affordable for most people. Routers above AC3200 are always premium models for which you pay a lot of money.
- Whether the router is single band, dual-band or tri-band: routers up to AC1000 are always single band, and emit their WiFi signal on the slow 2.4 GHz frequency. AC1200 routers up to AC3200 are dual-band routers that emit their signal both on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. Routers with a naming convention above AC3200 are tri-band wireless routers.
- The features you get: routers up to AC1750 tend to be affordable, and they only have the basic features people need. Routers above that tend to offer more and more advanced features, like included antivirus protection, advanced parental controls, or gaming-oriented services.
- How powerful their hardware is: routers up to AC1750 have single-core processors, with limited hardware resources. When you go up to AC3200, you get dual-core processors and more RAM and storage space on your router. Going close to AC5400, you get quad-core processors and lots of RAM. One rule to remember is that the better the hardware of your router, the more network clients it can serve, with better quality and speed.
To summarize our conclusions, we created the illustration below, to help you remember how the AC naming convention is used.

Are there any other questions left unanswered?
We at Digital Citizen have tested many wireless routers from many manufacturers: ASUS, TP-Link, Netgear, Tenda, D-Link, Linksys, Synology, and others. This article was made based on years of working in this field. We hope that we clarified the realities of this industry and that you now know a lot more about this naming convention and how it is used. If you have any questions left unanswered, comment below and let's discuss.










